
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
The bar shown in Figure Q1(a) has a mass of 15 kg and is subjected to a couple moment of M = 70 Nm and a force P = (209) N applied to the end of the bar. The spring has unstretched length of 0.4 m and remain in the vertical position due to roller guide at B.
URGENT!!! HELP!!
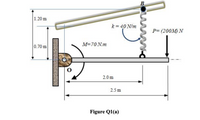
Transcribed Image Text:B
1.20 m
k = 40 N/m
P= (200M) N
M=70 N.m
0.70 m
2.0 m
2.5 m
Figure Q1(a)

Transcribed Image Text:Q1 (a) The bar shown in Figure Q1(a) has a mass of 15 kg and is subjected to a couple
(200M) N applied to the end of the bar. The
moment of M = 70 Nm and a force P
spring has unstretched length of 0.4 m and remain in the vertical position due to roller
guide at B.
Note; Use your last three digit of matrix number to determine the value of force P as
follows;
Example of matrix number, CD190234
M = (2+3+4) = 9
Therefore, P = 200M = 200+9 = 209 N
Draw the free body diagram of the bar to account for all the forces that act on
%D
(i)
it.
(ii)
Determine the total work done by all the forces acting on the bar when it has
rotated downward from 0 = 0° to 0 = 90°.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- help me, please, is mecanica vectorialarrow_forwardBased on Problem 5-40 from the textbook. Determine the stiffness k of each spring so that the applied force F cause the bar to tip = 15 degrees when the force is applied. Originally the bar is horizontal and the springs are unstretched. Neglect the weight of the bar. F=30N b=1.7m a=0.8 m Unique Values for Each Student: C F a www B k b wwwarrow_forwardProblem 7. We have a line of two equal masses m connected by three springs with spring constants c₁ = 1, c₂ = 1, and c3 = S. Spring 1 is fixed at the top and spring 3 at the bottom, so xo = x3 = 0. (a) Find the stiffness matrix K in the equation Kx = f for the mass displacements. (b) Solve for the displacements x₁ and x2. (c) If the third spring constant S becomes very large or very small (S→∞ and S→ 0) what are the limiting values of the displacements x₁ and .x₂? (d) If the third spring constant S becomes very large or very small (S→∞ and S→ 0) what are the limiting values of the spring forces y1, y2, and y3? 91 www m 3-WW www C₁ X₁ "Xo = 0 C2₂ X2 C3 X3 = 0arrow_forward
- Dont forget to draw the FREE BODY DIAGRAMS ALSO PLEASE! (:arrow_forwardplease do it neatly and correct and fast pleasearrow_forward4-44. Blocks A and B each require 30-N cable tension to start them sliding (Figure P4-44). Deter- mine force P and angle to cause them to start sliding simultaneously. FIGURE P4-44 2m PF 20⁰ 80° 4 m Barrow_forward
- Item 2 Consider the following hanging mass system for the following problems. Before answering the questions below, draw two separate free-body diagrams of ring C and then ring B. Be sure the FBDS are neat a properly labeled. You will turn them in with your written work. (Figure 1) Figure 30° E 45° F 1 of 1 Part A cb Deturmine the tension developed in cable if cylindar E weighs 40 lb and 0= 15°. FCB= Submit ▾ Part B WF = 5 ΑΣΦ 11 vec Submit Request Answer If cylinder E weighs 40 lb and 0 = 15°, determine the weight of cylinder F. Express your answer with the appropriate units. 15. ΑΣΦ ↓↑ vec ? Request Answer ? lb 2 of 5arrow_forwardThe structure ABCD (shown below) is designed to support a finite mass hanging from a cable, DF, attached to the structure at point D. x=8m, y=6 m, and z-15 m. The structure is mounted to the ground by a hinge at B and a roller at C and is also supported by a horizontal cable, AE, attached to the wall. The mass of the object hanging from cable DF is 500 kg. The tension in the support cable AE is 1.000 × 10³ N. Determine the force in each member and the reaction forces. E Darrow_forwardForce between A and B: 200lb Angle on D: 35 deg Angle on C: 50 degarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY