
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
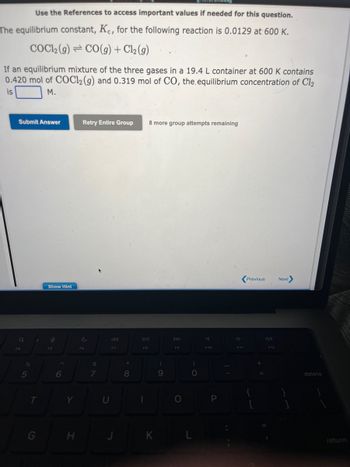
Transcribed Image Text:Use the References to access important values if needed for this question.
The equilibrium constant, Kc, for the following reaction is 0.0129 at 600 K.
COC12 (g) CO(g) + Cl₂ (g)
If an equilibrium mixture of the three gases in a 19.4 L container at 600 K contains
0.420 mol of COC12 (g) and 0.319 mol of CO, the equilibrium concentration of Cl2
is
M.
Submit Answer
Q
F4
5
T
G
Show Hint
O
F5
6
Y
H
Retry Entire Group 8 more group attempts remaining
F6
&
7
K
F7
U
J
8
DII
F8
1
(
9
DD
F9
O
)
O
KI L
F10
P
F11
Previous
+
F12
Next
delete
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The equilibrium constant, Kc, for the following reaction is 0.0129 at 600 K. COC12 (g) CO(g) + Cl₂ (g) If an equilibrium mixture of the three gases in a 16.3 L container at 600 K contains 0.497 mol of COC1₂(g) and 0.339 mol of CO, the equilibrium concentration of Cl2 is || M.arrow_forwardUse the References to access important values if needed for this question. The equilibrium constant, Kỵ, for the following reaction is 55.6 at 698 K. H₂ (g) + I2(g) → 2HI(g) Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of reactants and product when 0.384 moles of H₂ and 0.384 moles of I2 are introduced into a 1.00 L vessel at 698 K. [H₂] = | M [12] [HI] = = M Marrow_forward= [Review Topics] [References] Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. The equilibrium constant, Ke, for the following reaction is 10.5 at 350. K. 2CH₂Cl2 (9) CH4 (9) + CCl4 (9) = Calculate the equilibrium concentrations of reactant and products when 0.315 moles of CH₂Cl2 (g) are introduced into a 1.00 L vessel at 350. K. [CH₂Cl₂] = [CH4] [CC14] = = Submit Answer Show Hint NOV 30 Q F4 M M M Retry Entire Group 9 F5 + tv ♫ 8 9 more group attempts remaining MacBook Air C F6 < F7 DII F8 Previous Email Instructor F9 O Next Save and Exit J F10arrow_forward
- A chemist is studying the following equilibirum, which has the given equilibrium constant at a certain temperature: -2 N2(g) + 3 H,(g) 2 NH3(g) K,=4. x 10 He fills a reaction vessel at this temperature with 9.0 atm of nitrogen gas and 4.5 atm of hydrogen gas. Use this data to answer the questions in the table below. dla O yes Can you predict the equilibrium pressure of NH, using only the tools available to you within ALEKS? O no If you said yes, then enter the equilibrium pressure of NH, at right. ||atm Round your answer to 1 significant digit. Explanation Check © 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy | Accessibilityarrow_forwardPlease help.arrow_forwardUsing the general properties of equilibrium constants At a certain temperature, the equilibrium constant K for the following reaction is 924.: CO(g) + H₂O(g) → CO₂(g) + H₂(g) Use this information to complete the following table. Suppose a 17. L reaction vessel is filled with 0.75 mol of CO₂ and 0.75 mol of H₂. What can you say about the composition of the mixture in the vessel at equilibrium? What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Round your answer to 3 significant digits. CO₂(g) + H₂(9) CO(g)+H₂O(g) What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Round your answer to 3 significant digits. 3 CO(g) + 3H₂O(g) P 3 CO₂(g) + 3H₂(9) There will be very little CO and H₂O. There will be very little CO2 and H₂. Neither of the above is true. K = 0 K = 0 ■ x10 X ? 00. Ar 8.arrow_forward
- Suppose a 500. mL flask is filled with 1.2 mol of CO, 2.0 mol of H,0 and 0.90 mol of CO,. The following reaction becomes possible: Co(2) + H,0(g) – Co,(3) +H,(g) The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 0.545 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of H,0. Round your answer to two decimal places.arrow_forwardSuppose a 500. mL flask is filled with 0.10 mol of NO,, 1.8 mol of NO and 0.50 mol of CO,. The following reaction becomes possible: 2' NO, (g) +CO(g) – NO(g) + CO, (g) The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 1.08 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of NO,. Round your answer to two decimal places. olo OM Ar G Explanation Check © 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | Privacy Center | Accessibility .......................................... .................................arrow_forwardSuppose a 500. mL flask is filled with 0.70 mol of CO, 1.7 mol of NO and 1.0 mol of CO,. The following reaction becomes possible: NO, (g) +CO(g)- NO(g) +CO, (g) The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 5.97 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of CO. Round your answer to two decimal places. IM Continue MacBook Airarrow_forward
- Using the general properties of equilibrium constants At a certain temperature, the equilibrium constant k for the following reaction is 9.84 x 101: N,(g) + 0,(g) = 2 NO(g) Use this information to complete the following table. Suppose a 30. L reaction vessel is filled with 0.64 mol of N2 and There will be very little N, and O2. alo 0.64 mol of 0,. What can you say about the composition of the mixture in the vessel at equilibrium? There will be very little NO. Neither of the above is true. What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Round your answer to 3 significant digits. K 2 NO(g) N3(9)+Og(9) What is the equilibrium constant for the following reaction? Round your answer to 3 significant digits. K = 3 N,(9)+30,(9) 6 NO(g)arrow_forwardSuppose a 500. mL flask is filled with 0.70 mol of Cl,, 1.4 mol of CHCI, and 0.50 mol of CCl,. The following reaction becomes possible: 3 Cl,(g)+ CHC1,(g) – HC1 (g)+ CCl,(g) 4 The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 1.78 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of HCl. Round your answer to two decimal places. ||Marrow_forwardUse the References to access important values if needed for this question. The equilibrium constant, K for the following reaction is 6.50×10 at 298K. 2NOBR(g)=2NO(g) + Br,(g) If an equilibrium mixture of the three gases in a 17.2 L container at 29SK contains 0.369 mol of NOBR(g) and 0.435 mol of NO, the equilibrium concentration of Br, is M.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY