
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
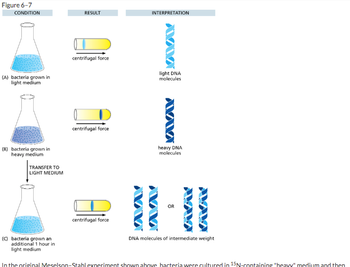
Transcribed Image Text:**Figure 6-7: Meselson-Stahl Experiment**
This figure illustrates the results and interpretations from the Meselson-Stahl experiment, which is crucial for understanding DNA replication.
**Condition A:**
- **Bacteria Grown in Light Medium**
- **Result:** When subjected to centrifugal force, the DNA forms a band towards the top of the tube.
- **Interpretation:** These are light DNA molecules. The DNA was synthesized with lighter nitrogen isotopes.
**Condition B:**
- **Bacteria Grown in Heavy Medium**
- **Result:** The DNA forms a band towards the bottom of the tube under centrifugal force.
- **Interpretation:** These are heavy DNA molecules, indicating synthesis with heavier nitrogen isotopes.
**Condition C:**
- **Bacteria Grown an Additional 1 Hour in Light Medium**
- **Transfer Step:** Bacterial DNA initially grown in heavy medium is transferred to light medium and grown for an additional hour.
- **Result:** After centrifugation, the DNA forms a band in the middle of the tube.
- **Interpretation:** These are DNA molecules of intermediate weight. This indicates that the DNA consists of one strand of heavy DNA and one strand of light DNA, supporting the semiconservative model of DNA replication.

Transcribed Image Text:Transcription:
---
transferred to "14N-containing "light" medium for one cell division. The results of this experiment ruled out the "conservative" model of DNA replication, but to distinguish between the "semiconservative" model and the "dispersive" model, the DNA had to be heated to separate the two strands.
You are repeating the experiment, but are unable to heat the DNA to perform the second part. However, you realize that allowing the bacteria to undergo a second round of division would also distinguish between the different models. Which of the following would you expect to see as a result after the second division in "light" medium?
Choose one:
- A. After the second division, one population of DNA would run at the same position as DNA from bacteria grown fully in "light" medium, and one population would run at a position halfway between fully "heavy" and fully "light" DNA.
- B. After the second round of replication, all of the DNA would run at a position intermediate between fully "heavy" DNA and fully "light" DNA, but closer to the "light" DNA than seen after the first round of replication (i.e., 3/4 "light").
- C. After the second round of replication, all of the DNA would run at a position halfway between fully "heavy" DNA and fully "light" DNA.
- D. After the second round of replication, 25% of the DNA would run at a position similar to fully "heavy" DNA, and 75% would run at a position similar to fully "light" DNA.
---
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 10arrow_forwardEach cycle of the polymerase chain reaction consists of a shift between three different temperatures (94 C, 60 C, and 72 C), explain what occurs at each of those temperatures.arrow_forwardHow does DNA replicate itself? Your explanation (in essay form) should include the following terms: helicase, origins of replication, primase, DNA polymerase (I, II and III), leading strand, lagging strand, Okazaki fragment, DNA ligase, and topoisomerase.arrow_forward
- 5'-GCGGTACGTTACGGCTTTACTGACCTGCAGGC-3' A. Convert this to a double strand DNA molecule by writing the complementary sequence. Be sure to correctly label the ends of the double stranded molecule B. Pick one of the two strands and write the sequence of an RNA molecule that could be transcribed from it. Again, you must correctly label the ends of the molecule.arrow_forwardImagine a bacterial cell with a mutation that renders helicase completely nonfunctional (note that this would be a lethal mutation). What, precisely, would go wrong with replication in this cell? Please describe what goes wrong, as well as all downstream effects.arrow_forwardPlease help me, this is from practice, double check your answers, previous tutors got it wrongarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education