
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Solve the Graph

Transcribed Image Text:You have built the majority of the tension testing machine, but much of the instrumentation is still being assembled. To test the machine, you perform a test on a steel specimen with known properties. The machine provides you with the given load data, and you manually record the lengths between the marks on the specimen at each point using an extensometer to obtain the table of data shown below.
| \( L \) (in) | 2.0012 | 2.0025 | 2.0350 | 2.0798 | 2.1313 | 2.1937 | 2.2804 | 2.4774 | 2.5791 | 2.6657 | 2.7281 | 2.7497 |
|--------------|--------|--------|--------|--------|--------|--------|--------|--------|--------|--------|--------|--------|
| \( P \) (kip)| 3.51 | 7.09 | 7.87 | 8.83 | 9.84 | 10.80 | 11.77 | 12.37 | 11.80 | 10.81 | 9.81 | 9.42 |
Use these results to calculate the stress and strain at the yield point, the ultimate strength point, and the fracture point.
**Express your answers to three significant figures.**
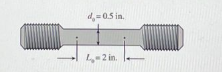
Transcribed Image Text:**Tensile Test Specimen**
**Diagram Explanation:**
The diagram on the left shows a steel tensile test specimen with defined dimensions. The specimen has a central cylindrical section with threads at both ends.
- **Central Section Diameter (\(d_o\))**: 0.5 inches
- **Gauge Length (\(L_o\))**: 2 inches
These parameters measure the deformation and strength of the specimen under tensile loading.
**Text Explanation:**
On the right, there's a table recording the results from a tensile test on the steel specimen. This table outlines the elongation measurements in inches at various applied loads in pounds (P).
**Load and Elongation Table**:
| \(P\) (lb) | \(l\) (in) |
|------------|-------------|
| 0 | 2.0021 |
| 3,551 | 2.0070 |
| 7,091 | 2.0350 |
| 8,882 | 2.0789 |
| 9,724 | 2.1931 |
| 10,197 | 2.2804 |
| 2,264 | 2.4774 |
| 2,579 | 2.5919 |
| 2,657 | 2.7081 |
| 2,728 | 2.7647 |
These data points enable the calculation of stress and strain at critical points, such as the yield point, ultimate strength point, and fracture point of the specimen.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1: Determine the given data

The diameter is
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 19 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Rotate the objects shown below by the indicated amount and sketch the result in the space provided. You do not need to include the coordinate axes in your sketch.arrow_forwardThe vertical distance above a reference datum to a point is called the point’sarrow_forward20 30 40. -30 100- Draw the three projections of the following figure 60arrow_forward
- Round off answer to 4 decimal placesarrow_forwardUse Share Sketch to create this part with one sketch. Pivot lock (dimensions are in inches. The circular features in the design are all aligned to the two centers at the base.arrow_forwardMake an orthographic projection based on the drawingarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY