
Concept explainers
Draw the major product obtained when each of the following
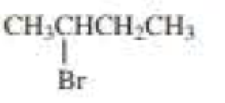
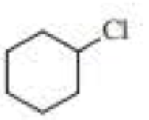
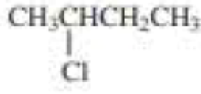
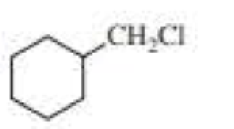
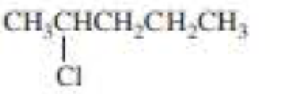
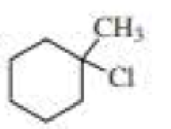
(a)
Interpretation:
Major product formed when given alkyl halides undergoes E2 reaction has to be drawn.
Concept Introduction:
An E2 reaction is a concerted, one-step reaction in which the proton and the halide ion are removed in the same step. A strong base favours an E2 reaction. A high concentration of a base favours an E2 reaction. If one of the reactants is charged, an E2 reaction will be favoured by the least polar solvent that will dissolve the reactant. If neither of the reactant is charged an E2 reaction is favoured by the protic polar solvent. The major product is a stable alkene, unless the reactants are sterically hindered.
Explanation of Solution
The product when given compound undergo E2 addition,
For an E2 reaction major product is the more stable alkene. The reactant is a secondary alkyl halide, undergo E2 reactions.
(b)
Interpretation:
Major product formed when given alkyl halides undergoes E2 reaction is to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
An E2 reaction is a concerted, one-step reaction in which the proton and the halide ion are removed in the same step.
Explanation of Solution
Chlorocyclohexane is a less stable conformer undergo E2 reaction as
The reactant is a secondary alkyl halide, undergo E2 reactions.
(c)
Interpretation:
Major product formed when given alkyl halides undergoes E2 reaction is to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
An E2 reaction is a concerted, one-step reaction in which the proton and the halide ion are removed in the same step. A strong base favours an E2 reaction. A high concentration of a base favours an E2 reaction. If one of the reactants is charged, an E2 reaction will be favoured by the least polar solvent that will dissolve the reactant. If neither of the reactant is charged an E2 reaction is favoured by the protic polar solvent. The major product is a stable alkene, unless the reactants are sterically hindered.
Explanation of Solution
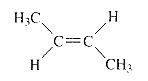
Product of given compound when undergo E2 reaction,
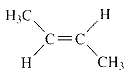
More substituted alkene is more stable therefore should be the major product.
(d)
Interpretation:
Major product formed when given alkyl halides undergoes E2 reaction is to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
An E2 reaction is a concerted, one-step reaction in which the proton and the halide ion are removed in the same step. A strong base favours an E2 reaction. A high concentration of a base favours an E2 reaction. If one of the reactants is charged, an E2 reaction will be favoured by the least polar solvent that will dissolve the reactant. If neither of the reactant is charged an E2 reaction is favoured by the protic polar solvent.
The major product is a stable alkene, unless the reactants are sterically hindered.
Explanation of Solution
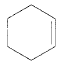
Product of given compound when undergo E2 reaction,
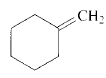
Chloromethyl cyclohexane on E2 reaction gives methylene cyclohexane. And E2 reaction is regioselective: major product is the more substituted stable alkene.
(e)
Interpretation:
Major product formed when given alkyl halides undergoes E2 reaction is to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
An E2 reaction is a concerted, one-step reaction in which the proton and the halide ion are removed in the same step. A strong base favours an E2 reaction. A high concentration of a base favours an E2 reaction. If one of the reactants is charged, an E2 reaction will be favoured by the least polar solvent that will dissolve the reactant. If neither of the reactant is charged an E2 reaction is favoured by the protic polar solvent.
The major product is a stable alkene, unless the reactants are sterically hindered.
Explanation of Solution
Product of given compound when undergo E2 reaction,
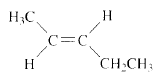
The reactant is a secondary alkyl halide, undergo E2 reactions.
(f)
Interpretation:
Major product formed when given alkyl halides undergoes E2 reaction is to be identified.
Concept Introduction:
An E2 reaction is a concerted, one-step reaction in which the proton and the halide ion are removed in the same step. A strong base favours an E2 reaction. A high concentration of a base favours an E2 reaction. If one of the reactants is charged, an E2 reaction will be favoured by the least polar solvent that will dissolve the reactant. If neither of the reactant is charged an E2 reaction is favoured by the protic polar solvent.
The major product is a stable alkene, unless the reactants are sterically hindered.
Explanation of Solution
Product of given compound when undergo E2 reaction,
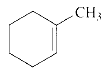
An E2 reaction is regioselective: major product is the more substituted stable alkene.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 10 Solutions
Organic Chemistry
- Draw a Lewis structure for each of the following species. Again, assign charges where appropriate. a. H-H¯ b. CH3-CH3 c. CH3+CH3 d. CH3 CH3 e. CH3NH3+CH3NH3 f. CH30-CH3O¯ g. CH2CH2 - h. HC2-(HCC) HC2 (HCC) i. H202×(HOOH) H₂O₂ (HOOH) Nortonarrow_forwardIs molecule 6 an enantiomer?arrow_forwardShow work. Don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forward
- Check the box under each structure in the table that is an enantiomer of the molecule shown below. If none of them are, check the none of the above box under the table. Molecule 1 Molecule 2 Molecule 3 ----||| Molecule 4 Molecule 5 Molecule 6 none of the above mm..arrow_forwardShow work. don't give Ai generated solutionarrow_forwardCheck the box under each structure in the table that is an enantiomer of the molecule shown below. If none of them are, check the none of the above box under the table. Molecule 1 Molecule 2 Molecule 3 ----||| Molecule 4 Molecule 5 Molecule 6 none of the above mm..arrow_forward
- Use the vapor-liquid equilibrium data at 1.0 atm. for methanol-water (Table 2-8 ) for the following: If the methanol vapor mole fraction is 0.600, what is the methanol liquid mole fraction? Is there an azeotrope in the methanol-water system at a pressure of 1.0 atmospheres? If water liquid mole fraction is 0.350, what is the water vapor mole fraction? What are the K values of methanol and of water at a methanol mole fraction in the liquid of 0.200? What is the relative volatility αM-W at a methanol mole fraction in the liquid of 0.200?arrow_forwardCheck the box under each structure in the table that is an enantiomer of the molecule shown below. If none of them are, check the none of the above box under the table. || |II***** Molecule 1 | Molecule 4 none of the above Molecule 2 Molecule 3 Х mm... C ---||| *** Molecule 5 Molecule 6arrow_forwardis SiBr4 Silicon (IV) tetra Bromine? is KClO2 potassium dihypochlorite ?arrow_forward
- "יוון HO" Br CI Check the box under each structure in the table that is an enantiomer of the molecule shown below. If none of them are, check the none of the above box under the table. Molecule 1 Molecule 2 Molecule 3 Br Br Br HO OH H CI OH ✓ Molecule 4 Molecule 5 Molecule 6 CI Br יייון H Br OH OH CI Br ☐ none of the above × Garrow_forwardUS2 Would this be Uranium (II) diSulfide?arrow_forwardnomenclature for PU(SO4)3arrow_forward
 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
