
Biochemistry
9th Edition
ISBN: 9781319114671
Author: Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher: W. H. Freeman
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
This is a diffusion topic: During the time the simulation ran, did the concentration of either the oxygen molecules or the carbon dioxide molecules ever reach a state of equilibrium inside and outside of the cell? Why or why not? If equilibrium was reached, how long did it last? Explain why.
The picture where the levels are not leveled was toward the beginning of the 30 seconds. The picture where the levels are even was towards the end of the 30 seconds.
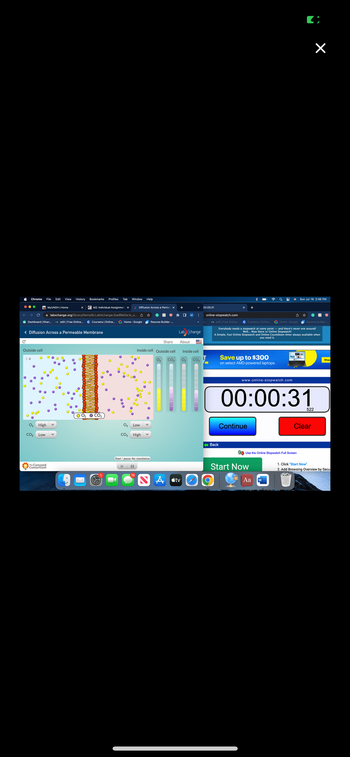
Transcribed Image Text:C
Chrome File Edit View History Bookmarks Profiles Tab Window Help
N MYUNOH | Home
< Diffusion Across a Permeable Membrane
O
Outside cell
→→ C labxchange.org/library/items/lb:LabXchange:2ee89d2e:lx_s...
Dashboard | Khan... ex edx | Free Online... C Coursera | Online... G Home: Google
0₂
High
CO₂ Low
M2: Individual Assignmen
The Concord
Consortium
-
00₂ O CO₂
> Diffusion Across a Permea X
B
O
0₂ Low
CO₂ High
☆
75
Inside cell Outside cell
O₂ CO₂
●
Start/pause the simulation
II
K
Resume Builder ....
Share
+
* ☐ M
D
Lab change
About
Atv
Inside cell
O₂ CO
00:00:31
online-stopwatch.com
in... ex edx | Free Online...
Back
Save up to $300
on select AMD-powered laptops.
☎
G Home: Google
Resume Builder
C Coursera | Online..
Everybody needs a stopwatch at some point and there's never one around!
Well... Now there is! Online Stopwatch!
A Simple, Fast Online Stopwatch and Online Countdown timer always available when
you need it.
www.online-stopwatch.com
Continue
Q
Start Now
00:00:31
Aa
C
. Sun Jul 16 2:46 PM
1 Use the Online Stopwatch Full Screen
×
Clear
522
Shop
1. Click "Start Now"
2. Add Browsing Overview by Secu
NA
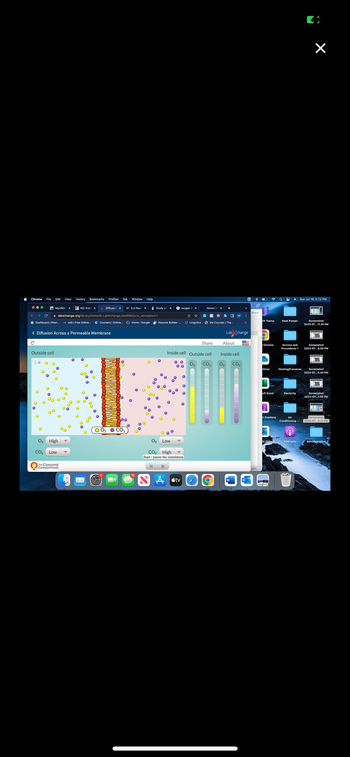
Transcribed Image Text:Chrome
с
File Edit View
M2: Indiv X X Diffusion x = 5.2 Passi X
→→ C labxchange.org/library/items/lb:LabXchange:2ee89d2e:lx_simulation:1
Dashboard | Khan... ex edX | Free Online.... C Coursera | Online.. G Home: Google
< Diffusion Across a Permeable Membrane
LA
N MYUNOH X
Outside cell
CO₂
O₂ High
History Bookmarks Profiles Tab Window Help
Low
The Concord
Consortium
Oo
002 O CO₂
75
Study of x
Resume Builder ....
oxygen a X
0₂ Low
CO₂ High
Start / pause the simulation
K
Atv
B ☆
LingoAce
Home | bi x
Inside cell Outside cell
* ☐
My Courses | The...
Share
+
About
M ⠀
V
Inside cell
Lab change
O₂ CO₂ 0₂ CO₂
>>>
O
$
Share
24%
☎
oft Teams
Chrome
Drive
oft Excel
it OneNote
ft Outlook
Q
Heat Pumps
Service and
Procedures 1
. Sun Jul 16 5:12 PM
Electicity
Air
Conditioning
C
Podcasts
NP
×
Heating/Furnaces Screenshot
Screenshot
2023-07...11.41 PM
Screenshot
2023-07...6.50 PM
2023-07...5.44 PM
Screenshot
2023-07...1.55 PM
Screenshot
2023-07...6.37 PM
Refridgeration
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Demonstrate the listed processesarrow_forwardThere are many things that need to be brought into and out of the cell for cellular respiration. When you look at cellular membranes, including the mitochondrial membrane you can find transporters for many of these things, including glucose and ATP. However, we never find transporters for Oxygen (O2) or Carbon Dioxide (CO2). Why would the cell not require transporters for these molecules?arrow_forwardWrite the chemical equation for cellular respirationarrow_forward
- If the oxygen level were to suddenly drop to near 0, initially how would you expect the cell to react (aka what would happen to the cell/what would the cell do in order to stay alive and functioning)? The cell would:arrow_forwardDiatomic oxygen (O2) exhibits which of the following membrane transport movements? A. it is not able to cross the membrane by passive transport, because it is big, polar, and inorganic it is not able to cross the membrane by active transport, because it is big, polar, and inorganic it is able to cross the membrane by facilitated diffusion, because it is small, polar, and organic it is able to cross the membrane by active transport, because it is big, nonpolar, and organic it is able cross the membrane by simple diffusion, because it is small, nonpolar, and inorganicarrow_forwardSIDE A SIDE B 5 g Glucose 0g Sucrose 100 mL Water jinarnitoij - 0.20M 0g Glucose 5 g Sucrose 100 mL Water Linannitol) 0.20 M Side A Side B How would you describe the level of water (the membrane is permeable to glucose but not permeable to sucrose) in this experiment after 5 days? Multiple Choice water level will be higher on side B water level will stay the same on both sides water level will be higher on side A water level will decrease on both sidesarrow_forward
- Suppose that initially there are 100 Nat and 25 K+ ions inside the cell, near the sodium-potassium pump. After how many cycles is the number of Na ions the same as the number of Kions inside the cell? With the initial values for each type of ion provided above, how many ions of each type are in the cell? What is the total number of ions at this time? Show your work and explain.arrow_forwardYou design a new matrix to regenerate skin during skin graft. The matrix have cells that need nutrients, such as glucose. You need to figure out the diffusion profile of glucose into the matrix. Assuming glucose has a radius of 1.0nm, you are interested in diffusion from the blood vessels into the matrix, which are 1cm away. The blood viscosity is 3cP, and the glucose concentration in the blood is 4mM. What is the initial flux of glucose? (use 1.38 * 10^-23 J/K for Boltzmann's constant).arrow_forwardb) If you soak an animal cell that is permeable to both water and glucose in either 5.5% glucose or 0.9% NaCl (both isosmotic solutions), the cell exposed to 5.5% glucose will gain water, while the cell exposed to 0.9% NaCl will not gain water. Predict why this is the case.arrow_forward
- So when a cell is in electrochemical equilibrium I know for Cl there is no net movemnet because the electrical and concentration gradients have an equal effect. I also know that when K is an electrochemical equilibrium that the concentration effect is bigger than the electrical effect. Which effect is greater for Na when it is in electrochemical equilibrium the electrical or concentration gradient??arrow_forwardYou treat cells with 2,4 dinitrophenol (DNP). This compound creates a temporary channel in the inner membrane of the mitochondria though the protons can move. Which of the following would you observe in these cells? Select all that apply The cells do not synthesize ATP in the presence of DNP The cells synthesize ATP in the presence of DNP The cells reduce oxygen in the presence of DNP The cells generate carbon dioxide in the presence of DNParrow_forwardDescribe the basic process of aerobic cell respiration, what molecules are needed to begin the process of each major step and what are the products of each major step, and where in the cell does each major step take place?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781319114671Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.Publisher:W. H. Freeman Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Lehninger Principles of BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781464126116Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. CoxPublisher:W. H. Freeman Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY
Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...BiochemistryISBN:9781118918401Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. PrattPublisher:WILEY BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305961135Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougalPublisher:Cengage Learning BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning
BiochemistryBiochemistryISBN:9781305577206Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. GrishamPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON
Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...BiochemistryISBN:9780134015187Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. PetersonPublisher:PEARSON

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781319114671
Author:Lubert Stryer, Jeremy M. Berg, John L. Tymoczko, Gregory J. Gatto Jr.
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781464126116
Author:David L. Nelson, Michael M. Cox
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Fundamentals of Biochemistry: Life at the Molecul...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781118918401
Author:Donald Voet, Judith G. Voet, Charlotte W. Pratt
Publisher:WILEY

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305961135
Author:Mary K. Campbell, Shawn O. Farrell, Owen M. McDougal
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Biochemistry
Biochemistry
ISBN:9781305577206
Author:Reginald H. Garrett, Charles M. Grisham
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of General, Organic, and Biological ...
Biochemistry
ISBN:9780134015187
Author:John E. McMurry, David S. Ballantine, Carl A. Hoeger, Virginia E. Peterson
Publisher:PEARSON