
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
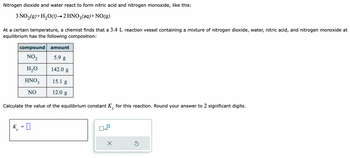
Transcribed Image Text:Nitrogen dioxide and water react to form nitric acid and nitrogen monoxide, like this:
3 NO₂(g) + H₂O(1)→2 HNO3(aq) + NO(g)
At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 3.4 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of nitrogen dioxide, water, nitric acid, and nitrogen monoxide at
equilibrium has the following composition:
compound
NO₂
H₂O
HNO3
NO
amount
5.9 g
142.0 g
15.1 g
12.0 g
Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.
с
K = D
0
C
x10
X
Ś
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Equilibrium constant Kc for a reaction is defined as the product of the molar concentrations of the products, each raised to the power equal to a stoichiometric coefficient divided by the product of the molar concentrations of the reactant each raised to the power equal to its stoichiometric coefficient .
& the most important convention to be kept in mind is that the active mass of a pure solid or pure liquid is considered to be constant.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Nitric acid and nitrogen monoxide react to form nitrogen dioxide and water, like this: 2 HNO,(aq)+NO(9)-3 NO,(g)+H,0(1) At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 5.0 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of nitric acid, nitrogen monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, and water at equilibrium has the following composition: compound amount HNO3 22.6 g NO 15.5 g NO2 21.9 g H,0 107.8 g Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K, for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K, = 0 Plecy Terms of Use ©2021 McGraw-Hl Education All Rights Reserved Check Explanationarrow_forward2. Initially, a system contains 1.00 mol of NOCI in a 2.00 L container. At equilibrium, the system contains 0.056 mol of Cl₂ in a 2.00 L container. Create an ICE table and determine the equilibrium concentrations and the value of Keq. 2 NOCI (g) = 2 NO(g) + Cl₂ (g)arrow_forwardA mixture of 30.0 mol of NO(g) and 18.0 mol of O2(g) is placed in an empty 3.00-liter flask held at a constant temperature. These gases react until the reaction represented below comes to equilibrium. At equilibrium, the vessel contains 26.4 moles of NO2. What is the value of the equilibrium constant at the constant temperature? 2NO(g) + O2(g) 2NO2(g)arrow_forward
- Carbon dioxide and water react to form methanol and oxygen, like this: 2 CO,(g)+4 H2O(g)→2 CH;OH(1)+3 02(g) At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 3.0 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of carbon dioxide, water, methanol, and oxygen at equilibrium has the following composition: ol. compound amount Ar CO2 3.88 g H2O 4.05 g CH,OH 2.21 g O2 1.49 g °C Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K, for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K_ = 0 x10arrow_forwardCalcium carbonate decomposes to form calcium oxide and carbon dioxide, like this: CaCO3(s) CaO(s) + CO₂(g) At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 2.8 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of calcium carbonate, calcium oxide, and carbon dioxide at equilibrium has the following composition: compound amount CaCO3 73.8 g CaO 42.1 g CO₂ 38.4 g Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K = [0]arrow_forwardNitric acid and nitrogen monoxide react to form nitrogen dioxide and water, like this: 2 HNO3(aq)+NO(g)→ 3 NO,(g)+H,0(1) At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 4.5 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of nitric acid, nitrogen monoxide, nitrogen dioxide, and water at equilibrium has the following composition: compound amount dlo HNO3 14.2 g 18 Ar NO 7.3 g NO, 19.2 g H,O 87.0 g Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K = 0 x10 ?arrow_forward
- Iron(III) oxide and hydrogen react to form iron and water, like this: Fe,0;(s)+3 H,(g)→2FE(s)+3H,O(9) At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 5.1 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of iron(III) oxide, hydrogen, iron, and water at equilibrium has the following composition: compound amount db Fe,O3 4.36 g H, 4.35 g Fe 3.23 g H,0 2.73 g Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K, for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. Explanation Check 2022 McGraw H LLC. A Rights Reserved Terms of Use Pvacy Center Accessibil DE P Type here to search JU P. Alt alexa ENADLEDarrow_forwardCarbon dioxide and water react to form methanol and oxygen, like this: 2 CO,(9)+4 H,0(g)→2 CH;OH(1)+3 O2(9) At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 7.2 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of carbon dioxide, water, methanol, and oxygen at equilibrium has the following composition: compound amount CO, 3.88 g H,0 4.38 g CH;OH 4.22 g O2 1.08 g Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K, for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K_ = 0arrow_forwardA mixture of 0.10 mole NO, 0.050 mole H₂, and 0.10 mole H₂O is placed in a 2.0 L vessel. The following equilibrium is established: + 2 H₂ (g) = N2(g) + 2 H₂O (g) 2 NO At equilibrium [NO] = 0.030 M. The initial concentration of N₂ was not mentioned so you must assume [N₂] = 0. Calculate the equilibrium concentrations (in M) of: More Information X H₂ (g) XN₂ (g) X H₂O (g) Question Answer Your answer -.020 is Your answer .035 is in Your answer .170 is i Tol: 0.0001 Tol: 0.001 Tol: 0.001arrow_forward
- Phosphorus pentachloride decomposes according to the chemical equation Ke = 1.80 at 250 °C PC15 (g) ⇒ PC13(g) + Cl₂(g) A 0.3606 mol sample of PC15 (g) is injected into an empty 3.95 L reaction vessel held at 250 °C. Calculate the concentrations of PC15 (g) and PC13 (g) at equilibrium. [PCI,] = [PC1₂] = M Marrow_forwardCalcium oxide and carbon dioxide react to form calcium carbonate, like this: CaO(s)+CO,(g)→CaCO3(s) At a certain temperature, a chemist finds that a 8.1 L reaction vessel containing a mixture of calcium oxide, carbon dioxide, and calcium carbonate at equilibrium has the following composition: compound amount СаО 43.8 g CO2 40.9 g CaCO3 55.4 g Calculate the value of the equilibrium constant K, for this reaction. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K = 0 x10arrow_forwardCalculating an equilibrium constant from a partial equilibrium composition Steam reforming of methane ( CH4 ) produces "synthesis gas," a mixture of carbon monoxide gas and hydrogen gas, which is the starting point for many important industrial chemical syntheses. An industrial chemist studying this reaction fills a 1.5 L flask with 4.3 atm of methane gas and 1.8 atm of water vapor, and when the mixture has come to equilibrium measures the partial pressure of hydrogen gas to be 3.2 atm. Calculate the pressure equilibrium constant for the steam reforming of methane at the final temperature of the mixture. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. K p 11] ☐ x10 ☑ ⑤arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY