
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
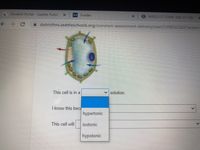
Transcribed Image Text:Student Portal - Seattle Public
SIS Grades
S WRLD LIT COMP 10A: S1 1(A)
districtIms.seattleschools.org/common-assessment-delivery/start/5398502362?action=
This cell is in a
v solution.
I know this bec
hypertonic
This cell will
isotonic
hypotonic
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- pls send me asnwer of this questions with full expalnation pls sir and i will gove you likearrow_forwardWhich solution is most hypertonic? And which solution is most hypotonic?arrow_forwardType of Solutes Non-permeable Permeable Solution A 300 0 Solution B 295 20 Solution C 270 30 A cell with an internal osmolarity of 295 mOsm/L (non-permeable solutes) is placed in solution A. Solution A has an effective osmolarity that is ____________ compared to the cell; after water movement has reached a steady state, the cell volume will be ___________. A) hypertonic; decreased B) hypotonic; increased C) isotonic; decreased D) hypertonic; increased A cell with an internal osmolarity of 295 mOsm/L (non-permeable solutes) is placed in solution B. Solution B has an effective osmolarity that is ____________ compared to the cell; after water movement has reached a steady state, the cell volume will be ___________. A) hypotonic; decreased B) hypertonic; decreased C) hypotonic; increased D) isotonic; unchanged A cell with an internal osmolarity of 295 mOsm/L (non-permeable solutes) is placed in solution C. Solution C has an effective osmolarity that is ____________ compared…arrow_forward
- Why does water enter a cell that is placed in a hypotonic solution?arrow_forwardThe plasma membrane has a hydrophobic interior due to the two present in each phospholipid found in the phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane. The plasma membrane allows some molecules to cross but not all. Therefore, the plasma membrane is said to be Molecules that are nonpolar and hydrophobic will cross the membrane with ease by Does this process require energy? When molecules move across the plasma membrane by passive transport, they will move down or with the_ from an area of concentration to an area of. concentration. Polar, hydrophilic molecules and charged ions will move across the plasma membrane by the process of_ This does not require energy, but it does require a A special case of diffusion is known as which is the movement of water across the plasma membrane. If a cell is placed into a solution that is hypertonic compared to the inside of the cell, the cell would If a cell is placed into a hypotonic solution compared to the inside of the cell, the cell water. would…arrow_forwardThis is for osmosis in animal cells.arrow_forward
- If the cell membrane was completely permeable the concentration inside the cell would be same as Outside give reasonarrow_forwardJust the answerarrow_forwardName the term which is given for the movement of water through a semipermeable membrane? O Endocytosis O Option 5 O Active transport Diffusion Osmosisarrow_forward
- Osmosis is a kind of passive transport, that O Both a and b O Does not need to energy Need to energyarrow_forwardOsmosis in Osmosis is the movement of water from an area of A Animal Cells high water concentration to an area of low process so it doesn't need energy.||water concentration. Osmosis is aarrow_forwardThe cell membrane is _______, which means that is allows some substances to pass through it while others cannot.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education