
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A block of mass m is on an inclined ramp. The ramp makes an
angle θ with respect to the horizontal, as shown. The ramp has
friction, with coefficient of kinetic friction μk and static friction μs.
This experiment takes place on earth.
The block has an initial speed of v up the ramp. It travels a
distance d along the ramp before it stops.
Answer using variables, please.
a) Draw a free body diagram clearly showing all the forces acting on the block while it is moving
up the ramp.
b) Calculate the work done by the Normal force as the block travels the distance d.
Is it positive, negative, or zero?
c) Calculate the work done by the Weight force as the block travels the distance d.
Is it positive, negative, or zero?
d) Calculate the work done by the Friction force as the block travels the distance d.
Is it positive, negative, or zero?
e) If the block comes to rest, how far has it travelled?
Use the work-energy principle and your results of parts b), c), and d).
f) Briefly (one sentence) explain why this problem could not be solved using conservation of
energy.
angle θ with respect to the horizontal, as shown. The ramp has
friction, with coefficient of kinetic friction μk and static friction μs.
This experiment takes place on earth.
The block has an initial speed of v up the ramp. It travels a
distance d along the ramp before it stops.
Answer using variables, please.
a) Draw a free body diagram clearly showing all the forces acting on the block while it is moving
up the ramp.
b) Calculate the work done by the Normal force as the block travels the distance d.
Is it positive, negative, or zero?
c) Calculate the work done by the Weight force as the block travels the distance d.
Is it positive, negative, or zero?
d) Calculate the work done by the Friction force as the block travels the distance d.
Is it positive, negative, or zero?
e) If the block comes to rest, how far has it travelled?
Use the work-energy principle and your results of parts b), c), and d).
f) Briefly (one sentence) explain why this problem could not be solved using conservation of
energy.
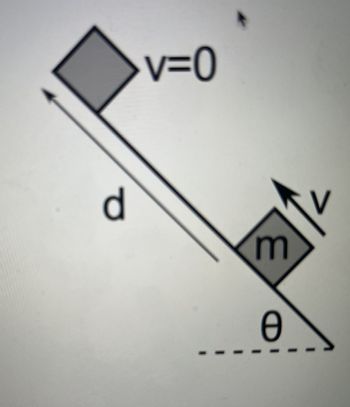
Transcribed Image Text:d
v=0
m
Ꮎ
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A two mass system is shown below. The block m1, 10 kg, sits on a 30 degree incline with a coefficient µs = 0.6 between the block and the incline. A mass m2 is attached to mi by a frictionless pulley system and the two blocks are released from rest. (a) Draw and label the free body diagram for the m1 block while it is moving on the ramp: Iml 30° (b) How much mass m2 is needed to pull the 10 kg block, m1, up the ramp? (c) If m2 = 15 kg, how long does it take the block to travel a distance 5m on the incline surface? Let uk = 0.3.arrow_forwardCalculate the magnitude of the normal force on a 17.7 kg block in the following circumstances. (Enter your answers in N.) The block is on a level surface and a force of 165 N is exerted on it at an angle of 40.8° above the horizontal. I don't know how to do this.arrow_forwardcan someone answer part E pleasearrow_forward
- Jill of the Jungle swings on a vine 7.00 m long. (a) What is the tension in the vine if Jill, whose mass is 65.0 kg, is moving at 3.00 m/s when the vine is vertical? (b) If the maximum tension that the rope can support is 750 N, what is the maximum speed that you can have on the rope?arrow_forwardA particle, which remains at rest, is acted on by three forces, P, Q and R, and no others, as shown in the diagram attached. The force P acts horizontally to the left, the force Q acts vertically upwards and the force R acts downwards and to the right at an angle of 30◦ to the horizontal. The magnitude of P is 52 N. Let the magnitudes of Q and R in newtons be Q and R respectively. Take the Cartesian unit vectors i and j to be in the opposite direction to P and in the same direction as Q, respectively. a) Find expressions for the component forms of the three forces P, Q and R. b) Hence or otherwise find Q to two significant figures.arrow_forwardEspecially part Carrow_forward
- A 9.80-kg hanging object is connected by a light, inextensible cord over a light, frictionless pulley to a 5.00-kg block that is sliding on a flat table. Taking the coefficient of kinetic friction as 0.218, find the tension in the string. (The block slides to the right in the diagram below.) N m₁ mąarrow_forwardA block accelerates at 4 m/s^2 down a rough ramp, inclined at 38 degrees. What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and ramp? Include a sketch of the system (with a coordinate system) and a free body diagram.arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution ....arrow_forward
- In the figure, a 4.00 kg block is sent sliding up a plane inclined at 0 = 39.0° while a horizontal force of magnitude F = 45.0 N acts on it. The %3D coefficient of kinetic friction between block and plane is 0.30. What is the magnitude and direction (up or down the plane) of the block's acceleration?arrow_forwardA 1,500-N crate is being pushed across a level floor at a constant speed by a force F of 370 N at an angle of 20.0° below the horizontal, as shown in the figure a below. F 20.0° / b 20.0° (a) What is the coefficient of kinetic friction between the crate and the floor? (Enter your answer to at least three decimal places.) 0.220 X Your response is within 10% of the correct value. This may be due to roundoff error, or you could have a mistake in your calculation. Carry out all intermediate results to at least four-digit accuracy to minimize roundoff error.arrow_forwardTwo Blocks having mass m=11.0 kg are connected by a light string passing through two pulleys as shown. The block on the left is resting on an inclined plane of angle 0=45.0° . The pulleys and the planes on which the blocks are resting are frictionless. The blocks are released from rest and allowed to move freely. a. Draw the free body diamgrams for each block and then write down newton's second law of motion for each one separately. b. Find the acceleration of the blocks and the tension in the string.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON