
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
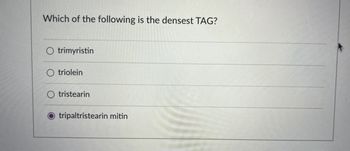
Transcribed Image Text:Which of the following is the densest TAG?
O trimyristin
O triolein
tristearin
tripaltristearin mitin
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Hi please can I have the solution for the 4 questionarrow_forward**ALL GROUPS HAVE A MUTATION MAKE SURE TO IDENTIFY THEM** Group B 5’-GGCAATGGGTTTGTGAAATTCTAAAAGTTTTTAATTC-3’ 3’-CCGTTACCCAAACACTTTAAGATTTTCAAAAATTAAG-5’ Group C 5’-GGCAATGGGTTTGTGCAATTCTAAGAGTTTTTAATTC-3’ 3’-CCGTTACCCAAACACGTTAAGATTCTCAAAAATTAAG-5’ Group D 5’-GGCAATGGGTTTGTGCAATTCTAACAGTTTTTAATTC-3’ 3’-CCGTTACCCAAACACGTTAAGATTGTCAAAAATTAAG-5’ Group E 5’-GGCAATGGGTTTTGCAATTCTAAAAGTTTTTAATTC-3’ 3’-CCGTTACCCAAAACGTTAAGATTTTCAAAAATTAAGarrow_forwardExplain why the X and the dot disappear and reappeararrow_forward
- Please convert it to past tense and passive voice. Each group will be provided with two 20 g double-stranded DNA oligomers A and B in STE buffer (0.1M NaCl/ Tris/ 10 mM EDTA, pH 7.4). The sequence of the two oligomers used in this experiment is:5’ GCATTGCGCAGGGCCGAG 3’ (GC rich) 3’ AATGGTACGTATACTTTAT3’ (AT rich)In this experiment, you are going to identity oligomer samples A and B, GC or AT rich, by UV spectrophotometric method.1. Pipet 1 ml of each oligomer into a 1.5 ml Eppendorf tube and label the two tubes A and B.2. The absorption wavelength is 260 nm. Use STE buffer provided to set blank.3. You will be provided with two cuvettes. Use separate cuvette for each DNA sample.4. Transfer 1 ml of DNA sample A to cuvette and measure the UV absorbance at 260 nm (A260) atroom temperature. Repeat this step for Sample B.5. Transfer the DNA back to the original Eppendorf tube, close it and heat it to 45C for 7 minutes.6. Quickly transfer the sample from Eppendorf tube to cuvette, and…arrow_forwardplease dont give hand writting solution pleasearrow_forwardQualitative Color Reactions Color Reaction Biuret Ninhydrin Xanthoproteic Millon's Hopkins-Cole Sakaguchi Nitroprusside Fohl's Test for Amide Pauly Intact Protein Acidic Hydrolyzed Protein Basic Enzymaticarrow_forward
- if egg yolk is used in Lugol's test will the results be brown? Yes or no and please explain why.arrow_forwardThe following gel was obtained using the Sanger method. What is the DNA sequence and what does the arrow represent?arrow_forwardPaper Chromatography Column Chromatography Gel Electrophoresisarrow_forward
- This answer is copied, a sign of plagarism, I need a explanation not from the internetarrow_forwardArial BIUA 11 + .. | I 1 I 3 I 4 i.) Fill in the table for each of the E. coli: (0) = No Activity (+) = Basal Activity and (+++) = High Activity E. coli chromosome F' Plasmid B-gal activity? Permease activity? When When When When Glucose is Lactose is Glucose is Lactose is present present present present a.) I+ P+ O+ Z+ Y+ Inone +++ +++ b.) I^[S] P+ O+ Z+ Y+ none c.) I+ P+ O^[c] Z+ Y+ none d.) I+ P+ O- Z- Y+ none e.) I+ P+ O+ Z+ Y+ I^[S] P+ O+ Z+ Y+ f.) I^[S] P+ O+ Z- Y+ I+ P+ O^[c] Z+ Y- g.) I^[TB] P+ O+ Z+ Y 1+ P+ O^[c] Z- Y+ h.) I+ P+ O^[c] Z+ Y- I+ P+ O+ Z** Y+ i.) I^[TB] P+ O^[c] Z+ Y- 1+ P+ O+ Z- Y+ Z** is a polar mutation ii. ) If the lac operon in 'a' carried a mutation in the CAP binding site that rendered it nonfunctional, how would that affect the level of ß-galactosidase protein activity with and without lactose present, why? MacBook Air 000arrow_forwardWhich of the following is NOT true about Base Excision repair? Group of answer choices Ligase is responsible for resealing the nick in the phosphodiester backbone. Endonuclease is used to remove the damaged nucleotide. It is a preferred method of removal for larger defects in the genetic code Polymerase creates the new nucleotide to replace the damaged one Glycosylase removes damaged the damaged base before the nucleotidearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON