
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
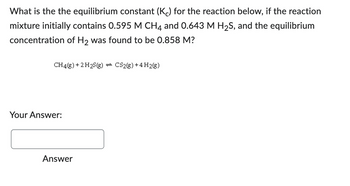
Transcribed Image Text:What is the the equilibrium constant (Kc) for the reaction below, if the reaction
mixture initially contains 0.595 M CH4 and 0.643 M H₂S, and the equilibrium
concentration of H₂ was found to be 0.858 M?
CH4(g) + 2 H2S(g) = CS2(g) +4 H2(g)
Your Answer:
Answer
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Suppose a 250. mL flask is filled with 0.70 mol of NO₂, 0.20 mol of NO and 1.9 mol of CO₂. The following reaction becomes possible: NO₂ (g) + CO (g) NO(g) + CO₂(g) The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 0.715 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of NO₂. Round your answer to two decimal places.arrow_forwardThe equilibrium constant, Kc, for the following reaction is 2.0. If the equilibrium mixture contains 1.8 M NO and 0.70 M Br2, what is the molar concentration of NOBr? 2NOB1(g) = 2NO(g) +Br2 (g) Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forwardSuppose a 500. mL flask is filled with 0.50 mol of N, and 0.90 mol of NO. This reaction becomes possible: N,(8) +O,(g) – 2NO(g) Complete the table below, so that it lists the initial molarity of each compound, the change in molarity of each compound due to the reaction, and the equilibrium molarity of each compound after the reaction has come to equilibrium. Use x to stand for the unknown change in the molarity of N,. You can leave out the Msymbol for molarity. NO initial change equilibriumarrow_forward
- At a certain temperature, the reaction: PCl5(g) ⇆ PCl3(g) + Cl2(g) has an equilibrium constant Kc = 6.7E-6. Calculate the equilibrium concentration of PCl3 if only PCl5 is present initially at a concentration of 0.30 M. Your answer should have two significant figures.arrow_forwardPart A For the reaction 3H2 (g) + N2 (g) = 2NH3 (g) at 225 °C the equilibrium contant is 1.7 × 102. If the equilibrium mixture contains 0.13 M H2 and 0.018 M N2 , what is the molar concentration of NH3 ? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forwardNitrogen dioxide and water react to form nitric acid and nitrogen monoxide, like this: 3 NO₂(9)+H₂O(1)→2 HNO3(aq) + NO(g) At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 4.4 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of nitrogen dioxide, water, nitric acid, and nitrogen monoxide at equilibrium has the following composition: compound amount NO₂ 10.6 g H₂O 138.4 g HNO3 21.8 g NO 19.6 g Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. с K = [] x10 ×arrow_forward
- Suppose a 250. mL flask is filled with 1.7 mol of NO2, 0.80 mol of CO and 0.70 mol of CO2. The following reaction becomes possible: NO2(g) + CO(g) = NO(g) + CO2(g) The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 2.90 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of NO. Round your answer to two decimal places.arrow_forwardSuppose a 500. mL flask is filled with 0.60 mol of CO, 0.30 mol of NO and 1.7 mol of CO,. The following reaction becomes possible: NO,(9) + CO(2) = No(g) + CO,(g) The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 0.953 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of NO. Round your answer to two decimal places. 0.37 M ?arrow_forwardUse the References to access important values if needed for this question. The equilibrium constant, Kc, for the following reaction is 0.0290 at 1150 K. 2SO3 (g)2SO2(g) + O2(g) If an equilibrium mixture of the three gases in a 19.7 L container at 1150 K contains 0.251 mol of SO3(g) and 0.353 mol of SO2, the equilibrium concentration of O₂ is M. Submit Answer Retry Entire Group 9 more group attempts remainingarrow_forward
- Suppose a 250. mL flask is filled with 1.4 mol of CO, 1.9 mol of H₂O and 1.0 mol of CO₂. The following reaction becomes possible: CO(g) + H₂O(g) + CO₂(g) + H₂(g) 2 The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 9.28 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of CO. Round your answer to two decimal places. M X Ś ?arrow_forwardCO2(g) + H2(g) « H2O(g) + CO(g) When H2(g) is mixed with CO2(g) at 2,000 K, equilibrium is achieved according to the equation above. In one experiment, the following equilibrium concentrations were measured. [H2] = 0.20 mol/L [CO2] = 0.30 mol/L [H2O] = [CO] = 0.55 mol/L (a) What is the mole fraction of CO(g) in the equilibrium mixture? (b) Using the equilibrium concentrations given above, calculate the value of Kc, the equilibrium constant for the reaction. (c) Determine Kp in terms of Kc for this system. (d) When the system is cooled from 2,000 K to a lower temperature, 30.0 percent of the CO(g) is converted back to CO2(g). Calculate the value of Kc at this lower temperature. (e) In a different experiment, 0.50 mole of H2(g) is mixed with 0.50 mole of CO2(g) in a 3.0-liter reaction vessel at 2,000 K. Calculate the equilibrium concentration, in moles per liter, of CO(g) at this…arrow_forwardWe don't see the answer written with a photo or pen, give the answer using the toolarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY