
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
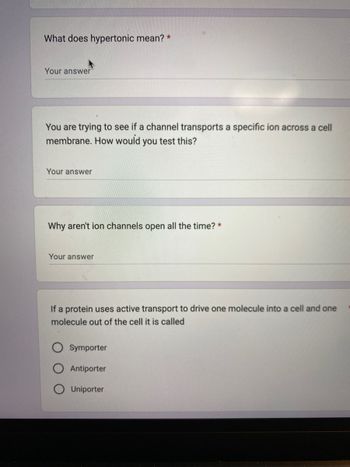
Transcribed Image Text:What does hypertonic mean? *
Your answer
You are trying to see if a channel transports a specific ion across a cell
membrane. How would you test this?
Your answer
Why aren't ion channels open all the time? *
Your answer
If a protein uses active transport to drive one molecule into a cell and one
molecule out of the cell it is called
Symporter
Antiporter
Uniporter
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
The plasma membrane of the cell regulates the movement of different molecules in and out of the cell and this function is regulated by the activity of different transporter proteins that are present in the plasma membrane and they are trans membrane proteins which allows the movement of large and hydrophilic molecules to cross the hydrophobic core of the plasma membrane.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Reset Help Receptor-mediated endocytosis Secondary active transport Facilitated diffusion Exocytosis Passive transport Primary active transport Phagocytosis Osmosis Simple diffusion Pinocytosis ATPase pump Solute (jon) Solutes Solute Solute Solute H,0 Carrier protein -Plasma membrane Solute Carrier/ channel protein ATPase pump Cytosol ADP ADP Partide Ligand Pseudo- Receptor. Receptor podium Protein-coated pit Protein-coated pit Forming veside Cytosol Veside Veside Vesidlearrow_forwardHow is osmosis different from simple diffusion? osmosis involves the movement of water, simple diffusion involves the movement of solutes simple diffusion utilizes energy in the form of a solute concentration gradient, osmosis utilizes energy in the form of ATP Osimple diffusion moves solutes with their concentration gradient, osmosis moves solutes against their concentration gradient osmosis is a form of active transport, simple diffusion is a form of passive transport Det betalen տներն ոգուarrow_forwardPlease answer both, thank youarrow_forward
- Rebuild the cell above that is hypertonic to the solution outside. By hitting the red button, add 20 solutes (green) to the inside of the cell and add 5 water (blue) to the inside of the cell. Also, add 20 water (blue) to the outside of the cell and 5 solutes (green) to the outside of the cell. Add blue gated channels to the membrane. Q: What happens to the water molecules in this situation? Q: Which of the above situations is closer to a living membrane system?arrow_forwardWhat type of membrane protein is shown in the figure below? HIN NH Cysteine-rich domain Protein tyrosine kinase domain COO "Ooc O Receptor protein O Transport protein Structural protein O Channel proteinarrow_forwardWhich is the definition of 'retrograde' with respect to membrane trafficking? movement from the endosome to the lysosome movement from the ER to the Golgi to either the plasma membrane or the endosome/lysosome movement from the cytoplasm to the nucleus movement from the Golgi to the ERarrow_forward
- What are the differences between sodium-potassium exchange pump and sodium-glucose transporter? Besides I am struggling with understanding the Vesicular Transport (Bulk transport) why it is a form of an active transport? Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion and osmosis are all passive transport. What are the differences between them and how can be an active form??? And why not concentration gradient is not involving??? Because it utilise transport proteins like receptor mediator endocytosis. It might changes some gradients. Am I misleading some concepts??? Endocytosis and Exocytosis concepts are confusing too. Thanks for reading my question :D I am really confusing of the membrane transportarrow_forwardThe experiment described in Figure 11-16 was performed at 37 °C. If the experiment were carried out at 10 °C, what effect would you expect on the rate of diffusion? Why?arrow_forwardI think it works by freezing the bilayer of the membrane and then hitting it sharply with a diamond knife. The sharp hit creates a fracture in the membrane and usually that fracture follows the plane between the two layers of the membrane lipid.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education