
Concept explainers

Ans 1.
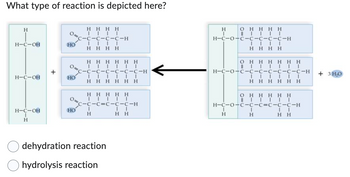
The reaction represented in the question is Dehydration Reaction
A dehydration reaction is a chemical reaction that involves the loss of water from the reacting molecule or ion. Dehydration reactions are common processes, the reverse of a hydration reaction.
Dehydration reactions can be divided into two categories: Condensation reactions: In these processes, a water molecule is taken out of two molecules, which subsequently combine to form a bigger molecule. Condensation reactions include, for instance, the dehydration of two amino acids to create a peptide bond.
Elimination reactions: In these processes, a water molecule is taken out of a single molecule and a double bond is created as a result. An elimination reaction is, for instance, the dehydration of an alcohol to produce an alkene.
The given reaction cannot be hydrolysis reaction because hydrolysis is a chemical reaction in which a molecule of water breaks one or more chemical bonds.. The term is used broadly for substitution, elimination, and solvation reactions in which water is the nucleophile.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

- Please step by step answer and don't use ASI Answer pleasearrow_forwardModify the structure to show the MAJOR product that would be formed in the following reaction. HNO3, H2SO4arrow_forwardSelect the product for the following cyclization CHO OH OH OH H OH OH Но HO HO OH но Но - OH HO HO Но. OH H- OH OH H H H ČH2OH 1 3 О 1&2 1 2arrow_forward
- Please show all your work please, thank you! Sorry, this question has many parts. The reaction O3(g)+O(g)→2O2(g), occurs via the following mechanism:Step 1: Cl(g)+ O3(g)→ClO(g)+O2(g); Ea=85 kJ/molStep 2: ClO(g)+ O(g)⇌Cl(g)+O2(g); Ea=10 kJ/mol a. Given the proposed mechanism above, identify any catalysts and any intermediates in this reaction. Be sure to distinguish between the two types of species in your answer. b. Using the proposed mechanism, derive a rate law. *Hint: use the activation energies to determine the slower step. Show all of your work. c. This mechanism was verified by kinetic measurements of the rate of depletion of ozone. How is the rate of change of oxygen gas concentration related to the rate of change of ozone concentration?arrow_forwardWhich of the compounds shown below exhibit a high negative free energy of hydrolysis equal to or larger than the free energy of hydrolysis for the phosphoanhydride of ATP? (Choose all that apply) В Α HPΗ Ho HO HO H2N-CH-C CH2 H2N-CH-C CH2 CH2 H2N-CH-Ö CH2 C CH2 D E O A O B O E O=p-00 O=p-00 O=-00 O=0-00 O=L-00arrow_forward1. Answer the following questions, based on this reaction: S+E P ES EP2 E + P | B)Where is the transition state located?arrow_forward
- Could you help me with the remaind of the reactions F to H? See picture of the mechanism below.arrow_forwardE* S P₁₁ P₂ E E-S₁ E-S₁-S₂ E-P₁-P₂ E*-P₂ E* Which of these 2 options represents a Sequential Ordered bisubstrate reaction? (label the other reaction as well) P₁ P₂ E-S₁-S₂ E-P₁-P₂ E-P₂ E is E E-S₁ S E◄arrow_forward1. Define what a decomposition reaction is: htaction in n 9 2. Synthesis reactions that use water in the reaction are ddralion Rodton 3. Collectively decomposition reactions are referred to as Calalomiomm C. Reversible Reactions 1. A chemical reaction in which the reaction can proceed from or from to to D. Oxidation-Reduction Reactions 1. Chemical reactions that result from the exchange of olootarce 2. The loss of an electron by a reactant is referred to as 3. refers to the gain of an electron by a reactant. E. Energy 1. Stored energy that is not doing work is called 2. Energy that is actually working and moving matter is 3. Mechanical Energy ina a. Results from the otal amnn of CoienH al and 4. Chemical Energy a. Potential energy stored 5. Heat Energy a. Energy that flows Speed of Chemical Reactions a. The activation energy is b. Substances that increase the rate of chemical reactions without being 6. used up in the reaction are called 1. Enzymes are Created by of ty C Page 3 of9arrow_forward
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education





