
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:<Homework 6
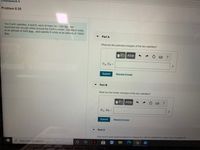
Problem 8.50
Two Earth satellites, A and B, each of mass m = 880 kg , are
launched into circular orbits around the Earth's center. Satellite A orbits
at an altitude of 4400 km , and satellite B orbits at an altitude of 13600
km
Part A
What are the potential energies of the two satellites?
UA, UB =
J
Submit
Request Answer
Part B
What are the kinetic energies of the two satellites?
να ΑΣφ
KA, KB =
Submit
Request Answer
Part C
How much work would it require to change the orbit of satellite A to match that of satellite B?
P Type here to search
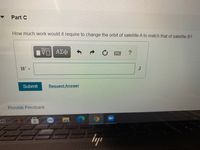
Transcribed Image Text:Part C
How much work would it require to change the orbit of satellite A to match that of satellite B?
Hν ΑΣφ
W =
J
Submit
Request Answer
Provide Feedback
lyp
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- N 8. You are riding a roller-coaster going around a vertical loop, on the inside of the loop. If the loop has a radius of 55.0 m, how fast must the cart be moving in order for you to feel 2.75 times as heavy at the bottom of the loop? m/s R 20 MacBook Air N J M K 17 1arrow_forwardQuestion: Three identical 5.6 kg spheres are located at 3 of the 4 corners (top left, top right, and bottom right) of a square whose sides are 2.8 m in length. How much work must be done on the gravitational field produced by the spheres in order to remove the top right sphere (place it at infinity)? Assume that the 2 spheres that are left behind (top left, bottom right) remain located on opposite corners of the square. A) 1.50 x 10-9 J B) 5.34 x 10-10 J C) 1.89 x 10-10 J D) 2.67 x 10-10 J E) 5.29 x 10-10 J OA E B. C.arrow_forwardA camera weighing 15 N falls from a small drone hovering 35 m overhead and enters free fall. What is the gravitational potential energy change of the camera from the drone to the ground if you take a reference point of a. the ground being zero gravitational potential energy? APE b. The drone being zero gravitational potential energy? APE What is the gravitational potential energy of the camera (with the reference point of zero gravitational potential energy taken to be a second person looking out of a building 30 m from the ground) c. before it falls from the drone? PE=| d. after the camera lands on the ground? PE Submit Questionarrow_forward
- 4. An object of mass m makes a loop-the-loop as shown. When it is upside down at point A, the normal force is found to be 2mg. a) What is the speed of the object at point A in terms of g and R? b) What is the normal force at point B, neglecting any friction of air resistance? Put your answer in terms of m and g. A Barrow_forward2. For a satellite in a circular orbit around the earth, the gravitational force from the earth on the satellite causes the centripetal acceleration. The amount of work done by the gravitational force from the earth on the satelliteA) is zeroB) is greater than zero.C) is less than zero.D) would be different if the masses of the earth and satellite were different.E) can’t be determined without a calculator and some data.i. Prove your answer by using the formula for work, W: (Hint: Consider just a short segment of the orbit, rather than the full revolution.) ii. Prove your answer by talking about the satellite’s kinetic energy, ∆?� ***also please do it i,ii and write a process detail.arrow_forwardA rocket with mass 7.00×103 kgkg is in a circular orbit of radius 7.50×106 mm around the earth. The rocket's engines fire for a period of time to increase that radius to 8.80×106 mm, with the orbit again circular. Part A What is the change in the rocket's kinetic energy? Does the kinetic energy increase or decrease? Express your answer with the appropriate units. Enter positive value if the kinetic energy increases and negative value if the kinetic energy decreases. ΔKΔK = nothingnothing SubmitRequest Answer Part B What is the change in the rocket's gravitational potential energy? Does the potential energy increase or decrease? Express your answer with the appropriate units. Enter positive value if the gravitational potential energy increases and negative value if the gravitational potential energy decreases. ΔUΔU = nothingnothing SubmitRequest Answer Part C How much work…arrow_forward
- As shown in the figure below, a small box is released from rest at point A along the horizontal diameter on the inside of a frictionless, hemispherical bowl. The box has a mass m = 295 g and the bowl has a radius R = 33.0 cm. 2R/3 (a) Calculate the gravitational potential energy of the box-Earth system (in J) when the box is at point A relative to point B. J (b) Calculate the kinetic energy of the box (in J) at point B. (c) Calculate its speed (in m/s) at point B. m/s (d) Calculate its kinetic energy (in J) when the box is at point C. (e) Calculate the potential energy (in J) when the box is at point C.arrow_forwardTwo 0.56-kg basketballs, each with a radius of 15 cm, are just touching. Part A How much energy is required to change the separation between the centers of the basketballs to 1.0 m ? (Ignore any other gravitational interactions.) Express your answer in joules. ► View Available Hint(s) AU = Submit Part B AU = VE ΑΣΦ Submit How much energy is required to change the separation between the centers of the basketballs to 14 m ? (Ignore any other gravitational interactions.) Express your answer in joules. ► View Available Hint(s) B VE ΑΣΦ ? X ? Jarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON