
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
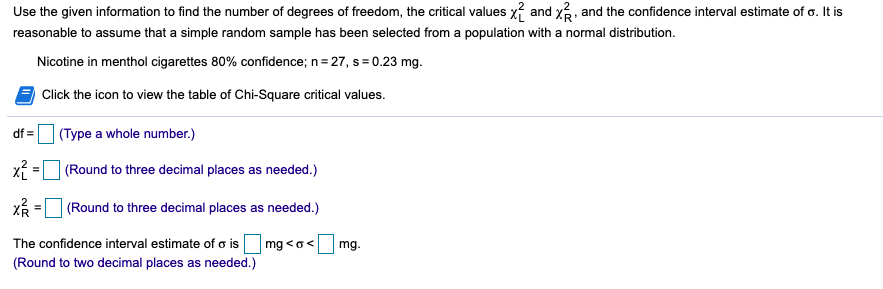
Transcribed Image Text:Use the given information to find the number of degrees of freedom, the critical values x? and x, and the confidence interval estimate of o. It is
reasonable to assume that a simple random sample has been selected from a population with a normal distribution.
Nicotine in menthol cigarettes 80% confidence; n= 27, s = 0.23 mg.
Click the icon to view the table of Chi-Square critical values.
df =
I(Type a whole number.)
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
(Round to three decimal places as needed.)
mg.
The confidence interval estimate of o is mg <o<
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
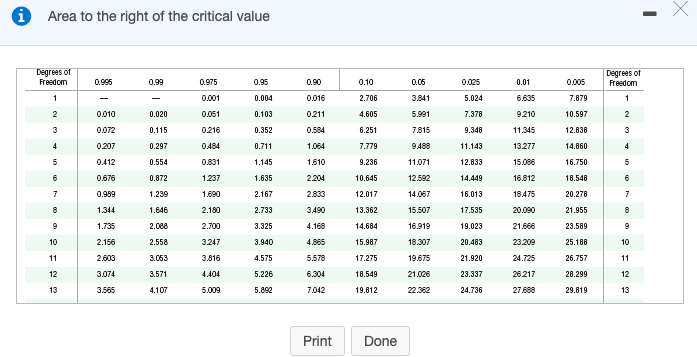
Transcribed Image Text:i Area to the right of the critical value
Degrees of
Freedom
Degrees of
Freedom
0.995
0.99
0.975
0.95
0.90
0.10
0.06
0.025
0.01
0.005
0.001
0.004
0.016
2.706
3.841
5.024
6.635
7.879
0.010
0.020
0.051
0.103
0211
4.605
5.991
7.378
9210
10.597
0.072
0.115
0216
0.352
0.584
6.251
7.815
9.348
11.345
12.838
4
0.207
0.297
0.484
0.711
1.064
7.779
9.488
11.143
13277
14.860
0.412
0.554
0.831
1.145
1.610
9.236
11.071
12.833
15.006
16.750
0.676
0.872
1.237
1.635
2204
10.645
12.592
14.449
16.812
18.548
0.989
1.239
1.690
2.167
2.833
12.017
14.067
16.013
18.475
20.278
1.344
1.646
2.180
2.733
3.490
13.362
15.507
17.535
20.090
21.955
8.
1.735
2.088
2.700
3.325
4.168
14.684
16.919
19.023
21.666
23.589
10
2.156
2.558
3247
3.940
4.865
15.987
18.307
20.483
23.209
25.188
10
11
2.603
3.063
3.816
4.575
5.578
17.275
19.675
21.920
24.725
26.757
11
12
3.074
3.571
4.404
5.226
6.304
18.549
21.026
23.337
26.217
28.299
12
13
3.565
4.107
5.009
5.892
7.042
19.812
22.362
24.736
27.688
29.819
13
Print
Done
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- I need help with part d pleasearrow_forwardริ 111 43% Show Your Work E... D 00:00:45 Question 1 with α-.01, the two-tailed critical region for a t test using a sample of n- 16 subjects would have boundaries of t2.602 t2.583 nt +2.947 Question 2 with α-.05, what is the critical t Dashboardarrow_forwardTo test Ho: µ= 103 versus H,: µ# 103 a simple random sample of size n= 35 is obtained. Complete parts a through e below. Click here to view the t-Distribution Area in Right Tail. (a) Does the population have to be normally distributed to test this hypothesis? Why? A. No, because n2 30. B. Yes, because n2 30. C. Yes, because the sample is random. D. No, because the test is two-tailed. (b) If x = 99.8 and s = 5.9, compute the test statistic. The test statistic is to =. (Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forward
- Assume that both populations are normally distributed. a) Test whether µ, > H, at the a = 0.10 level of significance for the given sample data. b) Construct a 90% confidence interval about u, - H2. Sample 1 Sample 2 n. 27 20 53 45.2 9.7 12.3 Click the icon to view the Student's t-distribution table. a) Perform a hypothesis test. Determine the null and alternative hypotheses. O A. Ho: H1 H2 O B. Ho: H1 > H2, H1: H1 H2 Determine the test statistic. t= (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Approximate the P-value. Choose the correct answer below. O A. P-value <0.01 O B. 0.01 < P-value < 0.05 OC. 0.05 < P-value < 0.10 O D. P-value 2 0.10 Should the hypothesis be rejected at the a = 0.10 level of significance? V the null hypothesis because the P-value is the level of significance. b) The confidence interval is the range from to (Round to two decimal places as needed. Use ascending order.)arrow_forwardwhen we have a double bell curve, how ?can we get the average for each peak Or what is the correct way to measure the average in it 25 30 35 Particle Size (nm) 40 45 50 55 N Number of Particles 14- Particle Lengtharrow_forward• The value of the test statistic is given by 1= • The p-value is the area under the curve to the right of the value of the test statistic. Student's t Distribution 0,4 + Step 1: Enter the number of degrees of freedom. 17 Step 2: Select one-tailed or two-tailed. 0.3+ O One-tailed O Two-tailed Step 3: Enter the test statistic. (Round to 3 decimal places.) 0.2+ 1.928 Step 4: Shade the area represented by the p-value. 0.1+ Step 5: Enter the p-value. (Round to 3 decimal places.) 0.0354 1= 1.928 (c) Based on your answer to part (b), choose what can be concluded, at the 0.05 level of significance, about the claim made by Ashley. Since the p-value is less than (or equal to) the level of significance, the null hypothesis is rejected. So, there is enough evidence to support the claim that the mean number of cases directly generated ? by one previous case is greater than 2.6. Since the p-value is less than (or equal to) the level of significance, the null hypothesis is not rejected. So, there is…arrow_forward
- 20arrow_forwardSAT math scores are normally distributed with the parameters below. μ=500σ=100μ=500σ=100 What is the probability a randomly selected score is more than 460 points ["", "", "", "", ""] What score separates the lowest 20% of scores from the rest?arrow_forwardA study asked respondents, "If ever married, how old were you when you first married?" The results are summarized in the technology excerpt that follows. Complete parts (a) through (d) below. One-Sample T: AGEWED Mean Variable StDev SE Mean 95.0% CI AGEWED 26970 22.530 4.712 0.029 (22.474, 22.586) Click the icon to view the table of critical t-values. (a) Use the summary to determine the point estimate of the population mean and margin of error for the confidence interval. x= 22.530 (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.) E= 0.056 (Type an integer or a decimal. Do not round.) (b) Interpret the confidence interval. A. One can be 95% confident that the mean age of people when first married is between 22.474 and 22.586 years. B. There is a 95% probability that the mean age of people when first married is between 22.474 and 22.586 years. C. There is a 95% probability that the mean age of people when first married is 22.530 years. D. One can be 95% confident that the mean age of…arrow_forward
- Find the critical value(s) and rejection region(s) for the type of z-test with level of significance α. Include a graph with your answer. Two-tailed test, α = 0.09 The critical value(s) is/are z = (Round to two decimal places as needed. Use a comma to separate answers as needed.)arrow_forwardTesting: Ηο:μ = 40.2 H₁:μ ‡ 40.2 Your sample consists of 48 values, with a sample mean of 39.2. Suppose the population standard deviation is known to be 2.63. a) Calculate the value of the test statistic, rounded to 2 decimal places. z = b) At a = 0.03, the rejection region is Oz -2.17 or z > 2.17 Oz -1.88 or z> 1.88 Oz > 1.88 Oz > 2.17 Oz < -1.88 Oz < -2.17 c) The decision is to Accept the alternative hypotheis Fail to reject the null hypothesis Reject the null hypothesis Accept the null hypothesis d) Suppose you mistakenly rejected the null hypothesis in this problem, what type of error is that? Type I Type IIarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman