
Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780534408961
Author: Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Don't use chat gpt plz Chatgpt means downvote
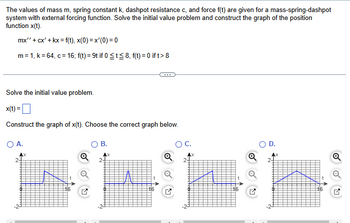
Transcribed Image Text:The values of mass m, spring constant k, dashpot resistance c, and force f(t) are given for a mass-spring-dashpot
system with external forcing function. Solve the initial value problem and construct the graph of the position
function x(t).
mx" + cx' + kx = f(t), x(0)=x'(0) = 0
m = 1, k=64, c = 16; f(t) = 9t if 0 ≤t≤8, f(t) = 0 if t> 8
Solve the initial value problem.
x(t)=
Construct the graph of x(t). Choose the correct graph below.
○ A.
2-
Ax
2
B.
Ax
✓
Q
✓

Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A. An object with mass 0.05 kg is dropped through a medium offering a resistance of 0.5 times the velocity. Formulate the IVP for the velocity if the initial velocity is vo m/s. Make a phase plot and slope field. What is the terminal velocity? (Ans:vo = 0.98 m/s)arrow_forwardneed some helparrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution ....arrow_forward
- 145 S N Q-3 T. Brady Problem sy = Voy⋅ t + kayt 11 21 60f 1664/5² W w ½gt² + Vyt-sy = 0 at² + bt+C =0 Q-3 Hmwk #2arrow_forwardJ Consider (Figure 1). Figure 10 ft 8 ft 8 ft 10 ft 16 A 6- FA-12 16 6 ft 1 of 1 > of 1 1 B 4 ft ▼ Part A Determine the projected component of the force F = 12 lb acting in the direction of cable AC. Express the result as a Cartesian vector. Express your answer in terms of the unit vectors i, j, and k. Use the 'vec' button to denote vectors in your answer. Express your answer in pounds to three significant figures. 195] ΑΣΦΗ Ivec FAC Submit Provide Feedback Request Answer D P Pearson a O PNING lb Next >arrow_forwardIn Problem 28 nd the critical points and phase portrait of the given autonomous rst-order differential equation. Classify each critical point as asymptotically stable, unstable, or semi - stable. By hand, sketch typical solution curves in the regions in the xy - plane determined by the graphs of the equilibrium solutions dy/dx = ye^y-9y/e^arrow_forward
- If you shake a magnetic compass e and then set it down, you can watch the needle bounce back and forth around its equilibrium position. If this motion is unimpeded by friction, it is an example of simple harmonic motion 2. You may learn more about simple harmonic motion in Phys 1230, but we'll be seeing another example soon in Unit 8. In this case, energy is being transferred continually between magnetic potential energy and kinetic energy, and the energy is conserved if there is no friction. When there is no kinetic energy, the needle is the maximally deflected and its magnetic potential energy is maximum; when the magnetic potential energy is minimum, the needle is moving the fastest. Conservation of energy shows that KE (0) +U (0) = Umax (functions of angle, not multiplication). For your compass, the measured angle between maximum deflection and equilibrium is 58°. What percent of the maximum kinetic energy does the needle have when it is only deflected 29° from equilibrium? Give…arrow_forwardA. D C What type of ave part shown by lemer D equrium te Thoank pu Cre wlengh amplitude 00000arrow_forwardTake F= 250 N and d = 1.0 m (Figure 1). Figure 1.5 m B C A F 1 of 1 Determine the force in cable AC needed to hold the 19-kg ball D in equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ► View Available Hint(s) FAC = Submit Part B μA Value 1 Units ? Determine the force in cable AB needed to hold the 19-kg ball D in equilibrium. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. ▸View Available Hint(s)arrow_forward
- For the mechanical system, use complex impedances to derive the transfer function matrix connecting the input forces ui and uz to the output displacements yı and y2 of the two point masses. Known are m, c, and k. Use a) matlab and b) Simulink to plot the displacements yı(t) and y2(t) of the mechanical system shown based on the transfer function matrix derived in that problem. Known are m = 1.2 kg, c =14 N s/m, and k=180 N/m. The input forces are u1= 50*e- 31*sin(16t) N and u2= 60/(t + 3) N. The initial conditions are zero. m marrow_forwardAn engineer wants to wind 10 turns of wire on a cylindrical rod. He/she measures the diameter of the rod to calculate using a mierometer to estimate the needed wire length. If the reading of the diameter is given in figure, calculate the required wire for 10 turns. 1 2 4 9. 10 Least significant bit= 0.05 mm, and zero error is 0. (Hint: 1 = 3, the length of the cylindrical bar is enough, and the windings do not overlap) A. 91.1 mm wire B. 83.7 mm wire C. 52.1 mm wire D. 62.4 mm wire E. 56.3 mm wirearrow_forwardPlease circle answerarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Modern Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781111794378
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. Moyer
Publisher:Cengage Learning