
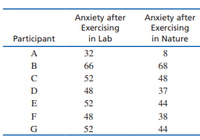
Exercise is known to produce positive psychological effects. Interestingly, not all exercise is equally effective. It turns out that exercising in a natural environment (e.g., jogging in the woods) produces better psychological outcomes than exercising in urban environments or in homes (Mackay & Neill, 2010). Suppose that a sports psychologist is interested in testing whether there is a difference between exercise in nature and exercise in the lab with respect to post-exercise anxiety levels. The researcher recruits n 5 7 participants who exercise in the lab and exercise on a nature trail. The data below represent the anxiety scores that were measured after each exercise session.
- Treat the data as if the scores are from an independent-measures study using two separate samples, each with n 5 7 participants. Compute the pooled variance, the estimated standard error for the
mean difference, and the independent-measures t statistic. Using a 5 .05, is there a significant difference between the two sets of scores? - Now assume that the data are from a repeated measures study using the same sample of n 5 7 participants in both treatment conditions. Compute the variance for the sample of difference scores, the estimated standard error for the mean difference, and the repeated-measures t statistic. Using a 5 .05, is there a significant difference between the two sets of scores?
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

- Tim is interested in studying whether Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) is an effective treatment for Obsessive Compulsive Disorder (OCD). Six people who were diagnosed with OCD participated in Tim's study, where he recorded the number of times they washed their hands per day for one month. They were then given a three week intensive CBT program before their hand-washing was monitored for another month. The average number of times per day each participant washed their hands over the two months of observation are as follows: Participant Month 1 Month 2 1 11 6 2 8 5 3 14 17 4 10 10 5 22 11 6 15 10 Compute the appropriate statistic to determine whether the program was effective and use this information to fill in the blanks: Q1. revealed that the number of times per day participants washed their hands following the CBT program was Q2. compared to the number of times per day participants washed their hands before the…arrow_forwardHelp please!!arrow_forwardCan You Tell a Story About Your Parents? In a study, young adults in the US were asked to recall a story that their parent(s) had told them about a time when their parent(s) were young. In a report of the study, it was stated that “more than 90% of teenagers and young adults can retell family stories when asked, even if they seemed uninterested when the stories were told.” The actual results of the study were that 244 young adults out of the 260 young adults who were asked about this were able to recall such a story. (a) If the standard error for the distribution is 0.015, find a 95% confidence interval for the proportion of young US adults who can recall a story that parent(s) told them about when the parent(s) were young. (b) Is the 90% value that was stated in the report consistent with the confidence interval?arrow_forward
- Read through this scenario and look at the data that was collected. State the null and all possible research hypotheses. Review the results below (I used SPSS) and answer the questions that follow. Scenario: A researcher wants to see if gender and / or income affects the total amount of help given to a stranger who is sitting on the side of a busy road with a sign asking for help. The independent variables are gender, income, and the interaction of gender and income. The dependent variable is total help. He wants to know if one or both factors – or the interaction of the two - affects the total amount of help offered. Because he is analyzing two independent variables (gender and income), he used a factorial ANOVA. His results show the main effect of each of the independent variables on the dependent variable (total help) and the interaction effect. The researcher is using a 95% confidence interval which means that he wants to be at least 95% sure that his independent variables…arrow_forwardSay Dr. Callahan measures her students' levels of narcissism. Her findings reveal that narcissism rates are higher in her male students versus her female students, a finding that is consistent with previous research. She also finds that the overall class average (11.5 out of 20) is lower than typical undergraduates' levels (15.5). Which of the following statements about this scenario is TRUE? She can conclude that being a SSU student is associated with lower levels of narcissism. She needs to be skeptical of her findings because she did not have a random sample. She needs to be skeptical of her findings because she did not have random assignment. She can conclude that her sample is externally valid because it replicates previous research. She can conclude that being a SSU student causes narcissism to decrease.arrow_forwardA psychologist develops an intervention designed to reduce test anxiety associated with taking the SAT. The psychologist claims that reduced test anxiety will lead to higher scores on the quantitative section of the SAT. Because she believes all students experience some degree of anxiety related to the SAT, she further claims her intervention should work for all students, not just those who report abnormal levels of test anxiety. She randomly selects 30 high school juniors, and with the consent of their parents, delivers her intervention. Subsequently, these students take the SAT, and she collects their scores. The quantitative section of the SAT has a mean of 500 and a standard deviation of 100 in the general population, and scores are normally distributed. a. What type of test should be used to analyze her data? i. Z-test ii. Single-sample t-test iii. Independent-measures t-test iv. Repeated-measures t-test b. What would the hypotheses be?arrow_forward
- A new researcher at the BCIE believes that the success of the "Dogs Anti Anxiety" program lies with the gender of the dog. Specifically, he believes that male dogs are better at relieving anxiety compared to female dogs. The head of the BCIE (Dr. Wolf) is not really convinced. She believes that the secret to relieving anxiety lies with the age of the dog. Together they devise an experiment to test this hypothesis. Specifically, they assign 28 participants to one of four therapy groups (male puppy, male senior dog, female puppy, female senior dog) for one week. At the end of the week, they measure the anxiety level of participants on a scale that ranges from 1 to 10 (with higher scores indicating more anxiety). The table below presents the data from their study. Please help the researchers solve the different steps in this factorial ANOVA. I have provided you with the formulas for a between groups factorial ANOVA and you need to fill in the 24 blanks to calculate SSage, SSgender.…arrow_forwardIn an early study of the effects of frustration on feelings of hostility, Miller and Bugelski (1948) had a group of boys at a camp rate their attitudes toward two groups (Mexicans and Japanese). The campers then participated in a long, difficult, frustrating testing session that kept them away from their weekly movie. Finally the boys again rated their attitudes towards the minority groups. The scores below represent the number of unfavorable traits attributed to minorities and are similar to those of miller and Bugelski. Participant Before After A 5 6 B 4 4 C 3 5 D 3 4 E 2 4 F 2 3 G 1 3 H 0 2 a. Does the intervening unpleasant task alter attitudes toward the two…arrow_forwardThe authors of a paper describe an experiment to evaluate the effect of using a cell phone on reaction time. Subjects were asked to perform a simulated driving task while talking on a cell phone. While performing this task, occasional red and green lights flashed on the computer screen. If a green light flashed, subjects were to continue driving, but if a red light Flashed, subjects were to brake as quickly as possible. The reaction time (in msec) was recorded. The following summary statistics are based on a graph that appeared in the paper. n = 49 x = 530 S = 65 USE SALT (a) Construct a 95% confidence interval for u, the mean time to react to a red light while talking on a cell phone. (Round your answers to three decimal places.) Interpret a 95% confidence interval for μ, the mean time to react to a red light while talking on a cell phone. We are 95% confident that the mean time to react to a red light while talking on a cell phone is between these two values. There is a 95% chance…arrow_forward
- In a small study, a local community college investigated different indicators of college success. They found that: 0.36 of enrolled students had a full time job, 0.75 of enrolled students were enrolled full-time, and 0.19 of students enrolled full-tme also had a full-time job. According to the results of this study, are the outcomes "have a full-time job" and "enrolled full-time independent?arrow_forwardIn an early study of the effects of frustration on feelings of hostility, Miller and Bugelski (1948) had a group of boys at a camp rate their attitudes toward two groups (Mexicans and Japanese). The campers then participated in a long, difficult, frustrating testing session that kept them away from their weekly movie. Finally the boys again rated their attitudes towards the minority groups. The scores below represent the number of unfavorable traits attributed to minorities and are similar to those of miller and Bugelski. Participant Before After A 5 6 B 4 4 C 3 5 D 3 4 E 2 4 F 2 3 G 1 3 H 0 2 a. Does the intervening unpleasant task alter attitudes toward the two…arrow_forwardMotivational speakers want to be perceived as trustworthy. One hypothesis is that speakers who exhibit immediacy behaviors such as making eye contact, smiling and leaning forward might be perceived as more trustworthy than those who do not engage in these behaviors. To test this hypothesis, a psychologist obtained data from 26 participants. For people in a non-immediacy group, the speaker did not engage in any immediacy behaviors. For the immediacy group, however, the speaker made eye contact, smiled and leaned forward while giving a speech. After the speech, participants rated the speaker on a scale of trustworthiness ranging from 1 (not at all trustworthy) to 9 (highly trustworthy). The following data were obtained. Test whether the immediacy behaviors of the speaker affect trustworthiness rating. No immediacy behavior Immediacy behavior 4 4 7 4 5 3 6 5 3 5 9 8 4 6 8 7 6 3 8 6 7 5 7 8 7 6…arrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





