
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
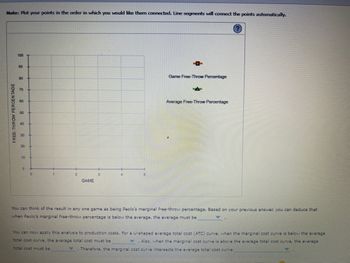
Transcribed Image Text:Note: Plot your points in the order in which you would like them connected. Line segments will connect the points automatically.
FREE-THROW PERCENTAGE
100
90
80
70
60
50
40
30
10
0
0
2
GAME
3
4
Game Free-Throw Percentage
Average Free-Throw Percentage
You can think of the result in any one game as being Paolo's marginal free-throw percentage. Based on your previous answer, you can deduce that
when Paolo's marginal free-throw percentage is below the average, the average must be
You can now apply this analysis to production costs. For a U-shaped average total cost (ATC) curve, when the marginal cost curve is below the average
total cost curve, the average total cost must be
Also, when the marginal cost curve is above the average total cost curve, the average
TU Therefore, the marginal cost curve intersects the average total cost curve
total cost must be
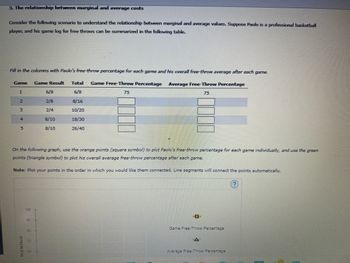
Transcribed Image Text:3. The relationship between marginal and average costs
Consider the following scenario to understand the relationship between marginal and average values. Suppose Paolo is a professional basketball
player, and his game log for free throws can be summarized in the following table.
Fill in the columns with Paolo's free-throw percentage for each game and his overall free-throw average after each game.
Game Result Total Game Free-Throw Percentage Average Free-Throw Percentage
6/8
75
8/16
10/20
18/30
26/40
Game
1
2
3
4
5
RCENTAGE
6/8
2/8
2/4
8/10
8/10
On the following graph, use the orange points (square symbol) to plot Paolo's free-throw percentage for each game individually, and use the green
points (triangle symbol) to plot his overall average free-throw percentage after each game.
Note: Plot your points in the order in which you would like them connected. Line segments will connect the points automatically.
90
75
Game Free-Throw Percentage
A
Average Free-Throw Percentage
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 6: For each of the total cost functions, write the expressions for the average cost, average fixed cost, average variable cost, and marginal cost: 1. TC (Q) = 5Q 2. TC (Q) = 120 +6Q 3. TC (Q) = 6Q² 4. TC (Q) = 140 +5Q²arrow_forwardSuppose that widgets can be produced using two different production techniques, A and B. The following table provides the total input requirements for each of five different total output levels. Q = 1 Tech. K L A B Q=2 K L 2 4 1 6 1 3 2 5 Total Cost L K Assuming that the price of labor (P₁) is $1 and the price of capital (PK) is $3, calculate the total cost of production for each of the five levels of output using the optimal (least-cost) technology at each level. Q=3 K L 4 9 4 8 To do this, complete the table below by calculating the total cost of production, filling in the missing values using the optimal (least-cost) technology at each level. (Enter your responses as whole numbers.) Q=4 K L 12 5 Total Cost How many labor hours (units of labor) would be employed at each level of output? How many machine hours (units of capital)? To answer this, complete the table below for the units of labor and units of capital that would be used to produce each level of output. (Enter your…arrow_forwardThe following table shows the capital and labor requirements for 10 different levels of production. Assuming that the price of labor (PL) is $9 per unit and the price of capital (PK) is $8 per unit, compute and graph total cost, marginal cost, and average cost for the firm. To do this, fill in the total cost for each output level in the table below. (Enter your responses as whole numbers.) q 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 K 0 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 20 L 0 3 7 10 13 17 23 31 41 53 67 TC 0arrow_forward
- Introduction to Calculus in Economics (continued): In the previous Problem Set question, we started looking at the cost function C (æ), the cost of a firm producing z items. An important microeconomics concept is the marginal cost, defined in (non- mathematical introductory) economics as the cost of producing one additional item. If the current production level is æ items with cost C (z), then the cost of computing h additionial (C(z+h)-C(z)) items is C (z + h). The average cost of those h items is . As we analyze the cost of just the last item produced, this can be made into a mathematical model by taking the limit as h → 0, i.e. the derivative C' (z). Use this function in the model below for the Marginal Cost function MC (x). Problem Set question: The cost, in dollars, of producing z units of a certain item is given by C (z) = 0.02a3 – 10z + 450. (a) Find the marginal cost function. MC (z) (b) Find the marginal cost when 50 units of the item are produced. The marginal cost when 50…arrow_forwardBack to Assignment Attempts: Keep the Highest: 1/4 3. The relationship between marginal and average costs Consider the following scenario to understand the relationship between marginal and average values. Suppose Edison is a professional basketball player, and his game log for free throws can be summarized in the following table. Fill in the columns with Edison's free-throw percentage for each game and his overall free-throw average after each game. Game Game Result Total Game Free-Throw Percentage Average Free-Throw Percentage 3/3 3/3 100 100 3/5 6/8 80 3 2/8 8/16 4 2/4 10/20 5/5 15/25 On the following graph, use the orange points (square symbol) to plot Edison's free-throw percentage for each game individually, and use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot his overall average free-throw percentage after each game. Note: Plot your points in the order in which you would like them connected. Line segments will connect the points automatically. 100 Tarrow_forwardQ.4 Marginal Cost is closely related to: (a) Total variable cost (b) Total cost (c) Total fixed cost (d) All of the abovearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education