
You wish to test the following claim (Ha) at a significance level of α=0.01.
Ho:p1=p2
Ha:p1<p2
You obtain 76.3% successes in a
Solution:
The null and alternative hypotheses are as follows:
Ho: p1=p2
Ha: p1<p2
Sine the alternative hypothesis contains "less than" (<) sign, it is a left tailed test.
The following information is given to us:
Sample size: n1=520 and sample proportion: p1 = 76.3% = 0.763
Sample size: n2=758 and sample proportion: p2 = 83.5% = 0.835
The formula of test statistic is as follows:
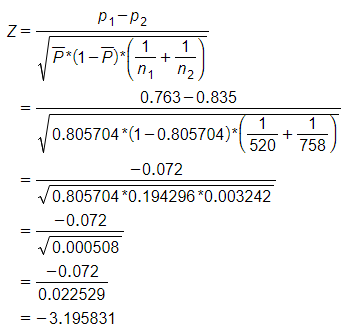
Thus, test statistic: Z = -3.195831
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

- You wish to test the following claim (HaHa) at a significance level of α=0.002. Ho:p1=p2 Ha:p1≠p2 You obtain 383 successes in a sample of size n1=498 from the first population. You obtain 318 successes in a sample of size n2=443 from the second population. For this test, you should NOT use the continuity correction, and you should use the normal distribution as an approximation for the binomial distribution.What is the test statistic for this sample? (Report answer accurate to three decimal places.)test statistic = What is the p-value for this sample? (Report answer accurate to four decimal places.)p-value = The p-value is... less than (or equal to) αα greater than αα This test statistic leads to a decision to... reject the null accept the null fail to reject the null As such, the final conclusion is that... There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the first population proportion is not equal to the second population proprtion. There is…arrow_forwardYou wish to test the following claim (HaHa) at a significance level of α=0.001α=0.001. Ho:p=0.8Ho:p=0.8 Ha:p<0.8Ha:p<0.8You obtain a sample of size n=232n=232 in which there are 177 successful observations. For this test, you should NOT use the continuity correction, and you should use the normal distribution as an approximation for the binomial distribution.What is the test statistic for this sample? (Report answer accurate to three decimal places.)test statistic = What is the p-value for this sample? (Report answer accurate to four decimal places.)p-value =arrow_forwardYou wish to test the following claim (HaHa) at a significance level of α=0.002. Ho:p1=p2 Ha:p1>p2You obtain 256 successes in a sample of size n1=326 from the first population. You obtain 469 successes in a sample of size n2=686 from the second population. For this test, you should NOT use the continuity correction, and you should use the normal distribution as an approximation for the binomial distribution. What is the p-value for this sample? (Report answer accurate to four decimal places.)p-value =arrow_forward
- You wish to test the following claim (Ha) at a significance level of α=0.005 Ho:p1=p2 Ha:p1>p2You obtain 734 successes in a sample of size n1=774 from the first population. You obtain 632 successes in a sample of size n2=696 from the second population. For this test, you should NOT use the continuity correction, and you should use the normal distribution as an approximation for the binomial distribution.What is the test statistic for this sample? (Report answer accurate to three decimal places.) test statistic = What is the p-value for this sample? (Report answer accurate to four decimal places.) p-value =arrow_forwardYou wish to test the following claim (Ha) at a significance level of α=0.002α=0.002. Ho:p1=p2 Ha:p1≠p2 You obtain 480 successes in a sample of size n1=647 from the first population. You obtain 562 successes in a sample of size n2=737 from the second population. For this test, you should NOT use the continuity correction, and you should use the normal distribution as an approximation for the binomial distribution. What is the standardized test statistic for this sample? (Report answer accurate to three decimal places.)arrow_forwardYou wish to test the following claim (Ha) at a significance level of α=0.10 Ho:p1=p2 Ha:p1≠p2You obtain 60.5% successes in a sample of size n1=650 from the first population. You obtain 57% successes in a sample of size n2=258 from the second population. For this test, you should NOT use the continuity correction, and you should use the normal distribution as an approximation for the binomial distribution.What is the test statistic for this sample? (Report answer accurate to three decimal places.)test statistic = What is the p-value for this sample? (Report answer accurate to four decimal places.)p-value = The p-value is... less than (or equal to) αα greater than αα This test statistic leads to a decision to... reject the null hypothesis accept the null hypothesis fail to reject the null hypothesis As such, the final conclusion is that... There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the first population proportion is not equal to the second…arrow_forward
- You wish to test the following claim (Ha) at a significance level of α=0.01. Ho:p1=p2 Ha:p1>p2You obtain 54.3% successes in a sample of size n1=529 from the first population. You obtain 47.9% successes in a sample of size n2=555 from the second population. For this test, you should NOT use the continuity correction, and you should use the normal distribution as an approximation for the binomial distribution.What is the test statistic for this sample? (Report answer accurate to three decimal places.) test statistic = What is the p-value for this sample? (Report answer accurate to four decimal places.) p-value = The p-value is... less than (or equal to) α greater than αarrow_forwardYou wish to test the following claim (HaHa) at a significance level of α=0.001 Ho:p1=p2 Ha:p1<p2You obtain 4.7% successes in a sample of size n1=299 from the first population. You obtain 7.8% successes in a sample of size n2=602 from the second population. For this test, you should NOT use the continuity correction, and you should use the normal distribution as an approximation for the binomial distribution.What is the test statistic for this sample? (Report answer accurate to three decimal places.)test statistic = What is the p-value for this sample? (Report answer accurate to four decimal places.)p-value = The p-value is... less than (or equal to) αα greater than αα This test statistic leads to a decision to... reject the null hypothesis accept the null hypothesis fail to reject the null hypothesis As such, the final conclusion is that... There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the first population proportion is less than the second…arrow_forwardYou wish to test the following claim (HaHa) at a significance level of α=0.005α=0.005. Ho:p=0.5Ho:p=0.5 Ha:p≠0.5Ha:p≠0.5You obtain a sample of size n=190n=190 in which there are 85 successful observations. For this test, you should NOT use the continuity correction, and you should use the normal distribution as an approximation for the binomial distribution.What is the test statistic for this sample? (Report answer accurate to three decimal places.)test statistic = What is the p-value for this sample? (Report answer accurate to four decimal places.)p-value =arrow_forward
- You wish to test the following claim (Ha) at a significance level of α=0.10. Ho:p1=p2 Ha:p1>p2You obtain 64.7% successes in a sample of size n1=286 from the first population. You obtain 57.7% successes in a sample of size n2=312 from the second population. For this test, you should NOT use the continuity correction, and you should use the normal distribution as an approximation for the binomial distribution.What is the test statistic for this sample? (Report answer accurate to three decimal places.) test statistic = What is the p-value for this sample? (Report answer accurate to four decimal places.) p-value = The p-value is... less than (or equal to) α greater than αarrow_forwardYou wish to test the following claim (HaHa) at a significance level of α=0.01. Ho:p1=p2 Ha:p1>p2You obtain 33.5% successes in a sample of size n1=260 from the first population. You obtain 22.6% successes in a sample of size n2=483 from the second population. For this test, you should NOT use the continuity correction, and you should use the normal distribution as an approximation for the binomial distribution.What is the test statistic for this sample? (Report answer accurate to three decimal places.)test statistic = What is the p-value for this sample? (Report answer accurate to four decimal places.)p-value = The p-value is... less than (or equal to) αα greater than αα This test statistic leads to a decision to... reject the null accept the null fail to reject the null As such, the final conclusion is that... There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the first population proportion is greater than the second population proportion. There…arrow_forwardYou wish to test the following claim (H) at a significance level of a = 0.05. Ho: P₁ = P2 Ha: P1 > P2 You obtain 58% successes in a sample of size n₁ = 790 from the first population. You obtain 48.6% successes in a sample of size n₂ = 276 from the second population. For this test, you should NOT use the continuity correction, and you should use the normal distribution as an approximation for the binomial distribution. What is the test statistic for this sample? (Report answer accurate to three decimal places.) test statistic = 1.552 x What is the p-value for this sample? (Report answer accurate to four decimal places.) p-value = 0.0603 x The p-value is... 03 less than (or equal to) a O greater than a This test statistic leads to a decision to... Oreject the null hypothesis O accept the null hypothesis O fail to reject the null hypothesis As such, the final conclusion is that... O There is sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the first population proportion is…arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





