
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
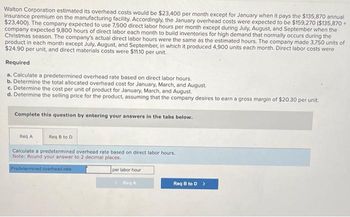
Transcribed Image Text:Walton Corporation estimated its overhead costs would be $23,400 per month except for January when it pays the $135,870 annual
insurance premium on the manufacturing facility. Accordingly, the January overhead costs were expected to be $159,270 ($135,870 +
$23,400). The company expected to use 7,500 direct labor hours per month except during July, August, and September when the
company expected 9,800 hours of direct labor each month to build inventories for high demand that normally occurs during the
Christmas season. The company's actual direct labor hours were the same as the estimated hours. The company made 3,750 units of
product in each month except July, August, and September, in which it produced 4,900 units each month. Direct labor costs were
$24.90 per unit, and direct materials costs were $11.10 per unit.
Required
a. Calculate a predetermined overhead rate based on direct labor hours.
b. Determine the total allocated overhead cost for January, March, and August.
c. Determine the cost per unit of product for January, March, and August.
d. Determine the selling price for the product, assuming that the company desires to earn a gross margin of $20.30 per unit.
Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below.
Req A
Req B to D
Calculate a predetermined overhead rate based on direct labor hours.
Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places.
Predetermined overhead rate
per labor hour
Reg A
Req B to D >
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Step 1: Define overhead rate
VIEW Step 2: a) Calculation of Predetermined Overhead rate by using direct labor hours:-
VIEW Step 3: b) Calculation of total allocated overhead cost for January, March and August :-
VIEW Step 4: c) Calculation of cost per unit of product for January, March, and August :-
VIEW Step 5: d) Calculation of selling pric
VIEW Solution
VIEW Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Gibson Manufacturing Co. expects to make 30,800 chairs during the year 1 accounting period. The company made 3,300 chairs in January. Materials and labor costs for January were $17,800 and $24,500, respectively. Gibson produced 1,400 chairs in February. Material and labor costs for February were $9,400 and $12,900, respectively. The company paid the $770,000 annual rental fee on its manufacturing facility on January 1, year 1. The rental fee is allocated based on the total estimated number of units to be produced during the year. Required Assuming that Gibson desires to sell its chairs for cost plus 25 percent of cost, what price should be charged for the chairs produced in January and February? (Round intermediate calculations and final answers to 2 decimal places.)arrow_forwardBenson Corporation expects to incur indirect overhead costs of $98,000 per month and direct manufacturing costs of $13 per unit. The expected production activity for the first four months of the year are as follows. Estimated production in units January 5,300 Required a. Calculate a predetermined overhead rate based on the number of units of product expected to be made during the first four months of the year. Required A Required B b. Allocate overhead costs to each month using the overhead rate computed in Requirement a. c. Calculate the total cost per unit for each month using the overhead allocated in Requirement b. Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required C February March 8,500 4,600 April 6,100 per unit Calculate a predetermined overhead rate based on the number of units of product expected to be made during the first four months of the year. Predetermined overhead ratearrow_forwardHarris Fabrics computes its plantwide predetermined overhead rate annually on the basis of direct labor-hours. At the beginning of the year, it estimated that 20,000 direct labor-hours would be required for the period’s estimated level of production. The company also estimated $94,000 of fixed manufacturing overhead cost for the coming period and variable manufacturing overhead of $2.00 per direct labor-hour. Harris's actual manufacturing overhead cost for the year was $123,900 and its actual total direct labor was 21,000 hours. Required: Compute the company's plantwide predetermined overhead rate for the year. Note: Round your answer to 2 decimal places.arrow_forward
- Cavy Company estimates that the factory overhead for the following year will be $2,829,000. The company has determined that the basis for applying factory overhead will be machine hours, which is estimated to be 34,500 hours. There are 4,690 machine hours for all of the jobs in the month of April. What amount will be applied to all of the jobs for the month of April?arrow_forwardBaird Manufacturing Co. expects to make 30,500 chairs during the year 1 accounting period. The company made 4,600 chairs in January. Materials and labor costs for January were $16,600 and $24,200, respectively. Baird produced 1,800 chairs in February. Material and labor costs for February were $9,900 and $13,700, respectively. The company paid the $518,500 annual rental fee on its manufacturing facility on January 1, year 1. The rental fee is allocated based on the total estimated number of units to be produced during the year. Required Assuming that Baird desires to sell its chairs for cost plus 30 percent of cost, what price should be charged for the chairs produced in January and February? (Round intermediate calculations and final answers to 2 decimal places.) January February Price per unitarrow_forwardRasmussen Corporation expects to incur indirect overhead costs of $80,000 per month and direct manufacturing costs of $12 per unit. The expected production activity for the first four months of the year are as follows. January February March April Estimated production in units 6,000 7,000 3,000 4,000 Required Calculate a predetermined overhead rate based on the number of units of product expected to be made during the first four months of the year. Allocate overhead costs to each month using the overhead rate computed in Requirement a. Calculate the total cost per unit for each month using the overhead allocated in Requirement b.arrow_forward
- The Production Department of Hruska Corporation has submitted the following forecast of units to be produced by quarter for the upcoming fiscal year: 1st Quarter 2nd Quarter 3rd Quarter 4th Quarter Units to be produced 10,800 9,800 11,800 12,800 Each unit requires 0.25 direct labor-hours and direct laborers are paid $13.00 per hour. In addition, the variable manufacturing overhead rate is $1.90 per direct labor-hour. The fixed manufacturing overhead is $88,000 per quarter. The only noncash element of manufacturing overhead is depreciation, which is $28,000 per quarter. Required: 1. Calculate the company’s total estimated direct labor cost for each quarter of the upcoming fiscal year and for the year as a whole. 2. and 3. Calculate the company’s total estimated manufacturing overhead cost and the cash disbursements for manufacturing overhead for each quarter of the upcoming fiscal year and for the year as a whole.arrow_forwardTannin Products Inc. prepared the following factory overhead cost budget for the Trim Department for July of the current year, during which it expected to use 14,000 hours for production: Variable overhead cost: Indirect factory labor $44,800 Power and light 10,360 Indirect materials 21,000 Total variable overhead cost $ 76,160 Fixed overhead cost: Supervisory salaries $54,380 Depreciation of plant and equipment 14,310 Insurance and property taxes 26,710 Total fixed overhead cost 95,400 Total factory overhead cost $171,560 Tannin has available 18,000 hours of monthly productive capacity in the Trim Department under normal business conditions. During July, the Trim Department actually used 13,000 hours for production. The actual fixed costs were as budgeted. The actual variable overhead for July was as follows: Actual variable factory overhead cost: Indirect factory labor $40,560…arrow_forwardWinston Company estimates that total factory overhead for the following year will be $1,347,500. The company has decided that the basis for applying factory overhead should be machine hours, which are estimated to be 38,500 hours. The actual total machine hours for the year were 54,300 hours. The actual factory overhead for the year was $1,927,000. Enter the amount as a positive number. a. Determine the total factory overhead applied. Round to the nearest dollar. b. Compute the over- or underapplied factory overhead for the year. c. Journalize the entry to transfer the over- or underapplied factory overhead to cost of goods sold. If an amount box does not require an entry, leave it blank.arrow_forward
- The Production Department of Hruska Corporation has submitted the following forecast of units to be produced by quarter for the upcoming fiscal year: 2nd Quarter 1st Quarter 10,400 3rd Quarter 11,400 4th Quarter 12,400 Units to be produced 9,400 Each unit requires 0.25 direct labor-hours and direct laborers are paid $12.00 per hour. In addition, the variable manufacturing overhead rate is $1.70 per direct labor-hour. The fixed manufacturing overhead is $84,000 per quarter. The only noncash element of manufacturing overhead is depreciation, which is $24,000 per quarter. Required: 1. Calculate the company's total estimated direct labor cost for each quarter of the the upcoming fiscal year and for the year as a whole. 2&3. Calculate the company's total estimated manufacturing overhead cost and the cash disbursements for manufacturing overhead for each quarter of the upcoming fiscal year and for the year as a whole.arrow_forwardsarrow_forwardTiger Equipment Inc., a manufacturer of construction equipment, prepared the following factory overhead cost budget for the Welding Department for May of the current year. The company expected to operate the department at 100% of normal capacity of 7,700 hours. Variable costs: Indirect factory wages $22,330 Power and light 15,862 Indirect materials 13,552 Total variable cost $51,744 Fixed costs: Supervisory salaries $14,700 Depreciation of plant and equipment 37,710 Insurance and property taxes 11,500 Total fixed cost 63,910 Total factory overhead cost $115,654 During May, the department operated at 8,200 standard hours. The factory overhead costs incurred were indirect factory wages, $24,020; power and light, $16,590; indirect materials, $14,700; supervisory salaries, $14,700; depreciation of plant and equipment, $37,710; and insurance and property taxes, $11,500. Required: Prepare a factory overhead cost…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education