
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
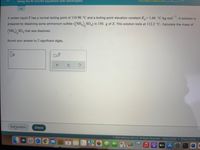
Transcribed Image Text:Using the Kf and Kb equations with electrolytes
A certain liquid X has a normal boiling point of 110.90 °C and a boiling point elevation constant K=1.66 °C-kg mol
-1
.A solution is
prepared by dissolving some ammonium sulfate ((NH SO,) in 150.g of X. This solution boils at 112.2 °C. Calculate the mass of
(NH), SO, that was dissolved.
Round your answer to 2 significant digits.
?
Explanation
Check
©2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use
Privacy Center |
étv A
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
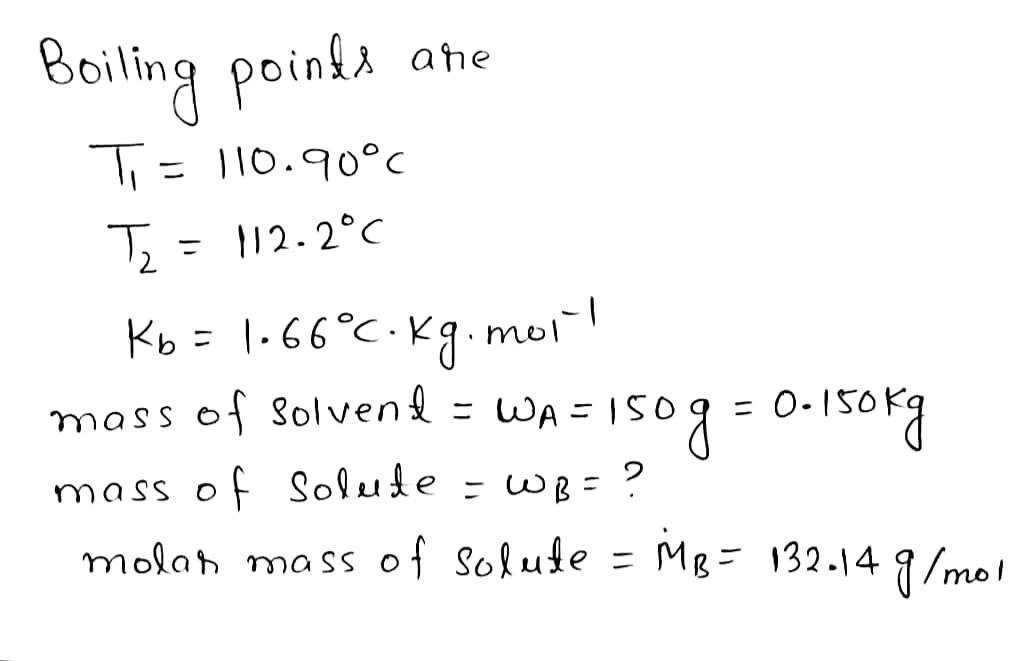
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- When 18.0 mL of a 7.93 x 10-4 M calcium nitrate solution is combined with 25.0 mL of a 7.19 x 10-4 M ammonium sulfate solution does a precipitate form? ( Ksp (CaSO4) 2.4 x 10-5) = OYes, the precipitate forms. O No, the precipitate doesn't form. For these conditions the Reaction Quotient, Q, is equal toarrow_forwardthanks for the help for reviewarrow_forwardTiny samples of aqueous solutions are sketched below, as if under a microscope so powerful that individual molecules could be seen. (The water molecules are not shown.) The two substances in each sample can interconvert. That is, each kind of molecule can turn into the other. The equilibrium constant K for each interconversion equilibrium is shown below the sketch. Decide whether each solution is at equilibrium. K= K=1 At equilibrium? At equilibrium? O yes O no O yes O no 000 000 000 - =+ K=- K= At equilibrium? At equilibrium? O yes O no O yes no Explanation Check Accessibility Privacy O 2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Usearrow_forward
- Determine the value of the equilibrium constant, Kgoal, for the reaction N2(g) + O2(g) + H2 (g) = ;N¿H4(g)+NO2(g), : ? by making use of the following information: 1. N2 (g) + O2 (g): = 2NO(g), K1 4.10 x 10-31 2. N2 (g) + 2H2 (g) = - N2H4(g), K2 7.40 x 10–26 3. 2NO(g) + O2 (g) = 2NO2(g), K3 = 6.00 x 10-13 Express your answer numerically. • View Available Hint(s) Vo AEO ? Kgoal =arrow_forwardWhile ethanol (CH3CH2OH) is produced naturally by fermentation, e.g. in beer- and wine-making, industrially it is synthesized by reacting ethylene (CH2CH2) with water vapor at elevated temperatures. A chemical engineer studying this reaction fills a 500. mL flask with 4.6atm of ethylene gas and 4.2atm of water vapor. When the mixture has come to equilibrium he determines that it contains 2.7atm of ethylene gas and 2.3atm of water vapor. The engineer then adds another 1.5atm of ethylene, and allows the mixture to come to equilibrium again. Calculate the pressure of ethanol after equilibrium is reached the second time. Round your answer to 2 significant digits.arrow_forwardSelect the reaction for which K, = Kc. 2 CO, (g) + 2 CF,(g) =4 COF, (g) NH,NO, (s) = N,O(g) + 2H,O(g) 2 H, S(g) + SO, (g) = 3 S(s) + 2 H,O(g) O 2 Na, O, (s) + 2CO,(g) =2 Na,CO;(s) + 0,(g)arrow_forward
- CS2 (g) + 4 H2 (g) <====> CH4 (g) + 2 H2S (g) Calculate the value of Keq if the equilibrium concentrations are [CS2] = 0.140, [H2] = 0.250, [CH4] = 0.0200, and [H2S] = 0.0400.arrow_forwardOnly typed sollution.arrow_forwardAt 25 °C and 765 Torr, carbon dioxide has a solubility of 0.0342 M in water. What is its solubility at 25 °C and 1410 Tor? M S =arrow_forward
- Suppose that 8.00 mol of both O2 and N₂O gases are introduced into a 4.00 L closed flask. When the system comes to equilibrium, 3.00 mol of nitrogen monoxide (NO) gas has formed, shown below. Determine the equilibrium concentrations of all entities in the flask. 2 N₂O(g) + O₂ (g) = = 4 NO(g) UPLOAD A FULL SOLUTION WITH AN ICE TABLE, CALCULATIONS, AND FINAL ANSWERS WITH UNITS AND THE CORRECT NUMBER OF SIGNIFCANT DIGITS.arrow_forwardThe answer is already given which is 0.173 mol H2 I'd like to know the complete solution. Thanks!arrow_forwardConsider the equilibrium at 25 °C 2 SO3(g) <==> 2 SO2(g) + O2(g) Kc= 3.58 x10-3 Suppose that 0.15 mol SO3(g), 0.01 mol SO2(g), and 0.0075 mol O2(g) are placed into a 10.0 L flask at 25 °C. Which of the following statements is true? Q > Kcand will shift from right to left. Q < Kc and will shift from right to left. Q > Kcand will shift from left to right. Q = Kcand the system is at equilibrium. Q < Kc and will shift from left to right.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY