
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
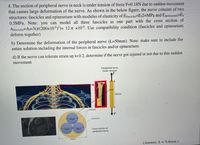
Transcribed Image Text:4. The section of peripheral nerve in neck is under tension of force F=0.18N due to sudden movement
that causes large deformation of the nerve. As shown in the below figure, the nerve consists of two
structures: fascicles and epineurium with modulus of elasticity of Efascicles=Ef2=MPa and Eepineurium=Ee
0.5MPA. Note: you can model all three fascicles as one part with the cross section of
Afascicles=A=3((200×10“)²)= 12 n x10*. Use compatibility condition (fascicles and epineurium
deform together)
b) Determine the deformation of the peripheral nerve (L=50mm). Note: make sure to include the
entire solution including the internal forces in fascicles and/or epineurium.
d) If the nerve can tolerate strain up to 0.2, determine if the nerve got injured or not due to this sudden
movement
Peripheral nerve
Under tension
AF
50mm
Fascicles
F
400μm
Epineurium
400um
400µm
Cross section of
peripheral nerve
1000um
(Answer: 8 9.4mm )
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A spring package with two springs and an external force, 200N. The short spring has a loin of 35 mm. Constantly looking for spring for short spring so that total compression is 35 mm (d). Known values: Long spring: Short spring:C=3.98 N/mm Lo=65mmLo=87.4mmF=c·fTotal compression is same for both spring. 200 = (3.98(c1) × 35) + (c₂ × 35) 200 = 139.3 + 35c₂ 200 - 139.3 = 35c₂ 60.7 = 35c₂ c₂ = 60.7/35 Short spring (c₂) = 1.73 N/mm According to my study book, the correct answer is 4.82N/mm What is wrong with the calculating?arrow_forwardPipe Pa Fluid Rigid rock Figure 1: A pipe embedded in rigid rock. Consider an isotropic linear elastic pipe of inner radius a and outer radius b embedded in rigid (i.e., non-deforming) material and holding a fluid at pressure Pa. Ignore the effects of gravity. This may be a good model for a PVC pipe embedded in rock or concrete. Assume the problem is symmetric and that strains out of the plane shown in Fig. 1are zero. (a) What state of strain exists in the pipe, plane strain or plane stress? (b) Determine the stress components, orr and σ00, and displacements, ur, in the pipe. (c) Is the stress difference orr - 000| greatest at r=a or r = b? Note: the location of the greatest stress difference is where plasticity will occur first (to be covered later in class).arrow_forwardInclude complete solutionarrow_forward
- Determine the possible range for R is the equivalent spring stiffness constant varies from 50 N/m to 500 N/marrow_forwardQuestion 7 Find the value of The reaction force at the support A .arrow_forwardA. A car's body has mass 100 slugs. This mass is supported by the car's 4 shock absorbers. The shock absorbers are identical vertical linear springs. Complete a FBD of the car's body (this would not include the car's wheels, axels etc. just the car's body) Each spring is compressed 1.25 inches. Determine the spring "k" value. Answer: 644 lb/inch. Find the compression of each spring if 4 people, each with mass 6 slugs, get into the car, Answer: 1.55" ii. iii.arrow_forward
- Plz solve correctlyarrow_forwardIn the graph the force versus displacement of a spring is given (the spring is shown in a separate figure--see below). The x-axis range is ±2 cm. The y-axis range is tFs, where Fs = 220 N. How much work does the spring do on the block (the mass "m") when the block moves from x₁ = 7.6 cm to 4.3 cm? W J y F. X -1.5 -0.5 0 10.5 1 1.5 -F How much work does the spring do on the block (the mass "m") when the block moves from x; = 7.6 cm to -7.6 cm? W = Question Help: Read Submit Question marrow_forward7. A spring is attached to the floor. When a 125 g mass is placed on top of the spring it compresses by 0.26 m. What is the spring constant of this spring?arrow_forward
- A fraternity brother finds an old bungee cord at a garage sale and is contemplating on having a bungee jump event. He measures the spring constant of the cord (assume it is a linear spring) by applying a 500 N force to it and measuring a stretch of 2.5 m. Your job is to help him estimate how tall the jump tower should be. He knows the cord is L = 40 m long, he expects the cord to stretch d for an average 60 kg guy like himself, and at maximum stretch he wants his feet to still be 10 m above the ground. Determine: a. The maximum distance, d, the cord would stretch if a 60 kg brother jumped from tower height, H. b. The force developed in the cord at his max stretch position. c. Calculate the expected tower height. d. The velocity of the brother 40 m below from the topmost level of the tower.arrow_forwardNeed Help With This Questionarrow_forwardFind the tension in each segment. 7 ft B 4 ft 50lb 4 ft 5 ft 3 ft 100 lb D Fbc = 47 #, Fba = 83 #, Fcd = 88 # Fbc = 40 #, Fba = 50 #, Fcd = 33 # Fbc = 27 #, Fba = 68 #, Fcd = 18 # ☐ none of the abovearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY