
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
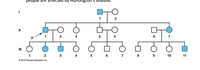
The following pedigree shows the inheritance of Huntington’s disease, a fatal genetic disorder that causes neurodegeneration. Since signs and symptoms usually do not appear until adulthood, many who are carriers may not realize their risk of passing on the disease-causing allele. The following pedigree represents a family in which some people are affected by Huntington’s disease.
- Using just the information on this pedigree, is Huntington’s disease caused by a dominant allele or recessive alleles?
- What are the genotypes of the grandparents (I-1 and I-2)?
- What are the genotypes of the parents (II-6 and II-7)?
- If the parents above have another child, what is the chance that they will be affected by the Hungtington’s disease allele?
- What are the genotypes of the unaffected children (III-8, 9, 10)?
- What is the chance that the unaffected children above will pass on a Huntington’s disease allele to their children?
- What is the genotype of the affected child (III-11)?
- What is the chance that the affected child above will pass on the Huntington’s disease allele to a child?
Transcribed Image Text:ople are dll
ngton s uisease.
1
II
3
4
5
6
7
III
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
© 2016 Pearson Education, Inc.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Mary and Ron don't have albinism. However, is it possible for them to have a child with albinism? Explain. Stephanie has normal color vision. Her husband Chris also has normal color vision. They have a son that is color blind and a daughter that has normal color vision. What is the genotype of the mother, father, son and the daughter? Andy and Anne do not have polydactyl. Is it possible for them to have a child with polydactyl? Explain. When examining a pedigree chart, I notice that only males are affected. What does this tell me about the inheritance pattern? A man with blood type A marries a woman with blood type B. Their child has blood type O. What are the genotypes of the parents?arrow_forwardA gene that controls the ability to see red and green is located on the X chromosome but not on the Y chromosome. There is a recessive nonfunctional allele for this gene that can cause red-green color blindness if the person possessing it does not also have the dominant normal gene. Consider the case of a carrier mother who is heterozygous for the red-green vision gene and a father who has normal vision. Use XB = normal vision, Xb = color-blind vision. What is the chance the parents would have a color-blind boy? A color-blind girl? What about a girl or boy with normal vision? Redo the Punnett square for a carrier mother (XBXb) and a color-blind father (XbY). Do the chances of having color-blind children change? How?arrow_forwardCystic fibrosis is an autosomal recessive disorder that runs in Ann's family. Consider the figure of a pedigree of the known occurrences of cystic fibrosis in her family. Ann Filled (red) circles represent affected females. Filled (red) squares represent affected males. Unfilled (tan) circles, such as Ann's circle, represent symptomless females. Unfilled (tan) squares represent symptomless males.arrow_forward
- The pedigree chart provided below traces the occurrence of a disease through the generations of a family. Determine what type of inheritance pattern this disease has.arrow_forwardAlbinism (lack of skin pigmentation) is caused by an autosomal recessive allele. A man and woman, both normally pigmented, have an albino child together. For this trait, what is the genotype of both parents? Options Below: homozygous recessive homozygous dominant heterozygous hemizygous unknown, because not enough information is providedarrow_forwardCystic fibrosis is a genetic disease that causes an abnormal production of mucus which in turn can cause damage and infection to the lungs and other organs. In the following pedigree, black indicates all those persons afflicted with cystic fibrosis (square symbols are males, circles are females). There's a healthy couple and they have two children. One is a 23-year-old daughter with cystic fibrosis who is married to a 24-year-old male who is healthy. The other child is a 15-year-old son who is healthy After studying the pedigree, write a logical hypothesis suggesting the cause of cystic fibrosis in terms of dominant or recessive alleles. On the basis of your hypothesis, write an appropriate genotype for both of the parents. Using a Punnett square, what is the probability of the parents having a child with cystic fibrosis? If the daughter's husband is a carrier of cystic fibrosis, what is the probability that they have a child with cystic fibrosis? Show your Punnett square.arrow_forward
- Cystic fibrosis in humans is caused by mutations in a single gene and is inherited as an autosomal (non-sex chromosome) recessive trait. An unaffected couple has two children. The first child has cystic fibrosis, and the second child is unaffected. What is the probability that the second child is a carrier (heterozygous) for the mutation that causes the disease? 2/3 1 1/2 3/4arrow_forwardAlbinism in humans is autosomal and fully recessive to normal color. A couple, who are both normal, have a daughter who is albino and a son who is normal. What is the probability that their normal son is a carrier of the albinism gene?arrow_forwardAssume that a particular unusual phenotype is caused by an autosomal recessive allele. John marries Jane, and they have a daughter Mia together who has the unusual phenotype. John has a brother Carlos who appears normal. Jane has a sister Margit with the unusual phenotype. John and Jane are not related, and none of their parents have the unusual phenotype. Draw a 3-generation pedigree that depicts the entire scenario and assign the most likely genotypes to each individual. (You can use any letter you wish to represent the gene.) Yes, you should include Jane's parents and sister, and also John's parents and brother, as part of the pedigree. And don't forget Mia!arrow_forward
- People with polydactyly have more than five fingers or toes on their hands or feet. Polydactyly results from an autosomal dominant genetic disorder. Draw a pedigree for a family with polydactyly, using the following information: Zack has polydactyly but his wife, Zoe does not. Zack and Zoe’s daughter Yolanda has polydactyly but their son Yogi does not. Yolanda has two children with her husband, Xavier, who does not have polydactyly: Wilma, who is normal and Wade, who has polydactyly. Use your pedigree to determine what is Zoe's genotype. A) DD B)dd C)Ddarrow_forwardNiemann Pick Type C disease is a recessive disorder that causes the accumulation of cholesterol and other lipids in lysosomes, ultimately affecting both the liver and the nervous system. Below are the genotypes and phenotypes of offspring of a family with a history of Niemann Pick. 7 NN ( all normal phenotype) 3 Nn (all normal phenotype) 4 nn (1 early onset dementia, 1 mid-life onset dementia, 2 late-onset dementia). From this information, Niemann-Pick disease is an example of: A) variable expressivity B) incomplete dominance C) incomplete penetrance D) variable expressivity and incomplete penetrance E) multiple allelesarrow_forwardIf individuals II-5 and II-4 have another child, the probability of this child having the polydactyly trait is ___%.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education