
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
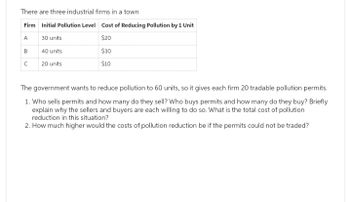
Transcribed Image Text:There are three industrial firms in a town
Firm Initial Pollution Level Cost of Reducing Pollution by 1 Unit
A
30 units
$20
40 units
20 units
B
с
$30
$10
The government wants to reduce pollution to 60 units, so it gives each firm 20 tradable pollution permits.
1. Who sells permits and how many do they sell? Who buys permits and how many do they buy? Briefly
explain why the sellers and buyers are each willing to do so. What is the total cost of pollution
reduction in this situation?
2. How much higher would the costs of pollution reduction be if the permits could not be traded?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 4 This is a graph reprinted from Section 12.1 the Economics of Pollution. Please explain the graph with particular attention paid to why there are two supply curves. How can a government use this graph to establish pollution controls?arrow_forwardģi Refer to the table below, which presents information on a market that provides positive externalities on society. Private marginal benefit Marginal cost $300,000 $340,000 $310,000 $330,000 $320,000 $320,000 $330,000 $310,000 $340,000 $300,000 $350,000 $290,000 Calculate the quantity that would be produced if society did not incorporate the social marginal benefits of this good or service. Type your answer... Quantity 6,000 7,000 8,000 9,000 10,000 11,000 F1 a 2 W JAN X Q 18 F2 # 3 20 F3 F $ 4 F4 R % 5 F5 T MacBook Air A 6 F6 Y & 887 stv F7 U * 00 8 FB O ( 9 Private+social marginal benefit $360,000 $350,000 $340,000 $330,000 $320,000 $310,000 F9 1 W 0 F10 Aa zoom P F11 Submit F12 = IT ľarrow_forwardAir pollution creates a negative externality—a cost suffered by a third party as a result of an economic transaction. A standard solution to a negative externality is a Pigouvian tax, a tax that raises the marginal private cost of pollution emissions to the level of the marginal social cost. The socially optimal quantity of pollution emissions is then determined by the intersection of the marginal private benefit, or demand, curve and the marginal social cost curve. The article notes that "putting a dollar value on the benefits of cleaner air has been difficult." Assuming this problem has been resolved, in the accompanying diagram, move the endpoints of line Smarginal social cost to show the marginal social cost curve. Then move the line labeled "Tax" to show the amount of the tax needed to limit emissions to the socially optimal level.arrow_forward
- In the film, The Dark Water 2019, Ducont a huge chemical firm dumps it's waste in air, land and water knowing it's has harmful effects to humans and animal. In reference to the firm answer the set of questions below: (a) What is the cause of the externality in the 2019 film The Dark Water? Determine whether the Coase theorem applies in the film, if not, what results in the theorem breaking down?arrow_forwardThe graph shows the unregulated market for electricity. The marginal external cost of the pollution created is equal to the marginal private cost of producing electricity at every quantity of electricity produced. Draw a point to show the marginal social cost when production is 500 kilowatts per day. Label it 1. Draw the marginal social cost curve. Label it MSC. ab Draw a point to show the quantity of electricity produced with no pollution control and the marginal social cost of the electricity generated. Label it 2. Draw a shape to show the deadweight loss with no pollution control. Label it DWL. The deadweight loss created by the pollution is $ >>> Remember that the price given on the y-axis in cents but you must answer in dollars. esc q a @ 2 W S #3 с e d $ 4 65. 1 14 t Oll 6 O & 7 Y 20arrow_forwardChapter 10 The first government employee suggests reducing pollution through regulation. To meet the pollution goal, the government requires each firm reduce its pollution by 2 units. Complete the following table with the total cost to each firm of reducing its pollution by 2 units. Firm Total Cost of Eliminating Two Units of Pollution (Dollars) Firm A Firm B Firm C ☐☐ Method 2: Tradable Permits Meanwhile, the other employee proposes using a different strategy to achieve the government's goal of reducing pollution in the area from 1 6 units. This employee suggests that the government issue two pollution permits to each firm. For each permit a firm has in its possession, i 1 unit of pollution. Firms are free to trade pollution permits with one another (that is, buy and sell them) as long as both firms can agree on For example, if firm A agrees to sell a permit to firm B at an agreed-upon price, then firm B would end up with three permits and would nee reduce its pollution by only 1 unit…arrow_forward
- Help plz graph plz 3 8arrow_forward5. Which of the following best describes the issuance of permits to pollute as a way of influencing the amount of pollution? Permits to pollute: a. encourage business to pollute.b. should be purchased by those whose pollution is the least expensive to eliminate.c. should be purchased by those whose pollution is the most expensive to eliminate.d. are preferable over taxes because they can be limited to exactly the efficient amount of pollution.arrow_forwardConsider a market with the following supply and demand. (It may help to draw a graph for these questions.) P 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 QS 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000 1100 QD 800 750 700 650 600 550 500 450 400 350 If there is an external cost of $3, what is the efficient quantity? If there is an external benefit of $3, what is the efficient quantity? For the remaining questions assume that there is a $3 external COST. If the government wants to get the efficient quantity with a per/unit tax, how much should the tax be? Now imagine that they use tradable allowances. If they cap the quantity at 400 what would the value of these allowance be in the market? (Assume the market is perfectly competitive and that "one allowance" lets you…arrow_forward
- 8arrow_forwardWhat is an externality in economics? Explain how a neighbor’s barking dog could be both a positive and a negative externality. Can pollution ever make us better off? How do we know? Should we aim to eliminate all pollution? If not, what should our goal be? Defend your answer. When thinking about types of goods, what does rivalry mean? What does excludability mean? What are the four categories of goods we can identify using those attributes, and what is an example of a good in each category?arrow_forwardK Steel production creates pollution. If a tax is imposed on steel production equal to the marginal external cost of the pollution it creates, O A. steel producers will continue to produce the inefficient quantity of steel OB. the deadweight loss created by steel producers will be cut to zero OC. steel producers will cut pollution to zero O D. the market price of steel will rise by the amount of the tax Submit te:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education