
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
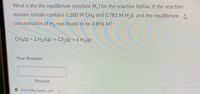
Transcribed Image Text:What is the the equilibrium constant (K) for the reaction below, if the reaction
mixture initially contains 0.500 M CH4 and 0.781 M H₂S, and the equilibrium
concentration of H₂ was found to be 0.896 M?
CH4(g) + 2 H₂S(g) = CS₂(g) + 4 H₂(g)
Your Answer:
Answer
CHM1046L_Namin....pdf
A
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the following reaction: SO₂Cl2 (g) SO₂ (g) + Cl₂ (g) A reaction mixture is made containing an initial [SO₂Cl₂] of 2.4×10-2 M. At equilibrium, [Cl₂] = 1.3×10-² M. Part A Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant (Kc). Express your answer to two significant figures.arrow_forwardHydrogen and chlorine react to form hydrogen chloride, like this: H,(g) + Cl,(g) 2 HCl(g) Also, a chemist finds that at a certain temperature the equilibrium mixture of hydrogen, chlorine, and hydrogen chloride has the following composition: compound concentration at equilibrium 0.86 M Cl, 0.30 M HC1 1.9 M Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K = 0arrow_forwardQ2 For the chemical reaction shown below select the correct the equilibrium constant expression for 4NH3(g) + 302(g) = 2N2(9) + 6H2O(g) Q3 4NH3(9) + 302(9) = 2N2(9) + 6H2O(9) If a chemist mixed 2.930 moles of ammonia (NH3) gas with 1.978 moles of oxygen (02) gas in a 7.95 Liter air tight metal flask at 127°C and after the pressures stabilizes at equilibrium and then draws an air sample and found 0.683 moles of nitrogen (N2) gas then how many moles of ammonia (NH3) is present at equilibrium? 4NH3(9) + 302(9) 2N2(9) + 6H2O(g) Q4 If a chemist mixed 2.930 moles of ammonia (NH3) gas with 1.978 moles of oxygen (02) gas in a 7.95 Liter air tight metal flask at 127°C and after the pressures stabilizes at equilibrium and then draws an air sample and found 0.683 moles of nitrogen (N2) gas then how many moles of water (H,O) is present at equilibrium? 4NH3(9) + 302(g) 2N2(9) + 6H2O(9) Q5 If a chemist mixed 2.930 moles of ammonia (NH3) gas with 1.978 moles of oxygen (02) gas in a 7.95 Liter air…arrow_forward
- Part A For the reaction 3H2 (g) + N2 (g) = 2NH3 (g) at 225 °C the equilibrium contant is 1.7 × 102. If the equilibrium mixture contains 0.13 M H2 and 0.018 M N2 , what is the molar concentration of NH3 ? Express your answer to two significant figures and include the appropriate units.arrow_forwardCalculate the equilibrium concentrations for each reactant and product in the following equation at initial concentrations of 0.0400 M SO2, 0.0500 M NO2, 1.300 M NO and 0.200 M SO3. The equilibrium constant for this reaction, Kc = 85.0. SO2(g) + NO2(g) ↔ NO(g) + SO3(g) Group of answer choices [SO2] = 0.0275, [NO2] = 0.0375, [NO] = 1.313, [SO3] = 0.213 [SO2] = 0.0309, [NO2] = 0.0409, [NO] = 1.309, [SO3] = 0.209 [SO2] = 0.0525, [NO2] = 0.0625, [NO] = 1.288, [SO3] = 0.188 [SO2] = 0.0491, [NO2] = 0.0591, [NO] = 1.291, [SO3] = 0.191arrow_forwardFor the reaction below, the concentrations at equilibrium are [SO₂] = 0.60 M, [O₂] = 0.25 M, and [SO₂] = 1.6 M. What is the value of the equilibrium constant, Ke? 2 SO₂(g) + O₂(g) →→→ 2 SO₂(g) • Report your answer using two significant figures. Provide your answer below:arrow_forward
- The equilibrium constant, Kc , for the following reaction is 5.10×10-6 at 548 K.NH4Cl(s) NH3(g) + HCl(g)If an equilibrium mixture of the three compounds in a 5.01 L container at 548 K contains 2.51 mol of NH4Cl(s) and 0.217 mol of NH3, the number of moles of HCl present is _____ moles.arrow_forwardWrite the equilibrium constant expression, K , for the following reaction: (If either the numerator or denominator is blank, please enter 1.) K=arrow_forward1.arrow_forward
- Mercury and oxygen react to form mercury(II) oxide, like this: 2 Hg(1)+O2(g)→2 HgO(s) At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 7.0 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of mercury, oxygen, and mercury(II) oxide at equilibrium has the following composition: compound amount Hg 7.0 g O2 5.8 g HgO 16.5 g Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K, for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K_ = | x10arrow_forwardThe following reaction has an equilibrium constant of 2.65 x10-3 at 300K. Br2 (g) + Cl2 (g) 2 BrCl (g) Which of the following statements is true? Question 5 options: The system has a higher concentration of reactant molecules than product molecules at equilibrium, but there are significant quantities of both. The system consists almost entirely of reactant molecules at equilibrium. The system consists almost entirely of product molecules at equilibrium. The system has approximately equal concentrations of product and reactant molecules at equilibrium. The system has higher concentrations of product molecules than reactant molecules at equilibrium, but there are significant quantities of both.arrow_forwardNitrogen dioxide and water react to form nitric acid and nitrogen monoxide, like this: 3 NO₂(g) + H₂O(1)→2 HNO3(aq) + NO(g) At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 3.4 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of nitrogen dioxide, water, nitric acid, and nitrogen monoxide at equilibrium has the following composition: compound NO₂ H₂O HNO3 NO amount 5.9 g 142.0 g 15.1 g 12.0 g Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. с K = D 0 C x10 X Śarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY