
Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
5th Edition
ISBN: 9780534408961
Author: Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
Don't use chat gpt plz Solve correctly

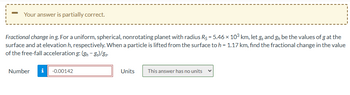
Transcribed Image Text:Your answer is partially correct.
Fractional change in g. For a uniform, spherical, nonrotating planet with radius Rs = 5.46 × 103 km, let g and g₁₂ be the values of g at the
surface and at elevation h, respectively. When a particle is lifted from the surface to h = 1.17 km, find the fractional change in the value
of the free-fall acceleration g: (gh-gs)/gs
Number i -0.00142
Units
This answer has no units
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Suppose the gravitational acceleration at the surface of a certain moon A of Jupiter is 2 m/s2. Moon B has twice the mass and twice the radius of moon A. What is the gravitational acceleration at its surface? Neglect the gravitational acceleration due to Jupiter, (a) 8 m/s2 (b) 4 m/s2 (c) 2 m/s2 (d) 1 m/s2 (e) 0.5 m/s2arrow_forward(a) What is the acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the Moon? (b) On the surface of Mars? The mass of Mars is SW 6.4181023kg and its radius is 3.38106m .arrow_forwardTwo planets in circular orbits around a star have speed of v and 2v . (a) What is the ratio of the orbital radii of the planets? (b) What is the ratio of their periods?arrow_forward
- Model the Moons orbit around the Earth as an ellipse with the Earth at one focus. The Moons farthest distance (apogee) from the center of the Earth is rA = 4.05 108 m, and its closest distance (perigee) is rP = 3.63 108 m. a. Calculate the semimajor axis of the Moons orbit. b. How far is the Earth from the center of the Moons elliptical orbit? c. Use a scale such as 1 cm 108 m to sketch the EarthMoon system at apogee and at perigee and the Moons orbit. (The semiminor axis of the Moons orbit is roughly b = 3.84 108 m.)arrow_forwardThe International Space Station (ISS) experiences an acceleration due to the Earths gravity of 8.83 m/s2. What is the orbital period of the ISS?arrow_forwardLet gM represent the difference in the gravitational fields produced by the Moon at the points on the Earths surface nearest to and farthest from the Moon. Find the fraction gM/g, where g is the Earths gravitational field. (This difference is responsible for the occurrence of the lunar tides on the Earth.)arrow_forward
- (a) Using the data in the previous problem for the asteroid Vesta which has a diameter of 520 km and mass of 2.671020kg , what would be the orbital period for a space probe in a circular orbit of 10.0 km from its surface? (b) Why is this calculation marginally useful at best?arrow_forwardSince March 2006, NASAs Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) has been in a circular orbit at an altitude of 316 km around Mars (Fig. P6.81). The acceleration due to gravity on the surface of the planet Mars is 0.376g, and its radius is 3.40 103 km. Assume the acceleration due to gravity at the satellite is the same as on the planets surface. a. What is MROs orbital speed? B. What is the period of the spacecrafts orbit? FIGURE P6.81arrow_forwardPlanetary orbits are often approximated as uniform circular motion. Figure P7.9 is a scaled representation of a planets orbit with a semimajor axis of 1.524 AU. a. Use Figure P7.9 to find the ratio of the Suns maximum gravitational field to its minimum gravitational field on the planets orbit. b. What is the ratio of the planets maximum speed to its minimum speed? c. Comment on the validity of approximating this orbit as uniform circular motion.arrow_forward
- What is the average speed in mi/h of a person at the equator as a result of the Earths rotation? (Take the radius of the Earth to be RE = 4000 mi.)arrow_forwardFor many years, astronomer Percival Lowell searched for a Planet X that might explain some of the perturbations observed in the orbit of Uranus. These perturbations were later explained when the masses of the outer planets and planetoids, particularly Neptune, became better measured (Voyager 2). At the time, however, Lowell had proposed the existence of a Planet X that orbited the Sun with a mean distance of 43 AU. With what period would this Planet X orbit the Sun?arrow_forwardIn Example 2.6, we considered a simple model for a rocket launched from the surface of the Earth. A better expression for the rockets position measured from the center of the Earth is given by y(t)=(R3/2+3g2Rt)2/3j where R is the radius of the Earth (6.38 106 m) and g is the constant acceleration of an object in free fall near the Earths surface (9.81 m/s2). a. Derive expressions for vy(t) and ay(t). b. Plot y(t), vy(t), and ay(t). (A spreadsheet program would be helpful.) c. When will the rocket be at y=4R? d. What are vy and ay when y=4R?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning