
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Please find attached questions. Thank you.
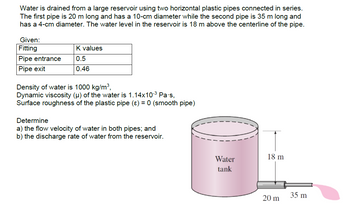
Transcribed Image Text:Water is drained from a large reservoir using two horizontal plastic pipes connected in series.
The first pipe is 20 m long and has a 10-cm diameter while the second pipe is 35 m long and
has a 4-cm diameter. The water level in the reservoir is 18 m above the centerline of the pipe.
Given:
Fitting
Pipe entrance
Pipe exit
K values
0.5
0.46
Density of water is 1000 kg/m³,
Dynamic viscosity (μ) of the water is 1.14x10-3 Pa·s,
Surface roughness of the plastic pipe (ε) = 0 (smooth pipe)
Determine
a) the flow velocity of water in both pipes; and
b) the discharge rate of water from the reservoir.
18 m
Water
tank
35 m
20 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A Pitot tube in a pipe in which air is flowing is connected to a manometer containing water asshown below. If the difference in water levels in the manometer is 10 cm, what is the velocity of flow in the pipe? Assume a tube coefficient of Cp = 0.99, specific weight of air is 12 N/ sq.m.arrow_forwardQ2- Water density =1000 kg/m and viscosity is 0.001 Ns/m², is pumped between two reservoirs at 0.2m/s through a 400 m of 8 cm diameter Cast Iron pipe and several minor losses as shown in the figure. Compute the pump power required in kW. Use the last one digit of your ID number for Z1 level in meter. Screwed Z2= 50 m regular 90° elbow Sharp exit Z;= ID m Sharp entrance Half-open gate valve `bend radius Pump Open globe valve 8 cm diameterarrow_forwardA pump delivers water from a tank (A)X water surface elevation-110m) to tank B (water surface elevation= 170m). The suction pipe is 45m long and 35cm in diameter the delivered pipe is 950m long 25cm in diameter. Loss head due to friction hf1 = 5m and h2 3m If the piping are from pipe(1)= steel sheet metal pipe(2)= stainless – steel Calculate the following i) ii) The discharge in the pipeline The power delivered by the pump.arrow_forward
- Please solve a question according to the data of the requestarrow_forwardAs shown in the figure below, a cylindrical tank with a hole in the bottom and an air vent in the top is being filled with water. Given the following: Dtank = 4 ft hill = 8 ft NOG height of water in tank when tank is filled Qin = 10 gal/min %3D NOT UPL TO CHE diameter of hole Find: volumetric flowrate into tank EGG EXAM into the tank in slugs/second OT UPS XAM O NOT U EXAM (c) The rate at which the water level in the tank is mass flowrate (in slugs/second) of the water (b) The mass flowrate (in slugs/second) out of the tank UPLOAD TO CHE NOT UPLOAD when the water level reaches the fill height DO NOT UPL rising (in inches/minute) when the water level NOT UPL PLOAD TO CHEGG NOT UPLOAD TO CHEGG EXAM TO CHEGG EXAM OD TO CHEGG UP reaches the filled height то снE LOAD vent Dtank DO DO DO NOT UPLOADTO EXAM EX DO 0 DONOT UPLOA T Dhole G EXAM TO CNGO UPLOA hole mdotoutarrow_forwardFor the piping system of Fig. , all pipes are concretewith a roughness of 0.04 in. Neglecting minor losses, computethe overall pressure drop p1 - p2 in lbf/in2 ifQ =20 ft3/s. The fluid is water at 20°C.arrow_forward
- The water is flowing through a pipe having diameters 30 cm and 21 cm at sections land 2 respectively. The rate of flow through pipe is 40 litres/s. The section 1 is 7 m above datum and section 2 is 3 m above datum. If the pressure at section 1 is 37 N/cm? , find the following by neglecting losses: (ENTER ONLY THE VALUES BY REFERRING THE UNIT GIVEN IN BRACKETS) ) Area of cross section of section1 (unit in m?) = Area of cross section of section2 (unit in m?) = velocity at section 1 (unit in m/s) = velocity at section 2 (unit in m/s) = (ii) difference in datum head (Unit in m) = Pressure head at section 1 (Unit in m) = pressure head at section 2 (unit in m) =arrow_forwardU - tube is used to pressure the difference in water channel. p1= 1000 kg/m3. The orange fluid in the U - tube has a density: p2= 2000 kg/m3. The height a = 10 cm and h = 15 cm. If the pressure at point ① is 111 kPa, what is the pressure at point ② ?arrow_forward5. The large tank shown in the figure is filled with water to a height of ho. Water exits the 5-cm- diameter pipe at A and is collected in a tub at B. The tub is 2 m below the pipe exit. You may assume no viscous losses. Ро ho 0 A Control volume for part b 2 m B Figure for problem 5. 1. (a) It is required that the tub be filled at a volume flow rate of 0.028 m³/s. At what height, ho, must the tank be filled to achieve this flow rate if po = 50 kPa? (b) Using the control volume shown in the figure, show that the velocity in the horizontal direction remains constant as the water flows from A to B. (Hint: there is no force in the x-direction acting on the control volume.) (c) Find the angle, 0, at which the stream hits the tub. 0 Figure for part c).arrow_forward
- A pipeline with roughness ks = 1.0mm and diameter D = 8.8cm connects two reservoirs. The reservoirs are both open to the atmosphere and differ in surface elevation by H = 40m. The two reservoirs with the connecting pipe are shown in the figure below. You can assume density of water = 1003kg/m³, dynamic viscosity of water = 0.001Pas and acceleration due to gravity 9.81m/s². Local losses must be considered; assume reasonable values as introduced in the ENGG2500 lectures. Reservoir 1 = Pipe with: D,K, m. H a) What is the friction factor of the pipe for a flow rate of Q =44L/s? Provide your answer to 3 decimal places. The friction factor f = = b) For this case, what is the length of the pipe? Provide your answer to 3 decimal places. The length is L Reservoir 2arrow_forwardA 100 m length of a smooth horizontal pipe is attached to a large reservoir. A attached to the end of the pipe to pump water into the reservoir at a volume flow rate of 0.01 m³/s. What pressure (gage) must the pump produce at the pipe to generate this flow rate? The inside diameter of the smooth pipe is 150mm. Dynamic Viscosity of water is 1*103 Kg/(m.s). K at the exit of the pipe is 1. pump 10 m D=150mm L= 100 m- Pumparrow_forwardWater flows through a 15m pipe with 1.3 cm diameter at 20 l/min. Determine the length of entrance region, le?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY