
Fundamentals Of Analytical Chemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781285640686
Author: Skoog
Publisher: Cengage
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
How do I find the Reaction Quotient, E0cell and Ecell?
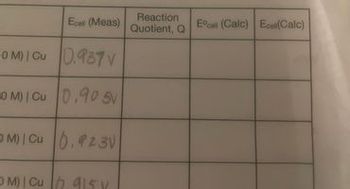
Transcribed Image Text:Reaction
Ecal (Meas) Quotient, Q
OM) Cu 0.937V
OM) | Cu 0.90 5V
OM) Cu 0.23V
OM) Cu415Y
Ecall (Calc) Ece(Calc)
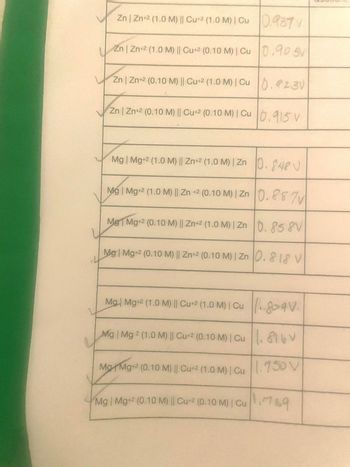
Transcribed Image Text:Zn | Zn+2 (1.0 M) || Cu+2 (1.0 M) | Cu 0.937 V
Zn | Zn+2 (1.0 M) || Cu+2 (0.10 M) | Cu 0.90 5V
Zn | Zn+2 (0.10 M) || Cu+2 (1.0 M) | Cu 0.923V
Zn | Zn+2 (0.10 M) || Cu+2 (0.10 M) | Cu 0.915 V
Mg | Mg+2 (1.0 M) || Zn+2 (1.0 M) | Zn 0.848V
Mg | Mg+2 (1.0 M) || Zn +2 (0.10 M) | Zn 0.887v
Me Mg+2 (0.10 M) || Zn+2 (1.0 M) | Zn 0.858V
Mg Mg+2 (0.10 M) || Zn+2 (0.10 M) | Zn 0.818 V
Mg | Mg+2 (1.0 M) || Cu+2 (1.0 M) | Cu 809V.
Mg | Mg 2 (1.0 M) || Cu+2 (0.10 M) | Cu 16V
Mg Mg+2 (0.10 M) || Cu+2 (1.0 M) | Cu 1.750 V
Mg | Mg+2 (0.10 M) || Cu+2 (0.10 M) | Cu789
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Use the following concentrations to calculate your experimental Ksp value for Ca(OH) 2 [Ca^ 2+ ]=0.021 M [OH^ - ]=0.042 Marrow_forwardCan you please help me with 5arrow_forward1. A student performed this experiment and obtained the following concentration values: 0.02813 M, 0.02802, and 0.02788 M a. what is the mean concentration? b. what is the standard deviation of these results? 3. how would the following errors affect the concentration of Cl- obtained in question 2b? give your reasoning in each case. a. the student read the molarity of AgNo3 as 0.02104M instead of 0.02014M b. the student was past the endpoint of titration when he took the final buret reading.arrow_forward
- Beaker Volume of KSCN No solution 1 0.50 mL 9.50 mL Part I: Data for Calibration Graph Accurate Concentration of potassium thiocyanate, KSCN stock solution: 0.001 M 0.2 M Fe(NO3)3- Iron(III)nitrate solution: 0.5M Volume of HNO3 solution 0.2 M Volume of 0.2 M Fe(NO3)3 solution 10.00 mL Absorbance 0.037 2 1.00 mL 9.00 mL 10.00 mL 3 2.00 mL 8.00 mL 10.00 mL 4 3.00 mL 7.00 mL 10.00 mL 0.122 0.313 0.547 5 4.00 mL 6.00 mL 10.00 mL 6 5.00 mL 5.00 mL 10.00 mL 0.791 0.868arrow_forwardWrite a balanced redox reaction for the following electrochemical cell: Pt | Cu* (aq); Cu²+ (aq) || Fe3+ (aq) | Fe What is the correct balanced reaction for the cell?arrow_forwardh Oxidation: Cr2+ → Cr³+ + e Reduction: Cu²+ + 2 e¯ → Cu Net: 2 Cr²+ + Cu²+ What is the standard potential, Eºnet ? Standard Reduction Potentials Eº net Reduction Half-Reaction E° (V) Co³+ + e- → Co²+ 1.82 Au³ + + 3e- → Au(s) 1.50 Pd²+ + 2 e- → Pd 0.987 Ag++ e- → Ag(s) 0.80 Fe³+ + e- → Fe²+ 0.771 → Cu(s) 0.52 → Cu(s) 0.337 → Cut 0.153 → H₂(g) 0.00 → Sn(s) -0.14 Cu++ e- Cu²++2 e- Cu²++ e- 2H+ + 2 e- Sn²+ + 2 e- Co²+ +2 e- Cr³++ e- Fe²+ +2 e- Cr³+ +3 e- Zn²++ 2 e- A1³+ + 3 e- → Cu + 2 Cr³+ = V →Co(s) -0.28 → Cr²+ -0.41 → Fe(s) -0.44 → Cr(s) -0.74 → Zn(s) -0.763 →Al(s) -1.66arrow_forward
- 4. In addition to finding the right answer can you explain what is Determinate error (I think the correct answer is the 3rd option here but not sure if right)arrow_forwardPlease help answer thisarrow_forwardYou begin preparation of the calibration curve to measure absorbance vs concentration of FeSCN2+. To do so, you add 2.422 mL of 0.200 M Fe(NO3)3 to a cuvette and then directly add 215 µL of 0.001 M KSCN. What is the resulting concentration of FeSCN2*, assuming complete conversion of SCN' to FeSCN2+? Enter your answer in units of mM to four digits after the decimal.arrow_forward
- how do you solve 0.2860=0.059/2log[Cu2+]arrow_forward4. You prepare several dilutions of an unknown compound. You measure the absorbance of each solution at 340 nm using a 1 cm cuvette (your results are listed in the table below). What is the extinction coefficient (in (M•cm)') of the compound? (Hint: assume that each of the individual values contains some degree of experimental error.) Concentration(uM) Absorbance at 340 nm 10.0 0.011 20.0 0.023 40.0 0.066 80.0 0.119 160.0 0.189arrow_forwardFrom the data in Table 2.5, compute the concentration of the undiluted and diluted ovalbumin samples (make sure to account for the appropriate dilution factors, DF, in the computation).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
