
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
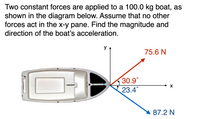
Transcribed Image Text:**Problem Description:**
Two constant forces are applied to a 100.0 kg boat, as shown in the diagram below. Assume that no other forces act in the x-y plane. Find the magnitude and direction of the boat’s acceleration.
**Diagram Analysis:**
- The diagram shows a top view of a boat.
- Two forces are applied to the boat at different angles.
- **Force 1:**
- Magnitude: 75.6 N
- Direction: 30.9° from the positive x-axis, pointing upwards (red arrow).
- **Force 2:**
- Magnitude: 87.2 N
- Direction: 23.4° from the positive x-axis, pointing downwards (blue arrow).
- The coordinate system is defined with the x-axis pointing horizontally to the right and the y-axis pointing vertically up.
**Objective:**
Find the magnitude and direction of the resulting acceleration of the boat using the given forces and angles. Apply Newton’s second law of motion: \( F = ma \), where \( F \) is the net force on the object, \( m \) is the mass of the object, and \( a \) is the acceleration.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Block B in the figure weighs 609 N. The coefficient of static friction between block and table is 0.21; angle e is 27°; assume that the cord between B and the knot is horizontal. Find the maximum weight of block A for which the system will be stationary. Knot A Number i Units >arrow_forwardA uniform density sheet of metal is cut into the shape of an isosceles triangle, which is oriented with the base at the bottom and a corner at the top. It has a base B = 43 cm, height H = 25 cm, and area mass density σ. - The horizontal center of mass of the sheet will be located: On the center line. Not enough information to determine. To the left of the center line. To the right of the center line. - The vertical center of mass of the sheet will be located: Below the mid height. Not enough information to determine. Above the mid height. At the mid height. - Write a symbolic equation for the total mass of the triangle. -Consider a horizontal slice of the triangle that is a distance y from the top of the triangle and has a thickness dy. Write an equation for the area of this slice in terms of the distance y, and the base B and height H of the triangle. - Set up an integral to calculate the vertical center of…arrow_forwardA block of mass ?=2.80 kg is being pulled by a force ?⃗of magnitude 12.0 N on a horizontal, smooth (frictionless) surface. The force makes an angle ?=30.0° abovethe horizontal, as shown in the figure. 1. Find the magnitude of the normal force exerted by the surface on block. 2. Find the acceleration of the box. 3. If the box starts from rest, what would be its speed after it travels 2.00 m?arrow_forward
- Two blocks rest on a frictionless surface as shown. The slope part has an angle of 40◦(A) Draw freebody diagrams for both objects.(B) Write out an equation for the acceleration of the lighter block. Leave all unknowns as letters and put in numerical values for all terms that you can.(C) Write out an equation for the acceleration of the heavier block. Leave all unknowns as letters and put in numerical values for all terms that you can.(D) Would it be possible to solve the system of equations you have written in parts (B) and (C) to find the acceleration? (If you have done everything correctly, it will be possible, but this question is asking about the equations you have written out. If you have done something incorrectly, you can get credit for realizing it.) You do not have to solve this system of equations.arrow_forwardA book of mass m is pushed against a smooth frictionless wall by a force P that makes an angle 0 the horizontal. Find: a) The normal force on the book. b) The acceleration of the block in terms of P, m, 0, and constants. c) Look at the special values of the angle to see if the above answers make sensearrow_forwardA 30kg barrel of oil is sitting in a holding container consisting of two walls one at an angle of 60o from the horizontal, and the other wall at 40o from the horizontal. What are the normal forces acting on the walls – N1 and N2? Draw a free body diagram and a resolved free body diagram.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON