
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
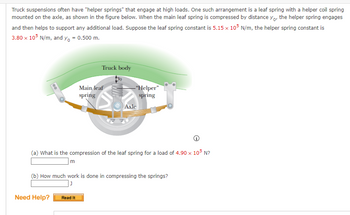
Transcribed Image Text:Truck suspensions often have "helper springs" that engage at high loads. One such arrangement is a leaf spring with a helper coil spring
mounted on the axle, as shown in the figure below. When the main leaf spring is compressed by distance yo, the helper spring engages
and then helps to support any additional load. Suppose the leaf spring constant is 5.15 x 105 N/m, the helper spring constant is
3.80 x 105 N/m, and y₁ = 0.500 m.
m
Need Help?
Truck body
Main leaf
spring
(a) What is the compression of the leaf spring for a load of 4.90 x 105 N?
Read It
-"Helper"
spring
Axle
(b) How much work is done in compressing the springs?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Problem 7. We have a line of two equal masses m connected by three springs with spring constants c₁ = 1, c₂ = 1, and c3 = S. Spring 1 is fixed at the top and spring 3 at the bottom, so xo = x3 = 0. (a) Find the stiffness matrix K in the equation Kx = f for the mass displacements. (b) Solve for the displacements x₁ and x2. (c) If the third spring constant S becomes very large or very small (S→∞ and S→ 0) what are the limiting values of the displacements x₁ and .x₂? (d) If the third spring constant S becomes very large or very small (S→∞ and S→ 0) what are the limiting values of the spring forces y1, y2, and y3? 91 www m 3-WW www C₁ X₁ "Xo = 0 C2₂ X2 C3 X3 = 0arrow_forwardProblem 3: Design a helical compression spring to be used to return a pneumatic cylinder to its original position after being actuated. At a length of 10.50 in, the spring must exert a force of 60 lb. At a length of 4.00 in, it must exert a force of 250 Ib. Severe service is expected. Use ASTM A231 steel wire.arrow_forwardx=8arrow_forward
- i.Considering the rod diagrammed below; calculate an equivalent spring constant or the rod using the length of the rod 1, its area A, and Young's nodulus E for a compressive force F that compresses the rod a distance x. Additionally, is a linear spring a useful model for a rod under compression? What if the rod is under tension? compressed rodarrow_forward1 m 1 m 1 m b B 30° 0.5 m 0.5 m b -1m 75 mm- 75 mm A 25 mm Section b-b Figure 3 (not to scale) A drum is suspended from the wooden frame ABC as shown in Figure 3. The mass of the drum is 20 kg. The frame ABC is supported by the 2 mm diameter, A-36 steel cable DB and by a pin support at A. You are required to: a Calculate all the internal forces acting at the cross section b-b and in cable BD. b Calculate the orientation of the plane and the magnitude of the maximum in- plane shear stress at point F, on section b-b, and represent this condition using a stress element. с Determine the factor of safety (F.S.) of the cable BD for this loading based on the maximum-distortion energy theory (von Mises).arrow_forwardA cable and D-pulley system is used to bring a 230 kg (ACB) pole to the vertical position, as shown in part (a) of the figure. The cable is subjected to a pulling force T and is secured at C. The length L of the pole is 6.0 m, the outside diameter is d= 140 mm and the wall thickness is t= 12 mm. The post rotates around a pin at A shown in detail in figure (b). if the allowable shear stress in the pin is 60 Mpa, find the minimum diameter of the pin at A to support the weight of the pole in the position shown in (a). Pole 10m Cable Pulley 50m ACB Pin Pin sapport plates 40 m (a)arrow_forward
- View In: English v In the below arrangement, all the string and pulleys are massless and the inclined plane is frictionless. At t 0, spring is unstretched and a constant force F = mg starts to act. Find the maximum extension in the spring. (Assume incline to be sufficiently long). Question 11 F=mg Options 8mg 1. O k 4 mg 2. O 5 k 8 mg 3. O 15 k 8mg 4. O 3karrow_forwardHelparrow_forward2. The mechanical system shown in figure is driven by the applied force fa(t). When x1 = x2 = x3 = 0, the springs are neither stretched nor compressed. a. Draw the free body diagram(s) and write the differential equations. X1 B₁ XXXXXX Hell M₁ K K B2 1 M3 fa(t) moo M₂ K relet K x2arrow_forward
- A crank shaft is operated as shown in the figure. A load F1 = 9.73 N is applied and the operator %3D dz applies a load P to counter. The system is in equilibrium and all of the bearings are perfectly dz aligned such that they do not produce moments on the rotating crank. The geometry is given by, w = 7.31 [m), dl = 9.69 m], d2 = 7.57 m). 6.14 (m), d5 = 3.7 (m), %3D d1 d3 = 9.87 (m), d4 %3D F2 and h1 4.4 (m), find the following: %3D F1 Part 1. Express the reaction forces exerted on the bar by the journal bearing at point B. Use the coordinate system shown in the diagram 10 5% 100% Submit [N] Part 2. Express the reaction forces exerted on the bar by the journal bearing at Point A. Use the coordinate system shown in the diagram. 5% 100% 10 Submit [N]arrow_forwardplease help solve and explainarrow_forwardProblem 2 In the system below, two rigid bodies (Nodes 1 and 3) are connected by four springs to walls on either side, as shown in the figure. Nodes 2 and 4 are fixed (wall). An external force of 10 N is applied to body 1 (Node 1). The spring constants are given as kı=10 N/m, k2=20 N/m, k3=30 N/m, and k4=40 N/m. Assume that the bodies can only undergo translation in x-direction (1 DOF). Using the direct method: a) Find the displacements of the two rigid bodies (Nodes 1 and 3). Hint: units! b) Find the reaction force at the left wall (Node 4). Hint: units! E1 E2 3) F1 www 4 Е4 Xarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY