
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
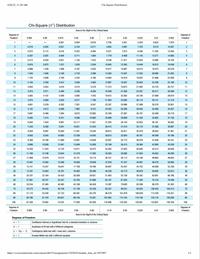
Use the given information to find the number of degrees of freedom, the critical values χ2L and χ2R,and the confidence interval estimate of σ. It is reasonable to assume that a simple random sample has been selected from a population with a normal distribution .
Nicotine in menthol cigarettes 95% confidence; n=20, s=0.28 mg.
LOADING...
Transcribed Image Text:4/26/22, 11:28 AM
Chi-Square Distribution
Chi-Square (X²) Distribution
Area to the Right of the Critical Value
Degrees of
Freedom
Degrees of
Freedom
0.995
0.99
0.975
0.95
0.90
0.10
0.05
0.025
0.01
0.005
1
0.001
0.004
0.016
2.706
3.841
5.024
6.635
7.879
1
0.010
0.020
0.051
0.103
0.211
4.605
5.991
7.378
9.210
10.597
2
0.072
0.115
0216
0.352
0.584
6.251
7.815
9.348
11.345
12.838
0.207
0.297
0.484
0.711
1.064
7.779
9.488
11.143
13.277
14.860
4
0.412
0.554
0.831
1.145
1.610
9.236
11.071
12.833
15.086
16.750
6.
0.676
0.872
1.237
1.635
2.204
10.645
12.592
14.449
16.812
18.548
7
0.989
1.239
1.690
2.167
2.833
12.017
14.067
16.013
18.475
20.278
7
8
1.344
1.646
2.180
2.733
3.490
13.362
15.507
17.535
20.090
21.955
9.
1.735
2.088
2.700
3.325
4.168
14.684
16.919
19.023
21.666
23.589
9
10
2.156
2.558
3.247
3.940
4.865
15.987
18.307
20.483
23.209
25.188
10
11
2.603
3.053
3.816
4.575
5.578
17.275
19.675
21.920
24.725
26.757
11
12
3.074
3.571
4.404
5.226
6.304
18.549
21.026
23.337
26.217
28.299
12
13
3.565
4.107
5.009
5.892
7.042
19.812
22.362
24.736
27.688
29.819
13
14
4.075
4.660
5.629
6.571
7.790
21.064
23.685
26.119
29.141
31.319
14
15
4.601
5.229
6.262
7.261
8.547
22.307
24.996
27.488
30.578
32.801
15
16
5.142
5.812
6.908
7.962
9.312
23.542
26.296
28.845
32.000
34.267
16
17
5.697
6.408
7.564
8.672
10.085
24.769
27.587
30.191
33.409
35.718
17
18
6.265
7.015
8.231
9.390
10.865
25.989
28.869
31.526
34.805
37.156
18
19
6.844
7.633
8.907
10.117
11.651
27.204
30.144
32.852
36.191
38.582
19
20
7.434
8.260
9.591
10.851
12.443
28.412
31.410
34.170
37.566
39.997
20
21
8.034
8.897
10.283
11.591
13.240
29.615
32.671
35.479
38.932
41.401
21
22
8.643
9.542
10.982
12.338
14.042
30.813
33.924
36.781
40.289
42.796
22
23
9.260
10.196
11.689
13.091
14.848
32.007
35.172
38.076
41.638
44.181
23
24
9.886
10.856
12.401
13.848
15.659
33.196
36.415
39.364
42.980
45.559
24
25
10.520
11.524
13.120
14.611
16.473
34.382
37.652
40.646
44.314
46.928
25
26
11.160
12.198
13.844
15.379
17.292
35.563
38.885
41.923
45.642
48.290
26
27
11.808
12.879
14.573
16.151
18.114
36.741
40.113
43.194
46.963
49.645
27
28
12.461
13.565
15.308
16.928
18.939
37.916
41.337
44.461
48.278
50.993
28
29
13.121
14.257
16.047
17.708
19.768
39.087
42.557
45.722
49.588
52.336
29
30
13.787
14.954
16.791
18.493
20.599
40.256
43.773
46.979
50.892
53.672
30
40
20.707
22.164
24.433
26.509
29.051
51.805
55.758
59.342
63.691
66.766
40
50
27.991
29.707
32.357
34.764
37.689
63.167
67.505
71.420
76.154
79.490
50
60
35.534
37.485
40.482
43.188
46.459
74.397
79.082
83.298
88.379
91.952
60
70
43.275
45.442
48.758
51.739
55.329
85.527
90.531
95.023
100.425
104.215
70
80
51.172
53.540
57.153
60.391
64.278
96.578
101.879
106.629
112.329
116.321
80
90
59.196
61.754
65.647
69.126
73.291
107.565
113.145
118.136
124.116
128.299
90
100
67.328
70.065
74.222
77.929
82.358
118.498
124.342
129.561
135.807
140.169
100
Degrees of
Freedom
Degrees of
Freedom
0.995
0.99
0.975
0.95
0.90
0.10
0.05
0.025
0.01
0.005
Area to the Right of the Critical Value
Degrees of Freedom
n- 1
Confidence Interval or Hypothesis Test for a standard deviation or variance
k - 1
Goodness-of-fit test with k different categories
(r - 1(c – 1) Contingency table test with rrows and c columns
k - 1
Kruskal-Wallis test with k different samples
https://vcccd.instructure.com/courses/46153/assignments/1543824?module_item_id=3931907
1/1
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Use the given information to find the number of degrees of freedom, the critical values x and x, and the confidence interval estimate of a. It is reasonable to assume that a simple random sample has been selected from a population with a normal distribution. Nicotine in menthol cigarettes 80% confidence; n=28, s=0.24 mg. Click the icon to view the table of Chi-Square critical values. df = 27 (Type a whole number.) x- Save (Round to three decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardUse the t-distribution to find a confidence interval for a mean given the relevant sample results. Give the best point estimate for μ, the margin of error, and the confidence interval. Assume the results come from a random sample from a population that is approximately normally distributed. A 95% confidence interval for using the sample results x = 92.1, s = 7.8, and n = 42 Round your answer for the point estimate to one decimal place, and your answers for the margin of error and the confidence interval to two decimal places. point estimate= i margin of error = The 95% confidence interval is Save for lat toarrow_forwardUse the given information to find the number of degrees of freedom, the critical values x and x, and the confidence interval estimate of a. It is reasonable to assume that a simple random sample has been selected from a population with a normal distribution. Nicotine in menthol cigarettes 80% confidence; n= 26, s=0.23 mg. E Click the icon to view the table of Chi-Square critical values. df =(Type a whole number.) Enter your answer in the answer box and then click Check Answer. 3 parts remaining Clear All Check Anwer MacBook Air 44 4) esc F5 F7 F6 19 10 F2 F3 %23 2$ % & * delete 2 4 5 6. 7 8 Q T Y tab A S F G K caps lockarrow_forward
- Use the given information to find the number of degrees of freedom, the critical values y? and y?, and the confidence interval estimate of o. It is reasonable to assume that a simple random sample has been selected from a population with a normal distribution. Nicotine in menthol cigarettes 95% confidence; n= 26, s= 0.27 mg. = Click the icon to view the table of Chi-Square critical values. df%3D (Type a whole number.)arrow_forwardA statistics class is estimating the mean height of all female students at their college. They collect a random sample of 42 female students and measure their heights. The mean of the sample is 65.3 inches and the sample standard deviation is 5.4 inches. Find the 90% confidence interval for the mean height of all female students in their school? Assume that the distribution of individual female heights at this school is approximately normal. 1. The t value is 1.3025 2. The standard error has a value of -- 3. The margin of error has a value of 4. Find the 90% confidence interval for the mean height of all female students in their schoolarrow_forwardUse the given information to find the number of degrees of freedom, the critical values y? and y?, and the confidence interval estimate of o. It is reasonable to assume that a simple random sample has been selected from a population with a normal distribution. Platelet Counts of Women 90% confidence; n= 23, s = 65.4. Click the icon to view the table of Chi-Square critical values. df = (Type a whole number.)arrow_forward
- Assume that we want to construct a confidence interval. Do one of the following, as appropriate: (a) find the critical value t/2, (b) find the critical value z,/2, or (c) state that neither the normal distribution nor the t distribution applies. 230, x 32.6 hg, s = 7.9 hg. The confidence level is 90% Here are summary statistics for randomly selected weights of newborn girls: n Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. A. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) В. Za/2 (Round to two decimal places as needed.) C. Neither the normal distribution nor the t distribution applies.arrow_forwardUse the given information to find the number of degrees of freedom, the critical values y? and y?, and the confidence interval estimate of o. It is reasonable to assume that a simple random sample has been selected from a population with a normal distribution. Platelet Counts of Women 80% confidence; n= 26, s = 65.4. Click the icon to view the table of Chi-Square critical values. df = (Type a whole number.) (Round to three decimal places as needed.) (Round to three decimal places as needed.) The confidence interval estimate of o isarrow_forwardUse the given information to find the number of degrees of freedom, the critical values x? and x, and the confidence interval estimate of o. It is reasonable to assume that a simple random sample has been selected from a population with a normal distribution. Nicotine in menthol cigarettes 99% confidence; n = 23, s = 0.23 mg. Click the icon to view the table of Chi-Square critical values. df = 22 (Type a whole number.) x = 8.643 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) %3D = 42.796 (Round to three decimal places as needed.) The confidence interval estimate of o is mgarrow_forward
- Use the given information to find the number of degrees of freedom, the critical values x? and x, and the confidence interval estimate of o. It is reasonable to assume that a simple random sample has been selected from a population with a normal distribution. Nicotine in menthol cigarettes 99% confidence; n=21, s= 0.26 mg. Click the icon to view the table of Chi-Square critical values. df = 20 (Type a whole number.) X = (Round to three decimal places as needed.) (Round to three decimal places as needed.) The confidence interval estimate of o is mgarrow_forwardUse the given data to find the 95% confidence interval estimate of the population mean μμ. Assume that the population has a normal distribution. IQ scores of professional athletes:Sample size n=30n=30Mean x¯¯¯=106x¯=106Standard deviation s=9s=9 <μ<<μ<arrow_forwardUse the given information to find the number of degrees of freedom, the critical values xf and x6, and the confidence interval estimate of o. It is reasonable to assume that a simple random sample has been selected from a population with a normal distribution. Nicotine in menthol cigarettes 98% confidence; n= 21, s = 0.26 mg. Click the icon to view the table of Chi-Square critical values. df = |(Type a whole number.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman