
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
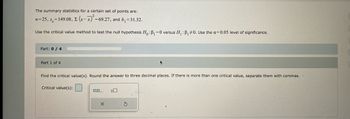
Transcribed Image Text:The summary statistics for a certain set of points are:
= 69.27, and b₁ = 31.32.
n=25, s=149.08, E (x-x)² =6
Use the critical value method to test the null hypothesis Ho: B₁=0 versus H₁ : B₁ #0. Use the a=0.05 level of significance.
Part: 0 / 4
Part 1 of 4
Find the critical value(s). Round the answer to three decimal places. If there is more than one critical value, separate them with commas.
Critical value(s):
0.0...
X
+
S
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- The test statistic of z = 2.05 is obtained when testing the claim that p > 0.4. Identify the hypothesis test as being two-tailed, left-tailed, or right-tailed. Find the P-value. Using a significance level of α = 0.10, should we reject H0 or should we fail to reject H0?arrow_forwardTest the claim that the proportion of men who own cats is smaller than the proportion of women who own cats at the .05 significance level.The null and alternative hypothesis would be: H0:μM=μFH1:μM<μF H0:pM=pFH1:pM<pF H0:pM=pFH1:pM>pF H0:pM=pFH1:pM≠pF H0:μM=μFH1:μM≠μF H0:μM=μFH1:μM>μF The test is: right-tailed left-tailed two-tailed Based on a sample of 20 men, 40% owned catsBased on a sample of 60 women, 55% owned catsThe test statistic is: (to 2 decimals)The p-value is: (to 2 decimals)Based on this we: Fail to reject the null hypothesis Reject the null hypothesisarrow_forwardAfter running a regression you conduct a hypothesis test of Ho: ß = 2.5 versus Hạ: B + 2.5 is performed using a = 0.10. The value of the test statistic z = -1.80 (the critical value is -1.645). If the true value of B is 2.5, does the conclusion you reach result in Type I, Type II error, or the correct decision? O Type II Error O Type I Error O correct decision not enough informationarrow_forward
- The test statistic of z = 0.53 is obtained when testing the claim that p > 0.5. Identify the hypothesis test as being two-tailed, left-tailed, or right-tailed. Find the P-value. Using a significance level of α = 0.05, should we reject H0 or should we fail to reject H0?arrow_forwardTest the claim that the mean GPA of night students is larger than 3.2 at the .005 significance level.The null and alternative hypothesis would be: H0:p=0.8H1:p<0.8 H0:p=0.8H1:p>0.8 H0:μ=3.2H1:μ>3.2 H0:μ=3.2H1:μ≠3.2 H0:μ=3.2H1:μ<3.2 H0:p=0.8H1:p≠0.8 Based on a sample of 55 people, the sample mean GPA was 3.22 with a standard deviation of 0.03The test statistic is (to 3 decimals)The critical value is (to 3 decimals)Based on this we fail to reject the null hypothesis reject the null hypothesisarrow_forwardTest the claim that the proportion of men who own cats is smaller than 90% at the .05 significance level.The null and alternative hypothesis would be: H0:μ=0.9H0:μ=0.9H1:μ>0.9H1:μ>0.9 H0:p=0.9H0:p=0.9H1:p>0.9H1:p>0.9 H0:p=0.9H0:p=0.9H1:p≠0.9H1:p≠0.9 H0:μ=0.9H0:μ=0.9H1:μ≠0.9H1:μ≠0.9 H0:μ=0.9H0:μ=0.9H1:μ<0.9H1:μ<0.9 H0:p=0.9H0:p=0.9H1:p<0.9H1:p<0.9 The test is: right-tailed two-tailed left-tailed Based on a sample of 65 people, 87% owned catsThe test statistic is: (to 2 decimals)The critical value is: (to 2 decimals)Based on this we: Fail to reject the null hypothesis Reject the null hypothesis I dont understand this.arrow_forward
- Test the claim that the mean GPA of night students is smaller than the mean GPA of day students at the 0.10 significance level.The null and alternative hypothesis would be: H0:μN=μDH0:μN=μDH1:μN≠μDH1:μN≠μD H0:μN≥μDH0:μN≥μDH1:μN<μDH1:μN<μD H0:pN≥pDH0:pN≥pDH1:pN<pDH1:pN<pD H0:pN=pDH0:pN=pDH1:pN≠pDH1:pN≠pD H0:μN≤μDH0:μN≤μDH1:μN>μDH1:μN>μD H0:pN≤pDH0:pN≤pDH1:pN>pDH1:pN>pD The test is: right-tailed left-tailed two-tailed The sample consisted of 55 night students, with a sample mean GPA of 2.32 and a standard deviation of 0.05, and 55 day students, with a sample mean GPA of 2.37 and a standard deviation of 0.02.The test statistic is: (to 2 decimals)The p-value is: (to 2 decimals)Based on this we: Fail to reject the null hypothesis Reject the null hypothesisarrow_forwardTest the claim that the proportion of men who own cats is significantly different than the proportion of women who own cats at the 0.2 significance level.The null and alternative hypothesis would be: H0:pM=pFH0:pM=pFH1:pM<pFH1:pM<pF H0:μM=μFH0:μM=μFH1:μM≠μFH1:μM≠μF H0:pM=pFH0:pM=pFH1:pM≠pFH1:pM≠pF H0:pM=pFH0:pM=pFH1:pM>pFH1:pM>pF H0:μM=μFH0:μM=μFH1:μM>μFH1:μM>μF H0:μM=μFH0:μM=μFH1:μM<μFH1:μM<μF The test is: two-tailed right-tailed left-tailed Based on a sample of 60 men, 30% owned catsBased on a sample of 40 women, 40% owned catsThe test statistic is: (to 2 decimals)The p-value is: (to 2 decimals)Based on this we: Reject the null hypothesis Fail to reject the null hypothesis Check AnswerQuestion 14arrow_forwardPreviously, 12.1% of workers had a travel time to work of more than 60 minutes. An urban economist believes that the percentage has increased since then. She randomly selects 80 workers and finds that 18 of them have a travel time to work that is more than 60 minutes. Test the economist's belief at the x = 0.1 level of significance. What are the null and alternative hypotheses? P = 0.121 versus H1: p Ho: p (Type integers or decimals. Do not round.) > 0.121 Because npo (1- Po) = < 10, the normal model may not be used to approximate the P-value. (Round to one decimal place as needed.)arrow_forward
- Test the claim that the proportion of men who own cats is significantly different than the proportion of women who own cats at the 0.2 significance level.The null and alternative hypothesis would be: H0:μM=μFH0:μM=μFH1:μM<μFH1:μM<μF H0:pM=pFH0:pM=pFH1:pM<pFH1:pM<pF H0:pM=pFH0:pM=pFH1:pM≠pFH1:pM≠pF H0:pM=pFH0:pM=pFH1:pM>pFH1:pM>pF H0:μM=μFH0:μM=μFH1:μM>μFH1:μM>μF H0:μM=μFH0:μM=μFH1:μM≠μFH1:μM≠μF The test is: right-tailed left-tailed two-tailed Based on a sample of 40 men, 25% owned catsBased on a sample of 20 women, 30% owned catsThe test statistic is: (to 2 decimals)The p-value is: (to 2 decimals)Based on this we: Reject the null hypothesis Fail to reject the null hypothesisarrow_forwardA student performs a test of Ho p = 0.75 versus H, p < 0.75 at the a = 0.05 significance level and gets a P-value of 0.22. The student writes: 'Because the P-value is large, we accept Ho. The data provide convincing evidence that the null hypothesis is true." What should the student have written for their conclusion? Because the P-value is large, we fail to reject Ho. The data do not provide convincing evidence that the alternative hypothesis is true. O Because the P-value is large, we fail to reject Ho. The data provide convincing evidence that the alternative hypothesis is true. Becaus the P-value is small, we reject Ho. The data provide convincing evidence that the alternative hypothesis is true. Because the P-value is large, we accept Ho. The data do not provide convincing evidence that the alternative hypothesis is true. What the student wrote is correct.arrow_forwardTest the claim that the mean GPA of night students is smaller than 2.5 at the 0.01 significance level.The null and alternative hypothesis would be: H0:p=0.625H0:p=0.625H1:p≠0.625H1:p≠0.625 H0:p≥0.625H0:p≥0.625H1:p<0.625H1:p<0.625 H0:μ≤2.5H0:μ≤2.5H1:μ>2.5H1:μ>2.5 H0:μ≥2.5H0:μ≥2.5H1:μ<2.5H1:μ<2.5 H0:p≤0.625H0:p≤0.625H1:p>0.625H1:p>0.625 H0:μ=2.5H0:μ=2.5H1:μ≠2.5H1:μ≠2.5 The test is: right-tailed two-tailed left-tailed Based on a sample of 35 people, the sample mean GPA was 2.48 with a standard deviation of 0.03The test statistic is: (to 2 decimals)The p-value is: (to 2 decimals)Based on this we: Reject the null hypothesis Fail to reject the null hypothesisarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman