
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
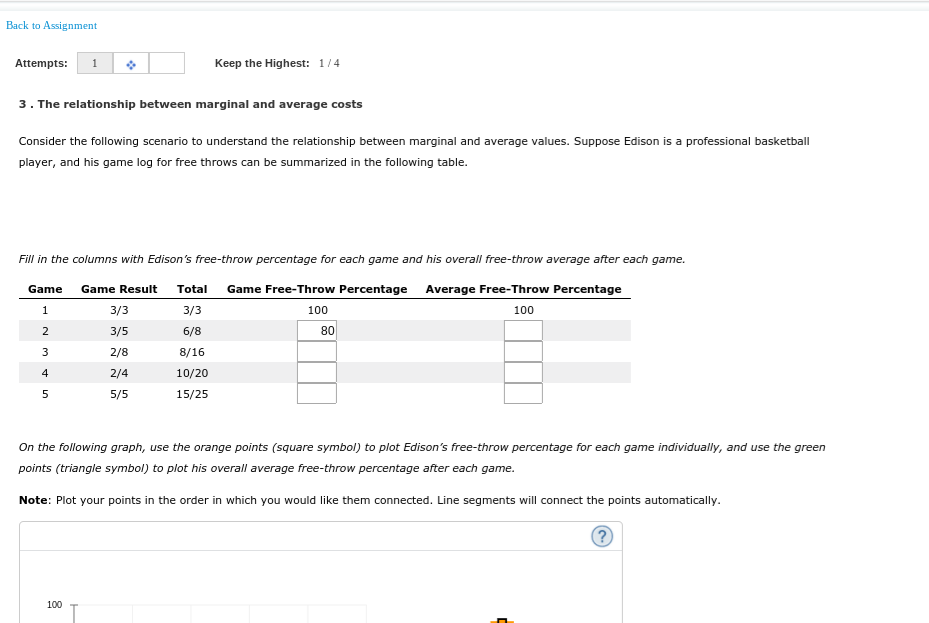
Transcribed Image Text:Back to Assignment
Attempts:
Keep the Highest: 1/4
3. The relationship between marginal and average costs
Consider the following scenario to understand the relationship between marginal and average values. Suppose Edison is a professional basketball
player, and his game log for free throws can be summarized in the following table.
Fill in the columns with Edison's free-throw percentage for each game and his overall free-throw average after each game.
Game
Game Result
Total Game Free-Throw Percentage Average Free-Throw Percentage
3/3
3/3
100
100
3/5
6/8
80
3
2/8
8/16
4
2/4
10/20
5/5
15/25
On the following graph, use the orange points (square symbol) to plot Edison's free-throw percentage for each game individually, and use the green
points (triangle symbol) to plot his overall average free-throw percentage after each game.
Note: Plot your points in the order in which you would like them connected. Line segments will connect the points automatically.
100 T
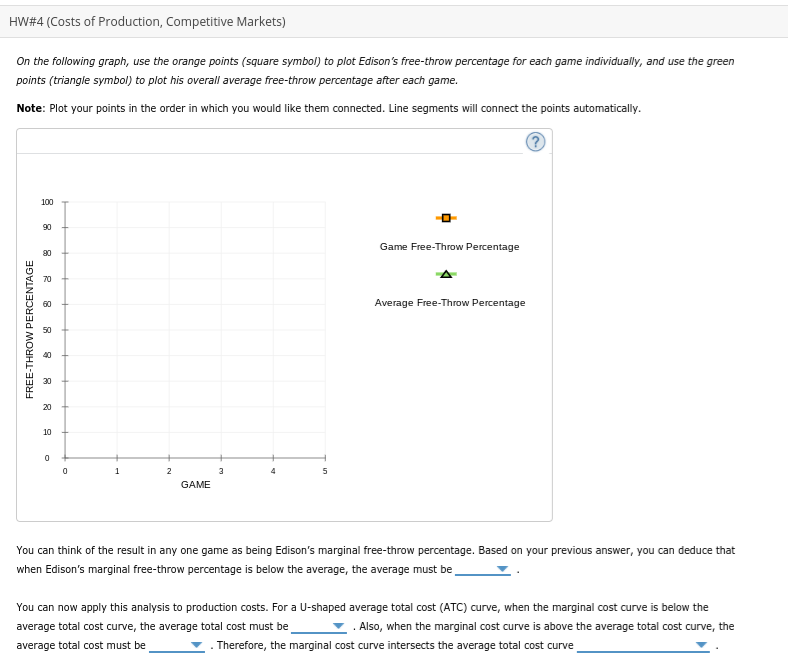
Transcribed Image Text:HW#4 (Costs of Production, Competitive Markets)
On the following graph, use the orange points (square symbol) to plot Edison's free-throw percentage for each game individually, and use the green
points (triangle symbol) to plot his overall average free-throw percentage after each game.
Note: Plot your points in the order in which you would like them connected. Line segments will connect the points automatically.
100
90
Game Free-Throw Percentage
90
70
60
Average Free-Throw Percentage
40
30
20
10
GAME
You can think of the result in any one game as being Edison's marginal free-throw percentage. Based on your previous answer, you can deduce that
when Edison's marginal free-throw percentage is below the average, the average must be
You can now apply this analysis to production costs. For a U-shaped average total cost (ATC) curve, when the marginal cost curve is below the
average total cost curve, the average total cost must be
Also, when the marginal cost curve is above the average total cost curve, the
average total cost must be
. Therefore, the marginal cost curve intersects the average total cost curve
FREE-THROW PERCENTAGE
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- help please answer in text form with proper workings and explanation for each and every part and steps with concept and introduction no AI no copy paste remember answer must be in proper format with all workingarrow_forwardEconomics: Industrial Economics Question: 1 Consider the following simultaneous move game: Player 1 selects rows and player 2 selects columns in a simultaneous move game. For every outcome, payoffs for player 1 are given by the first entry and payoffs for player 2 by the second. P1\P2 | A | B | C | D | 1 | (5,5) | (7,4) | (7,5) | (1,2) | 2 | (7,2) | (7,3) | (5,1) | (2,3) | 3 | (1,2) | (6,9) | (8,0) | (8,8) | The Nash Equilibrium is: Choices: A. (2,B) B. (3,D) C. (3,B) D. (1,C) Question: 2 In the patent pooling model, if there are four inputs that are required for production of the final goods and each one is produced by a patent-holding monopolist then 1. At the Nash Equilibrium the Lerner Index for the industry isChoices: A. Half as high as the Lerner index that would arise...B. Twice as high as the Lerner Index that would arise...C. Four times higher than the Lerner Index that we...D. Four times lower than the Lerner Index that we... 2. If the market for the final good were a…arrow_forward3. The relationship between marginal and average costs Consider the following scenario to understand the relationship between marginal and average values. Suppose Musashi is a professional basketball player, and his game log for free throws can be summarized in the following table. Fill in the columns with Musashi's free-throw percentage for each game and his overall free-throw average after each game. Game Game Result Total Game Free-Throw Percentage Average Free-Throw Percentage 1 8/10 8/10 80 80 4/10 12/20 3 2/8 14/28 4 2/4 16/32 6/8 22/40arrow_forward
- Anation with fixed quantities of resources is able to produce any of the following combinations of carpet and carpet looms Production Possibility Frontier Yards of carpet (Millions) Carpet looms (Thousands) 43 75 60 20 45 35 30 45 15 50 50 24- These figures assume that a certain number of previously produced looms are available in the current period for producing carpet. 1.) Using the multipoint curve drawing tool, plot the six points that make up the PPF given in the table above (with carpet on the vertical axis). Properly label your curve. Carefully follow the instructions above and only draw the required object. 45 Carpet (millions) 15 30 60 75 (spuesnou) suoo| jade)arrow_forward4arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements concerning location economies is FALSE? Explain Why? 1. Companies must determine where to sell and where to produce. 2.The Internet is an industry where companies must locate facilities near their foreign customers, so decisions on market and production location are connected. (difficult, page 382) 3.Companies may have excess production capacity already in place that will influence their ability to serve markets in different countries. 4. The process of determining an overall geographic strategy must be flexible because country conditions changearrow_forward
- You can think of the result in any one game as being Hilary’s marginal free-throw percentage. Based on your previous answer, you can deduce that when Hilary’s marginal free-throw percentage is below the average, the average must be (falling/rising). You can now apply this analysis to production costs. For a U-shaped average total cost (ATC) curve, when the marginal cost curve is below the average total cost curve, the average total cost must be (falling/rising) . Also, when the marginal cost curve is above the average total cost curve, the average total cost must be (falling/rising). Therefore, the marginal cost curve intersects the average total cost curve (at its maximum/at its minimun/when the ATC is at 0).arrow_forwardConsider the following scenario to understand the relationship between marginal and average values. Suppose Sam is a professional basketball player, and his game log for free throws can be summarized in the following table. Fill in the columns with Sam's free-throw percentage for each game and his overall free-throw average after each game. Game Result Total Game Free-Throw Percentage Average Free-Throw Percentage Game 1 8/10 80 12/20 14/28 16/32 22/40 2 3 4 5 8/10 4/10 2/8 2/4 6/8 80 On the following graph, use the orange points (square symbol) to plot Sam's free-throw percentage for each game individually, and use the green points (triangle symbol) to plot his overall average free-throw percentage after each game. Note: Plot your points in the order in which you would like them connected. Line segments will connect the points automatically.arrow_forwardAttempts: Keep the Highest: 14 3. The relationship between marginal and average costs Consider the following scenario to understand the relationship between marginal and average values. Suppose Charles is a professional basketball player, and his game log for free throws can be summarized in the following table. Fill in the columns with Charles's free-throw percentage for each game and his overall free-throw average after each game. Game Game Result Total Game Free-Throw Percentage Average Free-Throw Percentage 8/10 8/10 80 80 4/10 12/20 2/8 14/28 2/4 16/32 6/8 22/40arrow_forward
- Confused on how to solve correctlyarrow_forwardA company that produces brass hardware for doors has the ability to produce up to 6,500 hinges per week but then is unable to produce doorknobs. Or it can produce up to 650 doorknobs per week but then is unable to produce any hinges. In the graph below, use the straight-line tool to draw the company's production possibilities frontier, where the quantities are per week (do not use the point tool to plot endpoints). Then use the point tool to plot a point to indicate the company's maximum output where it is producing exactly three times as many hinges as doorknobs. To refer to the graphing tutorial for this question type, please click here. Quartity ofinge 000 7500 000 4000 000 100 1000 Quartity of doorknotarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education