
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
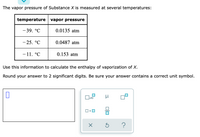
Transcribed Image Text:The vapor pressure of Substance X is measured at several temperatures:
temperature vapor pressure
- 39. °C
0.0135 atm
- 25. °C
0.0487 atm
- 11. °C
0.153 atm
Use this information to calculate the enthalpy of vaporization of X.
Round your answer to 2 significant digits. Be sure your answer contains a correct unit symbol.
х10
미
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A pure solid sample of Substance X is put into an evacuated flask. The flask is heated at a steady rate and the temperature recorded as time passes. Here is a graph of the results: temperature (°C) 90. 70. 50.- 30. 10. - 10. 10. What is the boiling point of X ? heat added (kJ/mol) Use this graph to answer the following questions: What phase (physical state) of X would you expect to find in the flask after 29 kJ/mol of heat has been added? °C 40. (check all that apply) solid O liquid Ogas 50.arrow_forwardUse the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the melting point of X when the pressure above the solid is 10. atm. لالا pressure (atm) 32. Doc 16. solid 100 liquid 200 gas 300 temperature (K) Note: your answer must be within 12.5 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct.arrow_forwardUse the phase diagram of Substance X below to find the boiling point of X when the pressure on the liquid is 3.7 atm. pressure (atm) 0- 8 solid liquid gas 100 temperature (K) 200 Note: your answer must be within 12.5 °C of the exact answer to be graded correct. ☐ °C Garrow_forward
- LL The vapor pressure of Substance X is measured at several temperatures: temperature vapor pressure -27. °C 0.0449 atm -16. °C 0.112 atm -5.°C 0.257 atm Use this information to calculate the enthalpy of vaporization of X. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. Be sure your answer contains a correct unit symbol. Continue O 2022 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Re EPIC MacBook Pro ロ号 F3 F4 F5 F2 24 4. 23 7. 6. 3. 5. A G D. B. N 8arrow_forwardConsider a liquid with a vapor pressure of 200. torr at 20.0 °C and a vapor pressure of 400. torr at 50.0 °C. What is the closest value to the normal boiling point of this liquid? 83.8 °C O 357 °C O 295 °C 18.2 °C 22.0 °Carrow_forwardkJ The enthalpy of vaporization of Substance X is 5.00 and its normal boiling point is 27. °C. Calculate the vapor pressure of X at -33. °C. mol Round your answer to 2 significant digits. atm x10arrow_forward
- How much heat is needed to convert 776. g of ice at -10.0 °C to steam at 126.0 °C? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. Note: Reference the Phase change properties of pure substances table for additional information. Water phase Specific heat Solid Liquid Gas kJ 2.03 4.184 x10 1.99 J g.°C J g.°C J g.°Carrow_forwardUse the observation in the first column to answer the question in the second column. observation At 1 atm pressure, Substance E boils at 11. °C and Substance F boils at 30. °C. At 37 °C, Substance C has a vapor pressure of 89. torr and Substance D has a vapor pressure of 79. torr. The enthalpy of vaporization of Substance A is smaller than that of Substance B. question Which has a higher vapor pressure? Substance E Substance F Neither, E and F have the same vapor pressure. It's impossible to know without more information. Which has a higher enthalpy of vaporization? Substance C Substance D Neither, C and D have the same enthalpy of vaporization. It's impossible to know without more information. At any temperature where both substances are liquid, which has the higher vapor pressure? Substance A Substance B Neither, A and B have the same vapor pressure. It's impossible to know without more information. X Śarrow_forwardA pure solid sample of Substance X is put into an evacuated flask. The flask is heated at a steady rate and the temperature recorded as time passes. Here is a graph of the results: temperature (°C) 160. 140. 120. 100. 80. 60. 0. 10. What is the boiling point of X ? Use this graph to answer the following questions: heat added (kJ/mol) 20. What phase (physical state) of X would you expect to find in the flask after 12 kJ/mol of heat has been added? 30. Пос (check all that apply) solid O liquid gas 40.arrow_forward
- Consider the phase diagram shown. What is the normal sublimation point at 1 atm? Pressure (not to scale) 72.9 atm 5.1 atm 1 atm O 0°C O 100°C -56.7 °C 31°C -78.5 °C SOLID LIQUID GAS -78.5 °C -56.7 °C Temperature (not to scale) 31 °Carrow_forwardThis question is not a grade question, its just a pratice problem.arrow_forwardTry Again Your answer is incorrect. The enthalpy of vaporization of Substance X is 23.0 Round your answer to 2 significant digits. 0.32 atm x10 X kJ and its normal boiling point is 10. °C. Calculate the vapor pressure of Xat - 18. °C. mol Sarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY