
Biochemistry
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781305577206
Author: Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
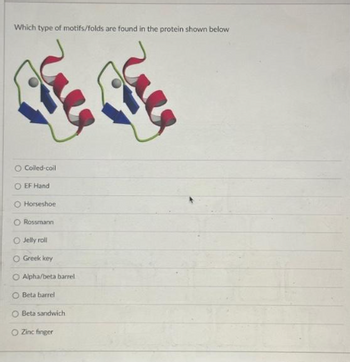
Transcribed Image Text:Which type of motifs/folds are found in the protein shown below
Coiled-coil
O EF Hand
O Horseshoe
O Rossmann
O Jelly roll
O Greek key
O Alpha/beta barrel
O Beta barrel
O Beta sandwich
OZinc finger
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Figure 15.16 Many antibiotics inhibit bacterial protein synthesis. For example, tetracycline blocks the A site on the bacterial ribosome, and chloramphenicol blocks peptidyl transfer. What specific effect would you expect each of these antibiotics to have on protein synthesis? Tetracycline would directly affect: tRNA binding to the ribosome ribosome assembly growth of the protein chain Chloramphenicol would directly affect tRNA binding to the ribosome ribosome assembly growth of the protein chainarrow_forwardBelow is the structure of glycine. Draw a tripeptide composed exclusively of glycine. Label the N-terminus and C-terminus. Draw a box around the peptide bonds.arrow_forwardUsing Figures 8.7 and 8.9 as a guide, draw a dinucleotide composed of C and A. Next to this, draw the complementary dinucleotide in an antiparallel fashion. Connect the dinucleotides with the appropriate hydrogen bonds. FIGURE 8.9 The two polynucleotide chains in DNA run in opposite directions. The left strand runs 5 to 3, and the right strand runs 3 to 5. The base sequences in each strand are complementary. An A in one strand pairs with a T in the other strand, and a C in one strand is paired with a G in the opposite strand. FIGURE 8.7 Nucleotides can be joined together to form chains caled polynucleotides. Polynucleotides are polar molecules with a 5 end (at the phosphate group) and a 3 end (at the sugar group). An RNA polynucleotide is shown at the left, and a DNA polynucleotide is shown at the right.arrow_forward
- A certain mRNA strand has the following nucleotide sequence: 5AUGACGUAUAACUUU3 What is the anticodon for each codon? What is the amino acid sequence of the polypeptide? (Use Figure 13-5 to help answer this question.) Figure 13-5 The genetic code The genetic code specifies all possible combinations of the three bases that compose codons in mRNA. Of the 64 possible codons, 61 specify amino acids (see Figure 3-17 for an explanation of abbreviations). The codon AUG specifies the amino acid methionine and also signals the ribosome to initiate translation (start). Three codonsUAA, UGA, and UAGdo not specify amino acids; they terminate polypeptide synthesis (stop).arrow_forwardHow many letters of an RNA molecule, in sequence, does it take to provide the code for a single amino acid? 1 2 3 4arrow_forwardExploring the Structure of the 30S Ribosomal Subunit Go to www.pdh.org and bring up PDB file 1GIX, which shows the 30S ribosomal subunit, the three tRNAs, and mRNA. In the box on the right titled ‘Biological Assembly.� click “More Images.� and then scroll down to look at the Interactive Vic By moving your cursor over the image, you can rotate it to view it from any perspective. a. How are the ribosomal proteins represented in the image? b. How is the 16S rRNA portrayed? c. Rotate the image to see how the tRNAs stick out from the structure. Which end of the tRNA is sticking out? d. Where will these ends of the tRNAs lie when the 50S subunit binds to this complex?arrow_forward
- The following is a portion of a protein: met-trp-tyr-arg-gly-pro-thr-Various mutant forms of this protein have been recovered. Using the normal and mutant sequences, determine the DNA and mRNA sequences that code for this portion of the protein, and explain each of the mutations. a. met-trp- b. met-cys-ile-val-val-leu-gln- c. met-trp-tyr-arg-ser-pro-thr- d. met-trp-tyr-arg-gly-ala-val-ile-ser-pro-thr-arrow_forwardFigure 28.41 gives some examples of recombination in IgG codons 95 and 96, as specified by the Vkand Jkgenes. List the codon possibilities and the amino acids encoded if recombination occurred in codon 97. Which of these possibilities is less desirable?arrow_forwardThe Consequences of Ribosome Complexity Eukaryotic ribosomes are larger and more complex than prokaryotic ribosomal. What advantages and disadvantages might this greater ribosomal complexity bring to a eukaryotic cell?arrow_forward
- Arrange the following terms in order of increasing specialization: oligopotency, pleuripotency, unipotency, multipotency. multipotency, pleuripotency, oligopotency, unipotency pleuripotency, oligopotency, multipotency, unipotency oligopotency, pleuripotency, unipotency, multipotency pleuripotency, multipotency, oligopotency, unipotencyarrow_forwardGiven the following tRNA anticodon sequence, derive the mRNA and the DNA template strand. Also, write out the amino acid sequence of the protein encoded by this message. tRNA: UAC UCU CGA GGC mRNA: protein: How many hydrogen bonds would be present in the DNA segment?arrow_forwardWatch this video (http://openstaxcollege.org/l/ribosome) to learn about ribosomes. The ribosome binds to the mRNA molecule to start translation of its code into a protein. What happens to the small and large ribosomal subunits at the end of translation?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...BiologyISBN:9781305117396Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa StarrPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...BiologyISBN:9781305251052Author:Michael CummingsPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology Today and Tomorrow without Physiology (Mi...
Biology
ISBN:9781305117396
Author:Cecie Starr, Christine Evers, Lisa Starr
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Human Heredity: Principles and Issues (MindTap Co...
Biology
ISBN:9781305251052
Author:Michael Cummings
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biology (MindTap Course List)
Biology
ISBN:9781337392938
Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. Berg
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781938168130
Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark Womble
Publisher:OpenStax College