
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
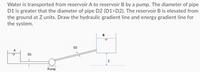
Transcribed Image Text:Water is transported from reservoir A to reservoir B by a pump. The diameter of pipe
D1 is greater that the diameter of pipe D2 (D1>D2). The reservoir B is elevated from
the ground at Z units. Draw the hydraulic gradient line and energy gradient line for
the system.
D2
A
D1
Pump
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A train has a weight of 100 tons (2,000lbf) is stopped from 4 mph in 1 ft by a hydraulic cushion.If rolling friction is 0.05 of the car weight, Find: • The stopping force using the gs method • The stopping force using the energy methodarrow_forward= Water flows into a tank and out through another pipe, as shown in the figure below. The water in the tank has a surface area, Asur f 5.6 m². At the bottom of the tank there is a door inclined at an angle = 25 degrees with respect to the horizontal. The door has a length L = 1.1 m and a width w=1 m (out of the page). The flowrate into the tank is Q₁ (t) flowrate out is Qo(t) = 0.05 m³/s At time t = Asurf = 0.26 m³/s and the 0, the water has a depth ho = 2.5 m. The density of water is p = 1000 kg/m³. Ө h(t) Qoutarrow_forwardA U-shaped tube is filled with water of density 1000 kg/m3 until the level of the liquid is 28 cm above the bottom of the tube. Then oil of specific gravity 0.78 is poured into one branch of the tube until the level of the liquid in the other branch is 34 cm above the bottom of the tube. (g=9.8m/s2) I) Find the level of the oil-water interface in the branch where the oil was spilled II) Find the level of the oil-air interface in the branch where the oil was spilledarrow_forward
- Help !! Don't copy from othersites ,write the variables clearly. Solve using the energy equation.arrow_forwardConsider the water pump shown in fig, Determine the power that the pump supplies to the water if the velocity of the water is at A is V= 2 m/s and the pressures at A and B are 175kPa and 350 kPa, respectively. Neglect friction losses.arrow_forwardLet the pressure gradient in the pipe be 1500 Pa/m and the diameter of the pipe be 4.0 mm. What is the average speed through this pipe of 20∘C motor oil? What is the average speed through this pipe of 100∘C motor oil?arrow_forward
- Q2/: As shown in the figure, the Assumptions of the flow through the venturi is steady, incompressible, irrational with negligible frictional effects , the effect of air column on the pressure change is negligible, the pressure can be assumed to be uniform at a given cross-section of the venturi meter and the flow is horizontal . Air is flowing through a venturi meter whose diameter is 2.6 in at the entrance part (location 1) and 1.8 in at the throat (location 2). The gage pressure is measured to be 12.2 psia at the entrance and 11.8 psia at the throat. Neglecting frictional effects, take the air density to be 0.075 lbm/ft. 1. Show that the volume flow rate can be expressed as: 2(P P2) | = A, p(1 – AŽIA}) 2. Find the flow rate of the air? 12.2 psia 11.8 psia Air 2.6 in 1.8 inarrow_forwardProblem 3: Water issues from a hole in a large tank, as shown in the attached figure.Assuming frictionless flow, find L.arrow_forwardThe flow of water from a reservoir is controlled by an L-shaped gate hinged at point A, as shown in the figure. The mass of the weight at B (a = 4 m to the right of A, b = 3 m above the base) is 5125 kg. If the gate opens when the water height is 1.75 m above the base, determine the width (in meters, not showing) of the gate.arrow_forward
- The upper part of a water tank is divided into two sections as shown in the figure, while a fluid with an unknown density is poured on one side, the water level on the other side rises to compensate for this effect. According to the final fluid heights shown in the figure, find the density of the liquid added to the left chamber. Assume that the added liquid is immiscible with water. (ρwater=1000 kg/m3)arrow_forwardWater flows inside a solid cylindrical pipe, which narrows as it goes up to a height h (see diagram below). The lower horizontal section has circular cross-sectional diameter d, whereas the upper horizontal section has diameter d/2. Let us denote A to be a point at the lower horizontal section and B to be a point at the upper horizontal section. The flow speed at A and B is uд and u, respectively. The pressure at A and B is PA and PB, respectively. РА UA Oom Ja d d/21 1 UB h (a) Assuming water to be incompressible, show that the flow speed at B is four times the flow speed at A. (b) Use Bernoulli's equation to find the drop in the water pressure from A to B. Express the result in terms of h, uд, the density of water p, and the acceleration of gravity g. (c) Above certain critical height h, vapour bubbles start to appear at the top horizontal section, which hinders water flow through the pipe. Explain why this happens.arrow_forwardA spherical water tank with an inner radius of 11 meters has its lowest point 3 meters above the ground. Water is pumped from ground level through an inflow pipe that meets the tank at its lowest point (see figure). Neglecting the volume of the inflow pipe, how much work is required to fill the tank if it is initially empty? Use 1000 kg/m³ for the density of water and 9.8 m/s² for the acceleration due to gravity. dy 11 m (Type exact answers, using à as needed.) inflow pipe Set up the integral that gives the work (in joules) required to fill the tank. Use a vertical axis whose origin corresponds with the center of the sphere and use increasing limits of integration. 3 marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY