
Concept explainers
Interpretation:
Concept Introduction:
Functional group: They are certain substitutes in the organic molecules which are determine the characteristic reactions taking place in it.
Alcohol: It is an organic compound where it contains at least one
Ether: Ether is a group of organic compound where two aryl or alkyl groups are connected by an oxygen atom. It is represented as
Depending on the number of carbon side chain of the nitrogen, different types of amines can form.
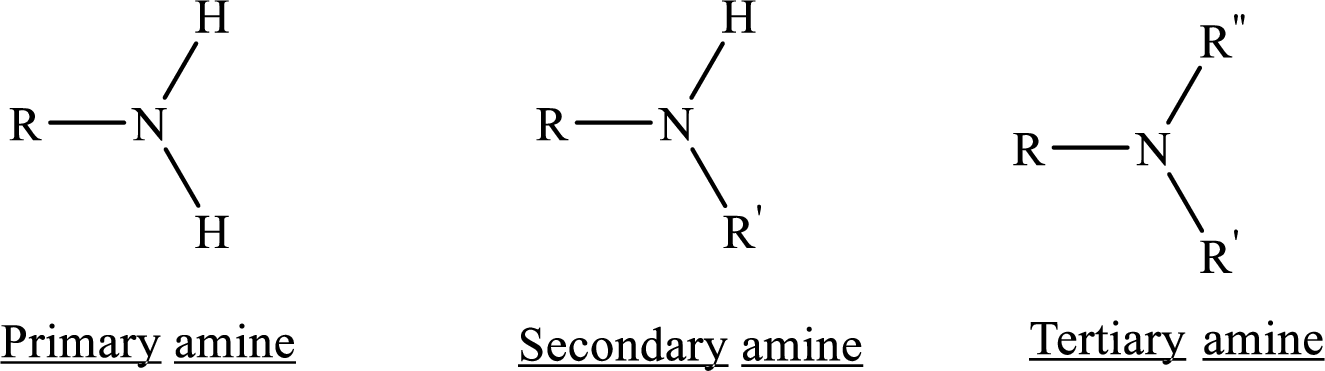
Ester: One
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 10 Solutions
Chemistry in Context
- Circle all the functional groups in each of these compounds.arrow_forward2. Some students confuse the ester and ether functional groups. Both linkages are formed by condensation reactions. a) Complete this statement: An ether linkage is formed by the condensation of: b) Use structures to show the condensation of cyclohexanol molecules to create the alternate synthesis product discussed in the report sheet of your Dehydration experiment (Lab 04).arrow_forwardDetermine the functional group(s) for the following molecule (choose all that apply).CHOOSE ALL THAT APPLY a. hemiacetal b. phenol c. acetal d. carboxylic acid e. ester f. aromatic g. ketone h. aldehydearrow_forward
- Describe the functional group similarities and differences among the four molecules shown below. Compare their polarities; explain your answer. H. H. H. H. H. H. H. HIIarrow_forwardNot handwritten pls.arrow_forwardBONUS. What is a functional group? Explain why it is helpful for organic chemists to classify molecules according to their functional groups?arrow_forward
- "Cyclohexene is a linear molecule with 6 carbon Describe the molecule cyclohexene and provide the chemical formula. atoms and 12 hydrogen atoms. There is a triple bond because it ends in - # 4 (Glycerina) ene. The chemical formula is C6H12" Which two functional groups are in the molecule shown below? Use the terms left and right to distinguish them. "The left functional group is a carboxylic acid. The right functional group is an #5 (Trinitress) alcohol." Harrow_forwardExplain Dr. Flor’s theory of “the intrinsic reactivity of all functional groups isconstant, independent of the molecular size”.arrow_forwardYou are teaching a class in organic chemistry to grade 12 students. Outline the differences in 3 physical properties between alkanes, alcohols, and carboxylic acids. Note: they all have the same hydrocarbon length.arrow_forward
- How does the structure of an alcohol differ from an ether? Describe how an aldehyde differs in structure from a ketone. Thiols are compounds which resemble alcohols, except that the oxygen atom is replaced by a sulfur atom. Draw the analogous thiol for the four carbon alcohol in Table 1. Describe the structural difference between carboxylic acids and esters. Are ethers polar molecules? Would you expect ethers to have higher or lower boiling points than alkanes (circle one)? Explain. Pentane (an alkane) has a boiling point of 36 °C. Does the data agree with your prediction? explain why this could be the casearrow_forward6. What type of organic molecule is this? он ketone alcohol aldehyde organic acidarrow_forwardCompare ethane with ethene. You should refer to their structure and bonding along with their reactions.arrow_forward
- Chemistry: Matter and ChangeChemistryISBN:9780078746376Author:Dinah Zike, Laurel Dingrando, Nicholas Hainen, Cheryl WistromPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill School Pub Co
 Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: An Active Learning Approa...ChemistryISBN:9781305079250Author:Mark S. Cracolice, Ed PetersPublisher:Cengage Learning Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER
Living By Chemistry: First Edition TextbookChemistryISBN:9781559539418Author:Angelica StacyPublisher:MAC HIGHER  Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
Introductory Chemistry: A FoundationChemistryISBN:9781337399425Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning



