
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
What are the three muscle types shown in slide 2 (between cardiac, skeletal, and smooth)? Label A, B, and C, and explain the reasoning for why you labeled each image as such. a. Compare the muscle types. What are the similarities and differences between each muscle type?
- Why is methylene blue used to stain cells? What does it bind to? Which type of microscopy should you use to visualize cells stained with methylene blue?
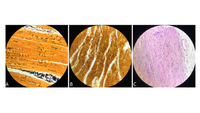
Transcribed Image Text:A
В
C
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Please help me answer thisarrow_forwardWhen utilizing microprocessor technology for testing muscle strength, you are typically looking at what form of muscle contraction? Concentric Isokinetic Isometric Eccentricarrow_forwardPlease answer the question along with the reason I'll definitely give a likearrow_forward
- Assuming the ultrasound beam strikes the muscle layer at 90◦ , how wide will the fat muscle boundary appear in the ultrasound image?arrow_forward1.Why is wavelenth the main limiting factor on limit of resoltuin in light microscopy? 2.Assuming that all other variables remain constant, explain why light of shorter wavelengths will produce a clearer image that light of longer wavelenths. 3. Why aren't the magnification of both ocular lenses of a binocular microscope used to calculate total magnification?arrow_forwardSelect all correct answers (i.e. more than one answer may be correct). What is the advantage of having a muscle with a bipennate muscle fiber orientation rather than a longitudinal fiber orientation? Assume that the general muscle volume is held constant between orientation types. Obipennate muscle has a smaller physiological cross-sectional area Obipennate muscle has larger force-producing capabilities Obipennate muscle has a greater muscle shortening capabilityarrow_forward
- Assume you are observing the diatom pictured in Figure 1 using the 10X lens in a compound light microscope. You move to the 40X lens and then again to the 100X lens by only rotating the turret (remember that the lenses are parfocal), without making any other adjustments to the microscope. c) After making your adjustments, you notice that the midline of the diatom is in focus while the remainder is blurry. Explain, based on microscopy principles, why this has occurred Provide a description of the procedure to prepare an acidic stain of bacteria using Nigrosin as it would appear in the Methods section.arrow_forwardLet's say you placed the letter "e" slide on the microscope stage so that it is in the normal, correct orientation. You centered over the light source and under the objective. 1. How would it appear through the ocular lens after focusing? Describe what you would see. 100 in Click or tap here to enter text. Smaller 2. When you move the slide to the left with the stage controls, how does it appear to move through the ocular lens? Click or tap here to enter text.arrow_forwardWhat part of the microscope adjusts the amount of light projected onto the slide? Group of answer choices A. rheostat B. on/off switch C. iris D. course adjustmentarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education