Question
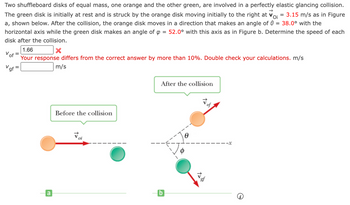
Transcribed Image Text:Two shuffleboard disks of equal mass, one orange and the other green, are involved in a perfectly elastic glancing collision.
Voi
= 3.15 m/s as in Figure
The green disk is initially at rest and is struck by the orange disk moving initially to the right at v
a, shown below. After the collision, the orange disk moves in a direction that makes an angle of 0 = 38.0° with the
horizontal axis while the green disk makes an angle of = 52.0° with this axis as in Figure b. Determine the speed of each
disk after the collision.
X
V of
Vgf=
1.66
Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. m/s
m/s
a
Before the collision
After the collision
b
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Two shuffleboard disks of equal mass, one orange and the other green, are involved in a perfectly elastic glancing collision. The green disk is initially at rest and is struck by the orange disk moving initially to the right at vo- 7.75 m/s as in Figure a, shown below. After the collision, the orange disk moves in a direction that makes an angle of e = 39.0° with the horizontal axis while the green disk makes an angle of 9 = 51.0° with this axis'as in Figure b. Determine the speed of each disk after the collision. Vof= m/s Vof- m/s After the collision Before the collisionarrow_forwardA steel ball of mass 0.850 kg is fastened to a cord that is 65.0 cm long and fixed at the far end. The ball is then released when the cord is horizontal, as shown in the figure. At the bottom of its path, the ball strikes a 3.30 kg steel block initially at rest on a frictionless surface. The collision is elastic. Find (a) the speed of the ball and (b) the speed of the block, both just after the collision. (a) Number (b) Numbe i i Unit Unitarrow_forwardA steel ball of mass 0.710 kg is fastened to a cord that is 89.0 cm long and fixed at the far end. The ball is then released when the cord is horizontal, as shown in the figure. At the bottom of its path, the ball strikes a 2.00 kg steel block initially at rest on a frictionless surface. The collision is elastic. Find (a) the speed of the ball and (b) the speed of the block, both just after the collision. (a) Number i Unit (b) Number i Unitarrow_forward
- Two shuffleboard disks of equal mass, one orange and the other green, are involved in a perfectly elastic glancing collision. The green disk is initially at rest and is struck by the orange disk moving initially to the right at vi = 4.40 m/s as in Figure a, shown below. After the collision, the orange disk moves in a direction that makes an angle of 8 = 40.0° with the horizontal axis while the green disk makes an angle of = 50.0° with this axis as in Figure b. Determine the speed of each disk after the collision. of=1 m/s m/s Vgf= Before the collision After the collision. b of Ⓡarrow_forwardtwo shuffleboard disks of equal mass, one orange, and the other green are involved in an elastic glancing collision. the green disk is initially at rest and is struck by the orange disk moving initially to the right at voi=5.95 m/s as in figure a, after the collision, the orange disk moves in a direction that make an angle of theatre =34.0 degrees with the horizontal axis makes an angle =56.0 degrees. determine the speed of each disk after the collision.arrow_forwardIn the figure, particle 1 of mass m1 = 3.4 kg slides rightward along an x axis on a frictionless floor with a speed of 4.0 m/s.When it reaches x = 0, it undergoes a one-dimensional elastic collision with stationary particle 2 of mass m2 = 4.5 kg. When particle 2 then reaches a wall at xw = 73 cm, it bounces from the wall with no loss of speed. At what position on the x-axis does particle 2 then collide with particle 1?arrow_forward
- Two objects, both with a mass of 1.92 kg are sliding across a horizontal, frictionless surface toward each other. If mass 1 has an initial velocity of 3.79 m/s i and mass 2 has an initial velocity of -2.39 m/s i, what is the change in total kinetic energy if they undergo a perfectly inelastic collision? Assume that total momentum is conserved.arrow_forwardA steel ball of mass 0.870 kg is fastened to a cord that is 85.0 cm long and fixed at the far end. The ball is then released when the cord is horizontal, as shown in the figure. At the bottom of its path, the ball strikes a 4.00 kg steel block initially at rest on a frictionless surface. The collision is elastic. Find (a) the speed of the ball and (b) the speed of the block, both just after the collision. (a) Number i Unit (b) Number i Unitarrow_forwardTwo gliders with mA = 0.50 kg, mB = 0.40 kg, collide elastically on a frictionless surface. Glider A with a spring bumper initially moves to the right with the speed of 4.0 m/s and glider B with a spring bumper initially moves to the left with the speed of 7.0 m/s. What is the final velocity of the glider A after collision?arrow_forward
- Two shuffleboard disks of equal mass, one orange and the other green, are involved in a perfectly elastic glancing collision. The green disk is initially at rest and is struck by the orange disk moving initially to the right at vOi = 5.80 m/s as in Figure a, shown below. After the collision, the orange disk moves in a direction that makes an angle of ? = 34.0° with the horizontal axis while the green disk makes an angle of ? = 56.0° with this axis as in Figure b. Determine the speed of each disk after the collision.arrow_forwardThe figure shows a 0.3 kg baseball just before and just after it collides with a bat. Just before, the ball has velocity v₁ of magnitude 10.9 m/s and angle 0₁ = 30.9°. Just after, it is traveling directly upward with velocity 2 of magnitude 8.80 m/s. The duration of the collision is 1.30 ms. What are the (a) magnitude and (b) direction (relative to the positive direction of the x axis) of the impulse on the ball from the bat? What are the (c) magnitude and (d) direction of the average force on the ball from the bat?arrow_forwardThe drawing shows a collision between two pucks on an air-hockey table. Puck A has a mass of 0.0190 kg and is moving along the x axis with a velocity of +4.08 m/s. It makes a collision with puck B, which has a mass of 0.0380 kg and is initially at rest. The collision is not head-on. After the collision, the two pucks fly apart with the angles shown in the drawing. Find the speed of (a) puck A and (b) puck B. (a) Number (b) Number At rest B 65 A 37 B Before collision After collision Units Unitsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios