
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
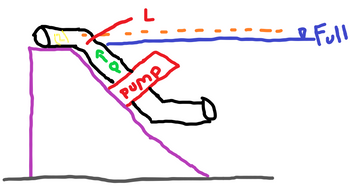
Water is being pumped (at Q) from a reservoir to a nearby storage facility for a local farm. The
water level in the reservoir varies throughout the year. When it is considered “full” the change in
elevation from the top of the water line to the centerline of the pipe at (2) is h. The pipe is made
of welded steel. Assuming there are both major and minor losses, determine the pressure in the
pipe at (2).
Clearly state the source(s) of minor losses.
Use the Haaland and Darcy-Weisbach equations.
Flowrate (Q), elevation difference (h), head from pump (hp), pipe length (L), and diameter (D)
are given below. State all assumptions.
Q =0.54 m^3/s, h =3.5 m, h_p=47.5 m, L = 23.33 m, D = 0.467m
Transcribed Image Text:18
PUMP
e Full
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 10 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Water is supplied in a 2-in. dia. pipe at the rate of 2 cfs to a 10-hp, SO-percent efficient pump. Determine the pressure rise if the exit pipe is of (a) 2-in. diameter and (b) 3-in. diameter.arrow_forward8. In the figure below a manometer uses oil with specific gravity of 0.8. (a) Calculate the discharge when R = 1 ft. (b) Repeat the problem if the pipe is inclined at 30° upward. oil R 6" 3" -- 6"arrow_forwardThe pressure through a section of pipe is 23 PSI and the velocity of the fluid is 3 ft/sec. If the velocity was increased to 5 ft/sec, what would the pressure drop be?arrow_forward
- A horizontal venturimeter with inlet and throat diameter of 160 mm and 60 mm respectivelyis used measure the flow of an oil of specific gravity 0.8. if the discharge of oil is 0.05 m3/s, find the deflection of oil mercury differential manometer. Take venturimeter constant=1.arrow_forward6. Water is flowing with flow rate 5 liter/s in a straight 50 mm diameter galvanized iron pipe as shown in the figure. Determine the pressure difference between point A and B by using: (a) Darcy-Weisbach formula, and (b) Hazen-William's formula. (Ans.: 835.5 kPa, 793.0 kPa) 70 marrow_forwardQ.9) If the faucet (gate valve), at E is fully opened and the pump produces a pressure of 350 kPa at A, determine the flowrate out from the faucet at E. The valve at B remain closed. The pipe has an inner diameter of 30 mm, and f=0.01. Include the minor losses of the tee (K=0.4), the two elbows (K=0.9), and the gate valve (K=0.19). 0.65 m 3 m B 5 marrow_forward
- A venturi meter having a throat diameter of 100mm is fitted into a pipeline which has a diameter of 250mm through which water is flowing. The pressure difference between the entry and throat tapping measured by a U-Tube Manometer containing mercury of a relative density of 13.6 and the connections are filled with the water flowing in the pipeline. If the difference of level indicated by the mercury in the U-tube is 0.63m, calculate: The theoretical volumetric flow rate and The actual volumetric flowrate if the coefficient of discharge is 0.9arrow_forwardWhat power must be supplied by the pump to the flow ifwater (T =20°C) is pumped through the 300 mm steel pipefrom the lower tank to the upper one at a rate of 0.314 m^3/s?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY