
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
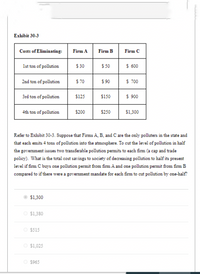
Transcribed Image Text:Exhibit 30-3
Costs of Eliminating:
Firm A
Firm B
Firm C
1st ton of pollution
$ 30
$ 50
$ 60
2nd ton of pollution
$ 70
$90
S 700
3rd ton of pollution
$125
$150
$ 900
4th ton of pollution
$200
$250
$1,300
Refer to Exhibit 30-3. Suppose that Firms A, B, and C are the only polluters in the state and
that each emits 4 tons of pollution into the atmosphere. To cut the level of pollution in half
the govemment issues two transferable pollution permits to each fim (a cap and trade
poliey). What is the total cost savings to society of decreasing pollution to half its present
level if firm C buys one pollution permit from fim A and one pollution permit from firm B
compared to if there were a government mandate for each firm to cut pollution by one-half?
$1,300
$1,380
$515
O $1,025
O $965
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 4 This is a graph reprinted from Section 12.1 the Economics of Pollution. Please explain the graph with particular attention paid to why there are two supply curves. How can a government use this graph to establish pollution controls?arrow_forward3. Suppose the EPA wants to reduce pollution to the socially optimal level. Based on the data in the table below, what is the optimal level of pollution? Total cleanup Total Total (tons) Benefit Cost 50 2 85 18 3 115 28 4 140 39 5 160 51 179 63 7 197 76 8 214 90 230 105 10 245 120 11 259 137 12 273 156 13 286 177 14 299 200 15 311 225arrow_forward3. The effect of negative externalities on the optimal quantityof consumption Consider the market for pharmaceuticals. Suppose that a pharmaceutical factory dumps toxic waste into a nearby river, creating a negative externality for those living downstream from the factory. Producing additional pharmaceuticals imposes a constant per-unit external cost of $280. The following graph shows the demand (private value) curve and the supply (private cost) curve for pharmaceuticals. Use the purple points (diamond symbol) to plot the social cost curve when the external cost is $280 per unit. PRICE (Dollars per unit of pharmaceuticals) 800 720 640 560 480 400 320 240 160 80 O 1 2 3 □ O O ㅁ 4 Supply (Private Cost) Demand (Private Value) 5 6 7 QUANTITY (Units of pharmaceuticals) Social Cost ? The market equilibrium quantity is units of pharmaceuticals, but the socially optimal quantity of pharmaceuticals production is units. To create an incentive for the firm to produce the socially optimal…arrow_forward
- 1. why marine pollution is considered a negative externality? 2. Suggest a relevant government policy that would yield an efficient outcome and carefully explain the process through which the implementation of the government policy will lead to the optimal outcome as it relates to marine pollution. 3. How will the imposition of the chosen government policy impact consumer surplus, producer surplus, and total surplus as it relates to marine pollution.arrow_forwardPrice 24 20 16 12 1 1 I 1 I I I I 1 I 20 28 K 36 MSC MPC MSB Quantity 1. What type of externality does the graph above show? 2. Without government intervention, how much will be produced in this market? 3. Without government intervention, what price will be charged in this market? 4. If the government wants to intervene in this market to eliminate externalities, which of the following is the best choice?arrow_forwardRefer to Figure. Which of the following statements is correct? Price 22 24 22 81 18 16 Social cost (private cost and external cost) Supply (private cost) Demand (private value) 120 160 Quantity a. The private cost of producing the 160th unit of output is $16 b. The social cost of producing the 160th unit of output is $22. c. d. The external cost of producing the 160th unit of output is $6. All of the above are correct.arrow_forward
- The effect of external costs on the efficient level Consider the market for steel. Suppose that a steel manufacturing plant dumps toxic waste into a nearby river, creating a negative externality for those living downstream from the plant. Producing an additional ton of steel imposes a constant external cost of 5330 per ton. The foliowing graph shows the demand (private value) curve and the supply (private cost) curve for steel.arrow_forwardPRICE (Dollars per ton) 70 63 56 49 42 35 28 + 21 T 14 7 0 Demand +++ 0 40 80 120 160 200 240 280 320 360 400 QUANTITY (Millions of tons) Graph Input Tool Daily Demand for Pollution Rights Price (Dollars per ton) Quantity Demanded (Millions of tons) 7 360 Suppose the government has determined that the socially optimal quantity of particulate matter is 120 million tons per day. One way governments can charge firms for pollution rights is by imposing a per-unit tax on emissions. A tax (or price in this case) of $ of particulate matter emitted will achieve the desired level of pollution. ? per ton Now suppose the U.S. government does not know the demand curve for pollution and, therefore, cannot determine the optimal tax to achieve the desired level of pollution. Instead, it auctions off tradable pollution permits. Each permit entitles its owner to emit one ton of particulate matter per day. To achieve the socially optimal quantity of pollution, the government auctions off 120 million…arrow_forwardAsap solvearrow_forward
- Help plz graph plz 3 8arrow_forward5. Which of the following best describes the issuance of permits to pollute as a way of influencing the amount of pollution? Permits to pollute: a. encourage business to pollute.b. should be purchased by those whose pollution is the least expensive to eliminate.c. should be purchased by those whose pollution is the most expensive to eliminate.d. are preferable over taxes because they can be limited to exactly the efficient amount of pollution.arrow_forward3. Efficiency in the presence of externalities Roses confer many external benefits on society: the beauty they add to a room or garden, the wonderful aroma they give off, and so on. Therefore, the market equilibrium quantity of roses is not equal to the socially optimal quantity. The following graph shows the demand for roses (their private value), the supply of roses (the private cost of producing them), and the social value of roses (the private value and external benefits). Use the black point (plus symbol) to indicate the market equilibrium quantity. Next, use the purple point (diamond symbol) to indicate the socially optimal quantity.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education