
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
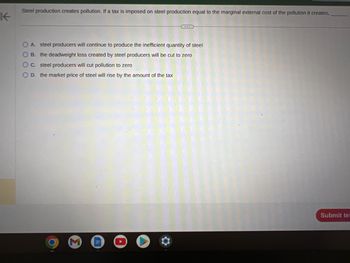
Transcribed Image Text:K
Steel production creates pollution. If a tax is imposed on steel production equal to the marginal external cost of the pollution it creates,
O A. steel producers will continue to produce the inefficient quantity of steel
OB. the deadweight loss created by steel producers will be cut to zero
OC. steel producers will cut pollution to zero
O D. the market price of steel will rise by the amount of the tax
Submit te:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Economicsarrow_forwardOnly typed answer You are an industry analyst that specializes in an industry where the market inverse demand is P = 100 - 3Q. The external marginal cost of producing the product is MCExternal = 6Q, and the internal cost is MCInternal = 14Q. Instruction: Round your answers to the nearest two decimal places. a. What is the socially efficient level of output? units b. Given these costs and market demand, how much output would a competitive industry produce? units c. Given these costs and market demand, how much output would a monopolist produce? units d. Which of the following are actions the government could take to induce firms in this industry to produce the socially efficient level of output. Instructions: You may select more than one answer. Click the box with a check mark for the correct answers and click twice to empty the box for the wrong answers. You must click to select or deselect each option in order to receive full credit. Pollution taxes…arrow_forwardSupply 10.00 9.00 8.00 7.00 6.00 MSC 5.00 4.00 Demand 3.00 2.00 1.00 25000 50000 75000 100000 125000 150000 175000 200000 If a tax or subsidy were used to correct the externality, what would be chosen? O a. tax = $4 O b. subsidy = $3 O C. tax = $3 O d. subsidy = $4 B.arrow_forward
- According to economists what is the optimal amount of pollution? O a. The optimal amount of pollution is where private costs equal social costs O b. Pollution should be reduced to a level as determined by government regulation O c. None, the goal is to completely eliminate pollution d. The point where the marginal benefit from further pollution reduction equals the marginal cost of further reductionarrow_forwardPrice of a vaccination $140 Supply 110 75 D, marginal social benefit D= marginal private benefit 550 800 Quantity of vaccinations Refer to the Externality graph above. Government could increase the quantity of vaccinations by: O a. subsidizing the producer to provide the vaccinations. O b. subsidizing the consumer to receive the vaccinations. Oc. Government provides the good or service altogether. O d. none of the above. O e. A, B, and C.arrow_forwardCarbon dioxide emissions have been linked to increased air pollution. Suppose that, to reduce carbon dioxide emissions, the government charges factories $100 for every ton of carbon dioxide they emit. This is an example of: O Effluent taxation O Emissions trading O Command-and-control policy (regulation) Which of the following is seen as one of the growing pains of emissions trading? O Hot spot problem Tragedy of the commons O Transaction costsarrow_forward
- Figure 1. The graph depicts the market for plastic containers. Price 16- 14- 12- 10 8- 6 200 500 650 Social Cost Private Cost Demand Quantity Refer to Figure 1. In order to reach the social optimum, the government could O offer a subsidy of $8 per unit on the production of plastic containers. O impose a tax of $8 per unit on the production of plastic containers. O offer a subsidy of $4 per unit on the production of plastic containers. O impose a tax of $4 per unit on the production of plastic containers.arrow_forward45 40 35 30 25 20 P ($) Social cost Supply 15 10 Demand 5 0 0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80 90 100 wanted to tax or subsidize this good to achieve the Refer to the figure above. If the government socially-optimal level of output, it would Select one: O a introduce a subsidy of $10 per unit. O b. impose a tax of $10 per unit. Oo impose a tax of $15 per unit. Od introduce a subsidy of $15 per unit. 8arrow_forward2. Consider the following free market. $300 $200 $100 500 1200 Quantity i. Calculate consumer and producer surplus in this market. ii. If the marginal external cost of production is $10, the socially optimal quantity is 400 and the socially optimal price is $205. Show the new consumer and producer surplus and calculate them. Also show the deadweight loss on the graph and calculate it.arrow_forward
- V1arrow_forward11.00 10.00 9.00 8.00 7.00 6.00 5.00 4.00 3.00 2.00 8 1.00 300 600 900 What kind of externality is depicted above? O a. A negative production externality O b. A positive consumption externality c. A positive production externality d. A negative consumption externality Demand 1200 1500 1800 2100 Supply Marginal Social Benefit 2400arrow_forwardA positive externality will cause a market to produce Select one: more than is socially desirable. O b. more than the same market would produce in the presence of a negative externality. O c. less than is socially desirable. O d. the socially optimal equilibrium amount. a.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education