
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
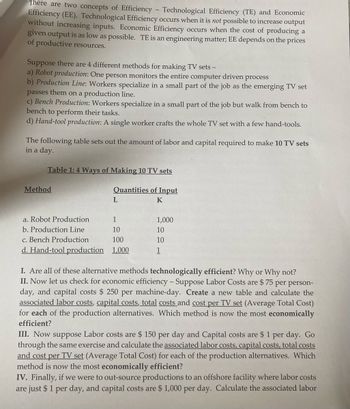
Transcribed Image Text:There are two concepts of Efficiency - Technological Efficiency (TE) and Economic
Efficiency (EE). Technological Efficiency occurs when it is not possible to increase output
without increasing inputs. Economic Efficiency occurs when the cost of producing a
given output is as low as possible. TE is an engineering matter; EE depends on the prices
of productive resources.
Suppose there are 4 different methods for making TV sets -
a) Robot production: One person monitors the entire computer driven process
b) Production Line: Workers specialize in a small part of the job as the emerging TV set
passes them on a production line.
c) Bench Production: Workers specialize in a small part of the job but walk from bench to
bench to perform their tasks.
d) Hand-tool production: A single worker crafts the whole TV set with a few hand-tools.
The following table sets out the amount of labor and capital required to make 10 TV sets
in a day.
Table 1: 4 Ways of Making 10 TV sets
Quantities of Input
K
Method
L
a. Robot Production
1
b. Production Line
10
c. Bench Production
100
d. Hand-tool production 1,000
1,000
10
10
1
I. Are all of these alternative methods technologically efficient? Why or Why not?
II. Now let us check for economic efficiency - Suppose Labor Costs are $ 75 per person-
day, and capital costs $250 per machine-day. Create a new table and calculate the
associated labor costs, capital costs, total costs and cost per TV set (Average Total Cost)
for each of the production alternatives. Which method is now the most economically
efficient?
III. Now suppose Labor costs are $ 150 per day and Capital costs are $ 1 per day. Go
through the same exercise and calculate the associated labor costs, capital costs, total costs
and cost per TV set (Average Total Cost) for each of the production alternatives. Which
method is now the most economically efficient?
IV. Finally, if we were to out-source productions to an offshore facility where labor costs
are just $ 1 per day, and capital costs are $1,000 per day. Calculate the associated labor
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Introduction to Calculus in Economics: Calculus is a powerful tool used in economics. One of the initial applications areas is the study of a firm, a topic in microeconomics. An important function is the cost function function C (x), the cost of producing z items (of whatever they are selling). This question deals with just the cost function C (x). Problem Set question: The cost, in dollars, of producing a units of a certain item is given by C (x) = 10x – 10T -9. Find the production level that minimizes the average cost per unit. The number of units that minimizes the average cost isarrow_forwardIntroduction to Calculus in Economics: Calculus is a powerful tool used in economics. One of the initial applications areas is the study of a firm, a topic in microeconomics. An important function is the cost function function C(x), the cost of producing items (of whatever they are selling). This question deals with just the cost function C'(x). Problem Set question: The cost, in dollars, of producing a units of a certain item is given by C(x) = 10x10√x - 8. Find the production level that minimizes the average cost per unit. The number of units that minimizes the average cost is Numberarrow_forwardPart 1 of 2 40%, 2 of 5 points Points: 0 of 1 Save The marginal cost of a product can be thought of as the cost of producing one additional unit of output. For example, if the marginal cost of producing the fiftieth product is $6.30, then it cost $6.30 to increase production from 49 to 50 units of output. Suppose that the marginal cost C (in dollars) to produce x digital cameras is given by C(x)=0.03x²-6x+350. How many digital cameras should be produced to minimize marginal cost? What is the minimum marginal cost? digital cameras should be produced to minimize marginal costarrow_forward
- 2. With reference to Example 9.5.1, let R(Q) = 80Q and C(Q) = Q2 + 10Q + 900. The firm can produce at most 50 units. (a) Draw the graphs of R and C in the same coordinate system. (b) Answer the following questions both graphically and by computation: (i) How many units must be produced for the firm to make a profit? (ii) How many units must be produced for the firm to maximize profits?arrow_forwardAnother farmer purchases nitrate and phosphate fertilizers to produce corn, and the more of any one input he uses, the lower the marginal productivity of that input. Suppose the farmer decides to maximize output for a given cost. (That is, imagine a given isocost line.) Suppose the price of nitrate is 36 cents per pound and the price of phosphate is 24 cents per pound. Moreover, suppose the farmer currently chooses an input combination such that the marginal product of a pound of nitrate is 4 bushels of corn and the marginal product of a pound of phosphate is 3 bushels of corn. Should the farmer use the current mix of nitrate and phosphate? Should he use more nitrate and less phosphate? Or, should he use more phosphate and less nitrate? Please carefully draw a diagram with pounds of nitrate plotted along the horizontal axis and pounds of phosphate plotted along the vertical axis to support your conclusion. Moreover, please report the slope of the isocost line. And please report the…arrow_forward3. For the cost function c = √q, show that marginal and average costs are always decreasing.arrow_forward
- Where average costs of production are lowest when all output is produced by a single firm.arrow_forwardIke's Bikes is a major manufacturer of bicycles. Currently, the company produces bikes using only one factory. However, it is considering expanding production to two or even three factories. The following table shows the company's short-run average total cost (SRATC) each month for various levels of production if it uses one, two, or three factories. (Note: Q equals the total quantity of bikes produced by all factories.) NOTE: the options for the blank question is this Suppose Ike's Bikes is expecting to produce 500 bikes per month for several years. In this case, in the long run, it would choose to produce bikes using _______ (once factory OR two factory OR three factory)arrow_forwardLet's play around with the concepts of total cost versus marginal cost Suppose a grocery store figures out that it costs $500 per week to hire a full time worker who can fill pickup orders. Create a table with room for 5 columns and 6 rows in your notes Use the top row for titles. The first (left) column should be titled Number of Workers and should have 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 as values. We're going to analyze whether the store should hire 0, 1, 2, 3 or 4 workers. Title the next column Total Cost (TC) and the third column Marginal Cost (MC). Put an X in the MC square corresponding to 0 workers. That would be the cost of going from negative 1 workers to 0 workers, let's leave it blank YOu'll see that marginal columns tend to start across from the first unit. We'll use the remaining columns later. What is the Marginal Cost per week of hiring the 4th worker? $500 O $1,000 O $1,500 $2,000arrow_forward
- Consider a production process where flowers are grown (the output) using gardeners (labor) and greenhouses (capital). The quantity of flowers grown per day with various combinations of labor and capital are shown in the table below. Suppose that each gardener is paid $160 per day and the greenhouse is rented for $400 per day. Fill in total cost in the table below. (Enter your responses as integers.) Labor 0 1 Labor 0 1 2 3 2345 5 Capital 1 1 1 1 1 Next, fill in average total cost in the table. (Enter your responses as real numbers rounded to two decimal places.) Capital Total Cost Average Total Cost $400 560 720 880 1,040 1,200 Output 0 80 Output 0 80 240 320 360 380 240 320 360 380 Total Cost $ 400 560 720 880 1040 1200arrow_forwardIntroduction to Calculus in Economics: Calculus is a powerful tool used in economics. One of the initial applications areas is the study of a firm, a topic in microeconomics. An important function is the cost function function C (z), the cost of producing z items (of whatever they are selling). This question deals with just the cost function C (z). Problem Set question: The cost, in dollars, of producing z units of a certain item is given by C (z) = 5z – 8/I – 3. Find the production level that minimizes the average cost per unit. The number of units that minimizes the average cost is Numberarrow_forwardSuppose that Flamerock Tires must decide where to produce one million tires: the US, where wages are 30 and the cost of capital is 5; or China, where wages are 5 and the cost of capital is 25. Production in each location follows the same technology (production function) given by: Q = f(L, K) = L^0.25 K^0.75 Computationally solve the cost - minimizing input levels in each location to produce the goal of 1 million tiresarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education