
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:5
+ | x
A& to
em Set: Module Er x
CengageNOWv2 | Online te x
Cengage Learning
X Cengage Learning
milm/takeAssignment/takeAssignmentMain.do?invoker=&takeAssignmentSessionLocator=&inprogress%3Dfalse
电 手
eBook
Show Me How
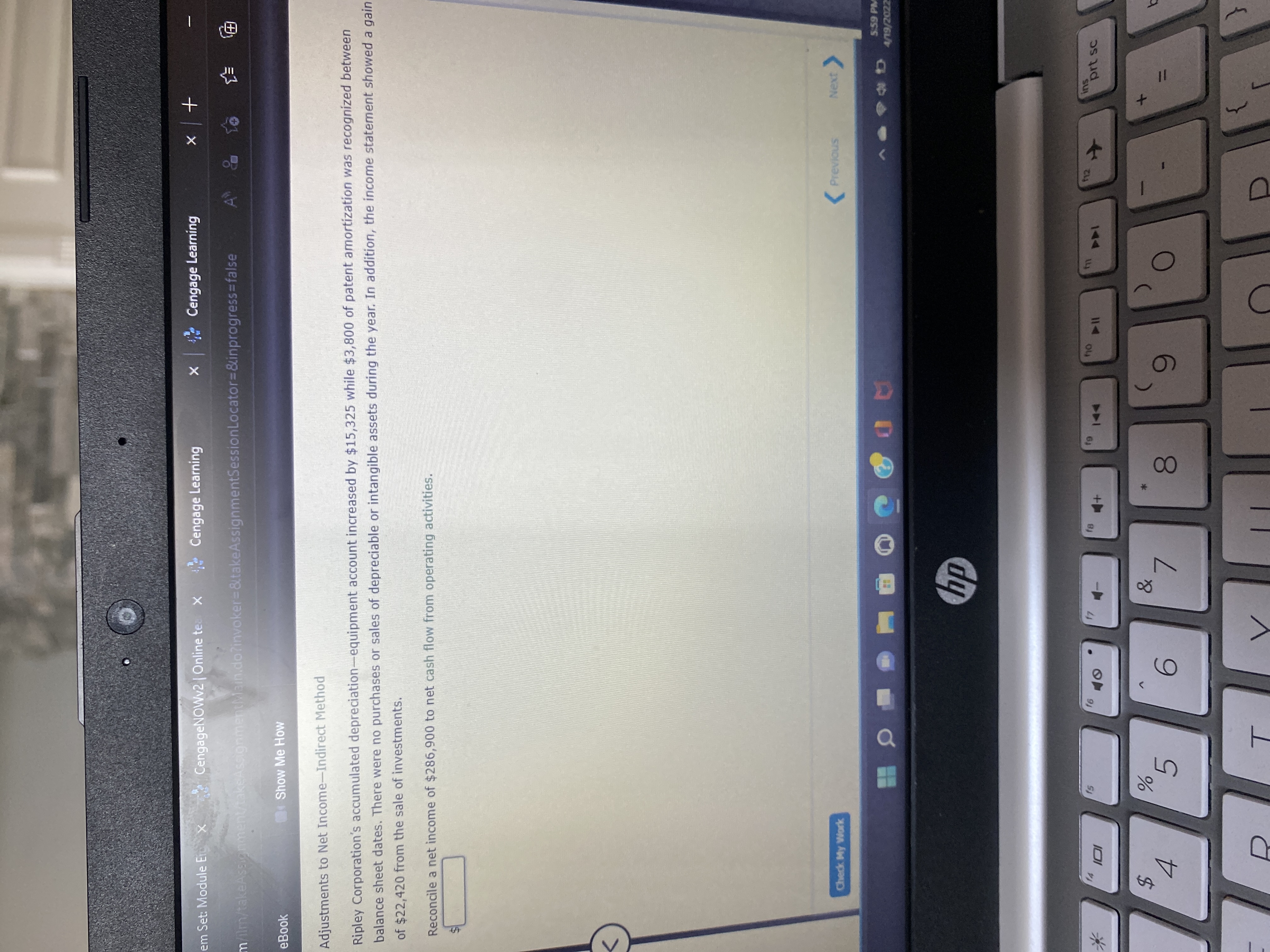
Adjustments to Net Income-Indirect Method
Ripley Corporation's accumulated depreciation-equipment account increased by $15,325 while $3,800 of patent amortization was recognized between
balance sheet dates. There were no purchases or sales of depreciable or intangible assets during the year. In addition, the income statement showed a gain
of $22,420 from the sale of investments.
Reconcile a net income of $286,900 to net cash flow from operating activities.
<>
Check My Work
(Previous
Next
5.59 PM
AD
zzoz/6/
ins
prt sc
114
144
%24
4.
6.
7.
8.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Durrand Corporation's accumulated depreciation increased by $13,721, while patents decreased by $3,862 between consecutive balance sheet dates. There were no purchases or sales of depreciable or intangible assets during the year. In addition, the income statement showed a gain of $3,766 from sale of land. The company earned a net income of $45,945. Assuming there were no changes in noncash current assets and liabilities, determine the net cash flows from operating activities under the indirect method. (Previous Next 3:28 PM e to search a 53°F Sunny 12/14/2021 delete 144 1sht SE YOUR SMARTCHONE TORarrow_forwardNonearrow_forward3. The net income reported on the income statement for the current year was $304,374. Depreciation recorded on fixed assets and amortization of patents for the year were $32,397 and $8,545, respectively. Balances of current asset and current liability accounts at the end and at the beginning of the year are as follows: End Beginning Cash $37,946 $53,537 Accounts Receivable 124,179 105,179 Inventories 113,951 87,274 Prepaid Expenses 3,330 8,740 Accounts Payable (merchandise creditors) 50,535 72,784 What is the amount of cash flows from operating activities reported on the statement of cash flows prepared by the indirect method? a.$282,800 b.$365,298 c.$299,639 d.$279,858arrow_forward
- Durrand Corporation's accumulated depreciation increased by $11,449, while patents decreased by $3,432 between consecutive balance sheet dates. There were no purchases or sales of depreciable or intangible assets during the year. In addition, the income statement showed a gain of $3,255 from sale of land. The company earned a net income of $45,501. Assuming there were no changes in noncash current assets and liabilities, determine the net cash flows from operating activities under the indirect method.arrow_forwardAmortization and Depletion Entries Data related to the acquisition of timber rights and intangible assets during the current year ended December 31 are as follows: a. On December 31, the company determined that $1,300,000 of goodwill was impaired. b. Governmental and legal costs of $7,360,000 were incurred on September 30 in obtaining a patent with an estimated economic life of 10 years. Amortization is to be for one-fourth of a year. c. Timber rights on a tract of land were purchased for $1,380,000 on February 4. The stand of timber is estimated at 6,000,000 board feet. During the current year, 1,600,000 board feet of timber were cut and sold. Required: 1. Determine the amount of the amortization, depletion, or impairment for the current year for each of the foregoing items. Do not round your intermediate calculation. Item Impairment, Amortization or Depletion Expense а. b. С.arrow_forwardFixed Assets & Depreciation At 31 July 20X6, Apollon International had non-current assets which had cost $310,000. At the same date, the accumulated depreciation on the assets was $120,000. The company had not disposed of any non-current assets during the year to 31 July 20X7 but acquired an asset at a cost of $79,200 on 1 January 20X7. Apollon International depreciates non-current assets at a rate of 25% per annum. Required: Compute the company’s depreciation charge for the year to 31 July 20X7 using: The straight-line method The reducing balance method Assume that depreciation is charged from the first year of acquisition with a full year’s charge.arrow_forward
- Depreciation by Three Methods; Partial Years Perdue Company purchased equipment on April 1 for $48,870, The equipment was expected to have a useful life of three years, or 4,320 operating hours, and a residual value of $1,350. The equipment was used for 800 hours during Year 1, 1,500 hours in Year 2, 1,300 hours in Year 3, and 720 hours in Year 4. Required: Determine the amount of depreciation expense for the years ended December 31, Year 1, Year 2, Year 3, and Year 4, by (a) the straight-line method, (b) units-of-activity method, and (c) the double-declining-balance method. Note: FOR DECLINING BALANCE ONLY, round the multiplier to four decimal places. Then round the answer for each year to the nearest whole dollar. a. Straight-line method Year Amount Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 b. Units-of-activity method Year Amount Year 1 Year 2 Year 3 Year 4 c. Double-declining-balance method Year Amountarrow_forwardCash Flows from (Used for) Operating Activities The net income reported on the income statement for the current year was $271,100. Depreciation recorded on equipment and a building amounted to $81,100 for the year. Balances of the current asset and current liability accounts at the beginning and end of the year are as follows: Endof Year Beginningof Year Cash $71,570 $75,860 Accounts receivable (net) 90,750 93,610 Inventories 178,930 161,280 Prepaid expenses 9,950 10,700 Accounts payable (merchandise creditors) 79,940 84,660 Salaries payable 11,520 10,540 A. Prepare the Cash Flows from (used for) Operating Activities section of the statement of cash flows, using the indirect method. Use the minus sign to indicate cash outflows, cash payments, decreases in cash, or any negative adjustments.arrow_forwardplease answer without image WITH DETAILED WORKINGarrow_forward
- Net Present Value Method The following data are accumulated by Geddes Company in evaluating the purchase of $158,800 of equipment, having a four-year useful life: Net Income Net Cash FlowYear 1 $44,000 $75,000 Year 2 27,000 58,000 Year 3 13,000 44,000 Year 4 (1,000) 29,000 Present Value of $1 at Compound InterestYear 6% 10% 12% 15% 20%1 0.943 0.909 0.893 0.870 0.8332 0.890 0.826 0.797 0.756 0.6943 0.840 0.751 0.712 0.658 0.5794 0.792 0.683 0.636 0.572 0.4825 0.747 0.621 0.567 0.497 0.4026 0.705 0.564 0.507 0.432 0.3357 0.665 0.513 0.452 0.376 0.2798 0.627 0.467 0.404 0.327 0.2339 0.592 0.424 0.361 0.284 0.19410 0.558 0.386 0.322 0.247 0.162 a. Assuming that the desired rate of return is 10%, determine the net present value for the proposal. Use the table of the present value of $1 presented above. If required, round to the nearest dollar. Present value of net cash flow $fill in the blank 1Amount to be invested $fill in the blank 2Net present value $fill in the blank 3b. Would…arrow_forwardDisposal of fixed assets Custer Construction Co. reported $8,300,000 for equipment and $4,950,000 for accumulated depreciation—equipment on its balance sheet. The equipment was sold in the first week of the fourth year for $23,300. The equipment was sold in the first week of the fourth year for $15,250 instead of $23,300. The equipment was sold at the end of four years for its estimated residual value of $10,000. The equipment was discarded at the end of its useful life with no residual value. The balance of the equipment and its related accumulated depreciation is $140,000. Indicate the effects on the liquidity metric free cash flow and profitability metric asset turnover for each of the above. If no account is affected, leave the corresponding number entry box blank. LiquidityFree Cash Flow ProfitabilityAsset Turnover 1. Equipment sold for $23,300 $_______ Choose answer (Higher, Lower or No effect) 2. Equipment sold for $15,250 $_______ (Higher, Lower or No effect) 3.…arrow_forwardThe following information is from Lacy's Inc. $ millions Prior Fiscal Year Current Fiscal Year Net Year-End Assets Revenue Income $21,330 14,403 $18,955 $1,070 a. Compute the asset turnover ratio for the current fiscal year. b. Compute the return on assets ratio for the current fiscal year. Numerator a. Asset Turnover Ratio $ Check b. Return on Assets Ratio $ Numerator Denominator / $ Denominator / $ || Result Resultarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education