
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
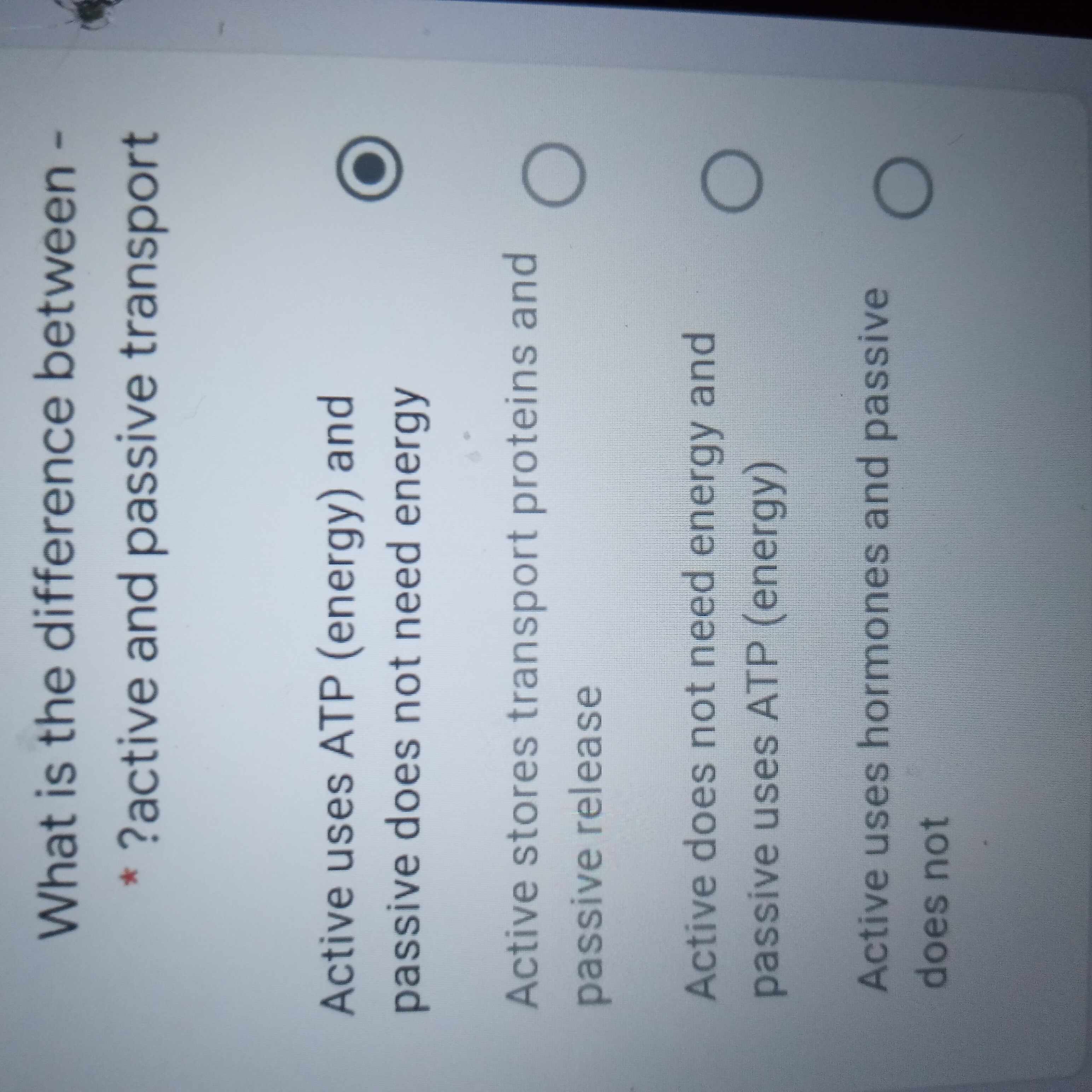
Transcribed Image Text:What is the difference between -
* ?active and passive transport
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following proteins is categorized as an integral, lipid-linked membrane protein? band 3.0 protein the Ras protein glycophorin A cytochrome c COX-1arrow_forwardThe plasma membrane has a hydrophobic interior due to the two present in each phospholipid found in the phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane. The plasma membrane allows some molecules to cross but not all. Therefore, the plasma membrane is said to be Molecules that are nonpolar and hydrophobic will cross the membrane with ease by Does this process require energy? When molecules move across the plasma membrane by passive transport, they will move down or with the_ from an area of concentration to an area of. concentration. Polar, hydrophilic molecules and charged ions will move across the plasma membrane by the process of_ This does not require energy, but it does require a A special case of diffusion is known as which is the movement of water across the plasma membrane. If a cell is placed into a solution that is hypertonic compared to the inside of the cell, the cell would If a cell is placed into a hypotonic solution compared to the inside of the cell, the cell water. would…arrow_forwardWhy it is important for the cell membrane to be amphipathic ?arrow_forward
- Proteins that do not possess a signal sequence of substantially non-polar amino acids, and that do not possess a signal sequence of several positively-charged amino acids, are destined for which cellular site? the mitochondria the peroxisome the chloroplast the nucleus the cytosolarrow_forwardIn biological systems, an ACTIVE transport process is one in which an important chemical component is moved from where it is in concentration, to where it is in concentration. Meanwhile, a PASSIVE transport (or diffusion) process is one in which an important chemical component moves from where it is in concentration to where it is in concentration. A FACILITATED transport process is a form of transport, where an important chemical component moves with the aid of a channel or similar structure. One specific example of a facilitated transport structure in the cell membrane is which aids in the movement of a particular chemical component, namelyarrow_forwardWhich type of membrane transporter requires a gradient to move molecules across the membrane? O Voltage-gated channels Leak channels O Ligand-gated channels All of the above require a gradient O None of the above require a gradientarrow_forward
- This type of passive transport :•does not require ATP•uses transport proteins to increase the rate of diffusion •helps transport polar molecules (H2O, H+). 2 wordsarrow_forwardThe outward movement of protons (H+), and the inward movement of sodium ions (Na+), across the plasma membrane of a muscle cell (using the existing sodium gradient), is: one example of facilitated diffusion one example of an antiport system one example of a symport system one example of a uniport system one example of simple diffusionarrow_forwardImportin Cytoplasm Pi NLS GDP Ran Protein Ran GAP CDP CDP Ran GEF Nucleus The cargo protein is released in the nucleus because: O it no longer contains a NLS. GDP-Ran binds preferentially to the cargo causing it to release importin. GTP-Ran binds to importin and displaces the cargo.arrow_forward
- Proteins that possess a signal sequence of substantially non-polar amino acids, but do not possess a signal sequence of several positively-charged amino acids, are destined for which cellular location? the peroxisome the endoplasmic reticulum the chloroplast the mitochondrion the cytosolarrow_forwardIn conditions of dehydration, plant cells can increase their water retention by regulating the function of some or all of their aquaporins, membrane-bound protein channels that allow water to move through the cell membrane via facilitated diffusion. Which of the following describes a likely mechanism by which aquaporins can be used to regulate the movement of water across the plant cell membrane? A B с D Synthesis of additional aquaporins by the plant cell ribosomes will allow the cell to coun- teract the movement of water out of the cell. Inhibition of ATP hydrolysis will make the aquaporins unable to remove water from the cell and cause more water to remain in the cell. Inactivation of aquaporins will make water molecules unable to move across the plant cell membrane and allow more water to remain in the cell. Inhibition of the plant cell Golgi apparatus will decrease the production rate of vesicles and slow down the exocytosis of water molecules.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education