
University Physics Volume 2
18th Edition
ISBN: 9781938168161
Author: OpenStax
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
and Determine the angle, θ, that the electron leaves the region between the parallel plates at.
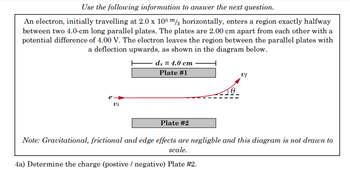
Transcribed Image Text:Use the following information to answer the next question.
An electron, initially travelling at 2.0 x 106 m/s horizontally, enters a region exactly halfway
between two 4.0-cm long parallel plates. The plates are 2.00 cm apart from each other with a
potential difference of 4.00 V. The electron leaves the region between the parallel plates with
a deflection upwards, as shown in the diagram below.
dx = 4.0 cm
Plate #1
e
Vi
Plate #2
Note: Gravitational, frictional and edge effects are negligble and this diagram is not drawn to
scale.
4a) Determine the charge (postive / negative) Plate #2.
SAVE
AI-Generated Solution
info
AI-generated content may present inaccurate or offensive content that does not represent bartleby’s views.
Unlock instant AI solutions
Tap the button
to generate a solution
to generate a solution
Click the button to generate
a solution
a solution
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Use the orders of magnitude you found in the previous problem to answer the following questions to within an order of magnitude. (a) How many electrons would it take to equal the mass of a proton? (b) How many Earths would it take to equal the mass of the Sun? (c) How many Earth-Moon distances would it take to cover the distance from Earth to the Sun? (d) How many Moon atmospheres would it take to equal the mass of Earth’s atmosphere? (e) How many moons would it take to equal the mass of Earth? (f) How many protons would it take to equal the mass of the Sun? For the remaining questions, you need to use Figure 1.4 to obtain the necessary orders of magnitude of lengths, masses, and times.arrow_forwardWhy do we need to be careful about work done on the system versus work done by the system in calculations?arrow_forwardIn nuclear fission. a nucleus splits roughly in half. (a) What is the potential 2.00 10-14 m from a fragment that has 46 protons in it? (b) What is the potential energy in MeV of a similarly charged fragment at this distance?arrow_forward
- In different experimental trials, an electron, a proton, or a doubly charged oxygen atom (O--), is fired within a vacuum tube. The particle's trajectory carries it through a point where the electric potential is 40.0 V and then through a point at a different potential. Rank each of the following cases according to the change in kinetic energy of the particle over this part of its flight from the largest increase to the largest decrease in kinetic energy. In your ranking, display any cases of equality, (a) An electron moves from 40.0 V to 60.0 V. (b) An electron moves front 40.0 V to 20.0 V. (c) A proton moves from 40.0 V to 20.0 V'. (d) A proton moves from 40.0 V to 10.0 V. (e) An O-- ion mines from 40.0 V to 60.0 V.arrow_forwardTwo parallel conducting plates, each of cross-sectional area 400 cm2, are 2.0 cm apart and uncharged. If 1.01012 electrons are transferred from one plate to the other, (a) what is the potential difference between the plates? (b) What is the potential difference between the positive plate and a point 1.25 cm from it that is between the plates?arrow_forwardA 12.0-V battery-operated bottle warmer heats 50.0 g of glass, 2.50102 g of baby formula, and 2.00102 g of aluminum from 20.0C to 90.0C . (a) How much charge is moved by the battery? (b) How many electrons per second flow if it takes 5.00 min to warm the formula? (Hint: Assume that the specific heat of baby formula is about the same as the specific heat of water.)arrow_forward
- Review. Two insulating spheres have radii r1 and r2, masses m1 and m2, and uniformly distributed charges q1 and q2. They are released from rest when their centers are separated by a distance d. (a) How fast is each moving when they collide? (b) What If? It the spheres were conductors, would their speeds be greater or less than those calculated in part (a)? Explain.arrow_forward(a) Would life be different if the electron were positively charged and the proton were negatively charged? (b) Does the choice of signs have any bearing on physical and chemical interactions? Explain your answers.arrow_forwardIntegrated Concepts: A 12.0 V battery-operated bottle warmer heats 50.0 g of glass, 2.50 102 g of baby formula, and 2.00 102 g of aluminum from 20.0°C to 90.0°C. (a) How much charge is moved by the battery? (b) How many electrons per second flow if it takes 5.00 mm to warm the formula? (Hint: Assume that the specific heat of baby formula is about the same as the specific heat of water.)arrow_forward
- The planetary model of the atom pictures electrons orbiting the atomic nucleus much as planets orbit the Sun. In this model you can view hydrogen, the simplest atom, as having a single electron in a circular orbit 1.061010 m in diameter. (a) If the average speed of the electron in this orbit is known to be 2.20106 m/s, calculate the number of revolutions per second it makes about the nucleus. (b) What is the electron's average velocity?arrow_forward(a) What is the final speed of an electron accelerated from rest through a voltage of 25.0 MV by a negatively charged Van de Graff terminal? (b) What is unreasonable about this result? (c) Which assumptions are responsible?arrow_forwardA long cylinder of aluminum of radius R meters is charged so that it has a uniform charge per unit length on its surface of . (a) Find the electric field inside and outside the cylinder, (b) Find the electric potential inside and outside the cylinder, (c) Plot electric field and electric potential as a function of distance from the center of the rod.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning


Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781938168000
Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger Hinrichs
Publisher:OpenStax College

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning