
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
5th Edition
ISBN: 9781133104261
Author: Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A 495 kg uniform beam is suspended by a vertically hanging rope at each end. The beam is tipped at an angle of 25.0 degrees with respect to the horizontal. A 105 kg construction worker stands at the very left end of the beam, as shown in the diagram below
A)) Let the system be the worker and the beam. On the diagram, label all of the external forces acting on the system, using arrows.
(b) Find the tension in the rope on the right side of the beam. Give your answer in Newtons. Assume the system is in static equilibrium
c) Find the tension in the rope on the left side of the beam. Give your answer in Newtons. Assume the system is in static equilibrium.
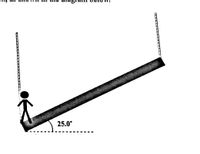
Transcribed Image Text:The diagram depicts a stick figure standing on an inclined beam suspended by two ropes. The beam is positioned at an angle of 25.0 degrees from the horizontal plane. The left end of the beam is on the ground, while the right end is elevated. The angle indicates the steepness of the incline, with the measure (25.0°) clearly labeled at the base of the beam near the figure. The ropes suggest points of suspension beyond the visible portion of the diagram.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- For what values of a are the vectors A = 2ai − 2j + ak and B = ai + 2aj + 2k perpendicular?arrow_forwardFor the two vectors find A − B and |A – B| component of B along A angle between A and B A × B (A − B) × (A + B)arrow_forwardFigure 1.19 shows two vectors lying in the xy-plane. Determine the signs of the x- and y-components of A, B, and A+B.arrow_forward
- What is the y component of the vector shown in Figure OQ1.9? (a) 3 cm (b) 6 cm (c) 4 cm (d) 6 cm (e) none of those answers Figure OQ1.9 Objective Questions 9 and 10.arrow_forwardIn a tug-of-war game on one campus, 15 students pull on a rope at both ends in an effort to displace the central knot to one side or the other. Two students pull with force 196 N each to the light, four students pull with force 98 N each to the left, five students pull with force 62 N each to the left, three students pull with force 150 N each to the right, and one student pulls with force 250 N to the left. Assuming the positive direction to the tight, express the net pull on the knot in terms of the unit vector. How big is the net pull on the knot? In what direction?arrow_forwardFind the angles that vector makes with the and axes.arrow_forward
- Vector B has x, y, and z components of 4.00, 6.00, and 3.00 units, respectively. Calculate (a) the magnitude of B and (b) the angle that B makes with each coordinate axis.arrow_forwardFind (a) the x- and (b) y-components of R = 2A B if A has components Ax = 15.0 m and Ay = 12.0 m whereas B has components Bx = 24.0 m and By = 8.00 m. (See Section 3.2.)arrow_forwardVector B is 5.0 cm long and vector A is 4.0 cm long. Find the angle between these two vectors when |A+B|=3.0cm and |AB|=3.0cm .arrow_forward
- What is the x component of the vector shown in Figure OQ3.9? (a) 3 cm (b) 6 cm (c) 4 cm (d) 6 cm (e) none of those answersarrow_forwardFind the horizontal and vertical components of the 100-m displacement of a superhero who flies from the top of a tall building following the path shown in Figure P1.40. Figure P1.40arrow_forwardWhat is the y component of the vector shown in Figure OQ3.9? (a) 3 cm (b) 6 cm (c) 4 cm (d) 6 cm (e) none of those answersarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Classical Dynamics of Particles and Systems
Physics
ISBN:9780534408961
Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. Marion
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...
Physics
ISBN:9781337553292
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning