
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
What can happen to animal cells when placed in a hypotonic solution? Explain.
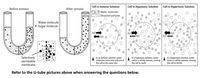
Transcribed Image Text:**Osmosis and Solutions: An Educational Overview**
**U-tube Diagram:**
- **Before Osmosis:** The U-tube contains two sides separated by a selectively permeable membrane. One side shows a higher concentration of sugar molecules (black dots) mixed with water molecules (white dots), while the other side mainly contains water molecules.
- **After Osmosis:** Water molecules move across the membrane to the side with more sugar molecules. This demonstrates the process of osmosis, highlighting the movement of water from an area of lower solute concentration to an area of higher solute concentration.
**Membrane Details:**
A close-up inset diagram shows the selectively permeable membrane, which allows only water molecules to pass through while blocking sugar molecules.
**Cell Solutions:**
1. **Cell in Isotonic Solution:**
- Water molecules (represented as dots) move in and out of the cell at the same rate.
- This maintains cell size as there is no net movement of water.
2. **Cell in Hypotonic Solution:**
- The solution outside the cell has a lower concentration of dissolved particles.
- Water enters the cell by osmosis, causing the cell to swell.
3. **Cell in Hypertonic Solution:**
- The solution outside the cell has a higher concentration of dissolved particles.
- Water leaves the cell by osmosis, causing the cell to shrink.
**Instructions:**
Refer to the U-tube and cell diagrams above to answer related questions regarding osmosis and the effects of different solutions on cells.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The following table depicts the rate of transport of a molecule into a cell as the external concentrations are changed. Based on what you know about the characteristics of membrane transport, the molecule is most likely transported by: a) passive transport b) simple diffusion across the membrane c) facilitated diffusion d) active transportarrow_forwardCan anyone provide a protocol or source for how to easily obtain plasma membrane sheets?arrow_forwardWhat is the role of lysozyme and a low ionic strength extraction buffer? Select all that apply. Cells absorb water from a low ionic strength extraction buffer, by osmosis, swell and lyse, releasing their contents Lysozyme breaks down bonds in the cellulose cell wall of plants, weakening the structure Cells release water into a low ionic strength extraction buffer by osmosis, shrink and lyse, releasing their contents Lysozyme is an enzyme found in lysosomes in cells Lysozyme breaks down bonds in the peptidoglycan cell wall of bacteria, weakening the structure Lysozyme is an antibiotic found in tears, saliva, human milk and mucus.arrow_forward
- b) If you soak an animal cell that is permeable to both water and glucose in either 5.5% glucose or 0.9% NaCl (both isosmotic solutions), the cell exposed to 5.5% glucose will gain water, while the cell exposed to 0.9% NaCl will not gain water. Predict why this is the case.arrow_forwardWhat is the independent variable of the experiment?arrow_forwardMark the flow of water with an arrow for cells that have been placed in solutions of differing tonicity. Indicate what will happen to a plant and animal cell under each of these conditions. Direction of osmosis Plant cell Animal cell shape shape minor swelling The solute concentration outside the cell is isotonic (or equal) to the inside of the cell. No change swelling and lysis plasmolysis crenation Reset Zoom (a) Outside isotonic The solute concentration outside the cell is hypertonic to the inside of the cell. (b) Outside hypertonic The solute concentration outside the cell is hypotonic to the inside of the cell. (c) Outside hypotonic Oo Solute Cytosol ©2018 McGraw-Hill Education. Check marrow_forward
- Explain (using the correct terminology and drawing an image) what happens to the cells in the following environments: A human blood cell (0.9% salt) is placed in a saltwater tank (27.5% salt). - A bacterial cell with 35% organic material in their cytoplasm is living in a tank filled with 35% sulfur. - A freshwater plant cell (75% water) is living in a pond that floods over.arrow_forwardRebuild the cell above that is hypertonic to the solution outside. By hitting the red button, add 20 solutes (green) to the inside of the cell and add 5 water (blue) to the inside of the cell. Also, add 20 water (blue) to the outside of the cell and 5 solutes (green) to the outside of the cell. Add blue gated channels to the membrane. Q: What happens to the water molecules in this situation? Q: Which of the above situations is closer to a living membrane system?arrow_forwardCan you assist me in answerig questions a, b, and c with the given data and graph provided, please?arrow_forward
- You are viewing two samples of mammalian red blood cells (erythrocytes) under a microscope. One first sample is made up of cells with a typical round shape. Most of the cells in the second sample had burst open. •Describe the properties of the solution that was used to prepare the second sample. • Identify one type of solute that can move through simple diffusion and does not affect osmotic pressure or require a membrane protein to cross a plasma membrane.arrow_forwardSuppose that you have a splinter that is embedded so deep in your foot that you cannot remove it with tweezers. How could you use what you learned in this unit as a first-aid remedy in this situation? Select one: O A. Use active transport to your advantage to draw water into your foot. O B. Use osmosis to your advantage by placing your foot in a hypotonic solution. C. Use osmosis to your advantage by placing your foot in a hypertonic solution. D. Use an artificial concentration gradient to draw water into your foot. E. Use osmosis to your advantage by placing your foot in an isotonic solution.arrow_forwardDescribe an additional experimental approach used to study the cytoskeleton in which the activity of cytoskeletal elements is affected in ways similar to those resulting from drug treatment.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education