
Concept explainers
A linear model of a diode is shown in Fig. P1.21. where Rd is the forward resistance of the diode and Von is the voltage that turns the diode ON. To determine the resistance Rd and voltage Von, two voltage values are applied to the diode and the corresponding currents are measured. The applied voltage Vs and the measured current I are given in Fig. P1.21. The applied voltage and the measured current satisfy the linear equation Vs=IRd+Von. (a) Find the equation of the line for Vs as a function of I and determine the resistance Rd, and the voltage Von.
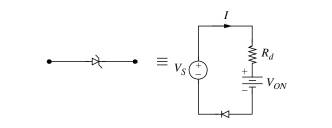
(b) Sketch the graph of Vs as a function of I. and clearly indicate the resistance Rd and the voltage Von on the graph.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 1 Solutions
Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applications
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Pre-Algebra Student Edition
University Calculus: Early Transcendentals (4th Edition)
Basic Business Statistics, Student Value Edition
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)
Introductory Statistics
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (14th Edition)
- Solve the given symbolic initial value problem and sketch a graph of the solution. y"+y=38 (1-2); y(0) = 0, y'(0) = 2arrow_forwardB\ Prove that if T is a spanning tree of G which contains e, then Te Is a spanning tree of G * e.arrow_forward9 Q/ Let G be agraph with n vertices, then G has at least two vertices which are not cut vertices.arrow_forward
- Find the first four nonzero terms in a power series expansion about x=0 for a general solution to the given differential equation w''-14x^2w'+w=0arrow_forwardIn this exercise, we will investigate a technique to prove that a language is notregular. This tool is called the pumping lemma.The pumping lemma says that if M = (S, I, f, s0, F ) is a DFA with p states (i.e., p = |S|) and if the wordw is in L(M ) (the language generated by M ) and w has length greater than or equal to p, then w may bedivided into three pieces, w = xyz, satisfying the following conditions:1. For each i ∈ N, xy^i z ∈ L(M ).2. |y| > 0 (i.e., y contains at least one character).3. |xy| ≤ p (i.e., the string xy has at most p characters). Use the pumping lemma to show the following language is not regular (HINT: Use proof by contradictionto assume the language is regular and apply the pumping lemma to the language):L = {0^k1^k | k ∈ N}arrow_forwardA prefix of length ℓ of some word w are the first ℓ characters (in order) of w.1. Construct a context-free grammar for the language: L = {w ∈ {a, b}∗ | every prefix of w has at least as many a’s as b’s}2. Explain why every word generated by your context-free grammar (in Part 1) is contained in L. Then,prove via induction that every w ∈ L is produced by your context-free grammar.arrow_forward
- Consider a simplified version of American football where on any possession ateam can earn 0, 3 or 7 points. What is the smallest number n0 of points such that for all n ≥ n0 and n ∈ Na team could earn n points. You must prove that your answer is correct via induction (HINT: Don’t forgetto show that n0 is the smallest number above which any number of points is reachable).arrow_forwardConsider a vocabulary consisting of the nucleotide bases V = {A, T, G, C}.Construct a DFA to recognize strings which end in AAGT .(a) Draw the DFA with clear markings of all states including start and acceptance state(s).(b) Simulate the DFA to show that string T GAAGT will be accepted by the DFA.(c) Simulate the DFA to show that string T AAGT G will not be accepted by the DFA.arrow_forwardA palindrome is a string that reads the same backward as it does forward. For example, abaaaba is a palindrome. Suppose that we need to define a language that generates palindromes.(a) Define a phase structure grammar that generates the set of all palindromes over the alphabet {a, b}clearly describing the recursive rules that generates palindromes. Use the notation Symbol → rule. Theempty set is denoted by λ. Clearly identify the terminal and non-terminal symbols in your grammar.(b) Show that the palindrome abaaaba can be recognized by your grammar. To show this, show all stepsof parsing the expression abaaaba using the rules you defined above.arrow_forward
 Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Linear Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305658004Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal LittellAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal LittellAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,





