
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
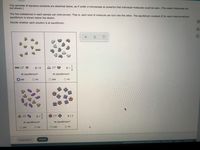
Transcribed Image Text:Tiny samples of aqueous solutions are sketched below, as if under a microscope so powerful that individual molecules could be seen. (The water molecules are
not shown.)
The two substances in each sample can interconvert. That is, each kind of molecule can turn into the other. The equilibrium constant K for each interconversion
equilibrium is shown below the sketch.
Decide whether each solution is at equilibrium.
do
K-
K=9
At equilibrium?
At equilibrium?
O yes
O no
O yes
O no
2
K=
3
K=3
At equilibrium?
At equilibrium?
O yes
O no
O yes
O no
Explanation
Check
2021 McGraw-Hill Education. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use Privacy Accessibility
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Thoroughly explain and answerarrow_forwardAt a particular temperature the equilibrium constant K = 2.50 for the following reaction in the gas phase: SO2(g) + NO2(g) = SO3(g) + NO(g). Calculate the equilibrium pressure of SO3(g) in the reaction if the initial pressures of SO2(g) and NO2(g) were both 1.00 bar. and no products had been formed. O 0.20 bar 0.39 bar 1.39 bar 0.61 bar 1.61 bararrow_forwardConsider the following chemical equilibrium: С (s)+ 2 Н, (g) — CH (g) Now write an equation below that shows how to calculate K, from K̟ for this reaction at an absolute temperature T. You can assume T is comfortably above room temperature. If you include any common physical constants in your equation be sure you use their standard symbols, found in the ALEKS Calculator. K¸ = []arrow_forward
- General Chemistry 4th Edition McQuarrie Rock Gallogly University presentedi The equilibrium constant for the chemical equation N,(g) + 3 H, (g) =2 NH,(g) is K, = 0.139 at 237 °C. Calculate the value of K. for the reaction at 237 °C. Ke =arrow_forwardConsider the following equilibrium reaction: PBr5(g) + 1/2 O2(g) = POB13(g) + Br2(g) Kc = 5.6 x 102 at 512 K Calculate K. for the reaction 2 PBr5(g) + O2(g) = 2 POBR3(g) + 2 Br2(g) at the same temperature. 24 1.1 x 103 280 5.6 x 102 O None of these 3.2 x 105arrow_forwardConsider the following chemical equilibrium: 4 NH, (g) +3 0, (g)=2N, (g) +6 H,Oo (g) Now write an equation below that shows how to calculate K, from K, for this reaction at an absolute temperature T. You can assume T is comfortably above room temperature. If you include any common physical constants in your equation be sure you use their standard symbols, found in the ALEKS Calculator. K_ = Iarrow_forward
- 19. Given the following reaction: NH.CI (s) S NH3 (g) + HCI (g) AH= +42.1 kcal Suppose the above substances in the reaction are at equilibrium at 600 K in volume V and at pressure P. State whether the partial pressure of NH3 (g) will have increased, decreased, or remained the same in order to the equilibrium to be reestablished following the disturbances of the original system. Note that some solid remains in the flask at all times. Provide a one to two sentence explanation (a) The temperature of the system is increased (b) The volume of the system is increased (c) A quantity of gaseous NH3 is added. (d) A small quantity if NH4C1 is added.arrow_forwardCalculating equilibrium composition from an equilibrium... 0/5 Suppose 500. mL flask is filled with 1.9 mol of H, and o0.50 mol of C1,. The following reaction becomes possible: H, (g) + Cl,(g) – 2HC1(g) The equilibrium constant K for this reaction is 3.61 at the temperature of the flask. Calculate the equilibrium molarity of H,. Round your answer to two decimal places. OMarrow_forwardI need to find the mols of CO, H2O, CO2, and H2 respectively within the mixture when it reaches equilibrium.arrow_forward
- At 400 K, an equilibrium mixture of H2, 12, and HI consists of 0.065 mol H2, 0.079 mol 12, and 0.13 mol HI in a 4.50-L flask. What is the value of K, for the following equilibrium? (R= 0.0821 L atm/(K • mol)) 2HI(g) = H2(g) + 12(8) 0.29 8.2 0.039 O 26 3.4arrow_forwardNote:- • Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. • Answer completely. • You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forwardCarbon disulfide is prepared by heating sulfur and charcoal. The chemical equation is S,(g) + C(s) = CS, (g) K. = 9.40 at 900 K How many grams of CS, (g) can be prepared by heating 13.0 mol S,(g) with excess carbon in a 5.70 L reaction vessel held at 900 K until equilibrium is attained? mass of CS,(g):arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY